A Glimpse into Imperial Germany: Exploring the 1900 Map
Related Articles: A Glimpse into Imperial Germany: Exploring the 1900 Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Glimpse into Imperial Germany: Exploring the 1900 Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Glimpse into Imperial Germany: Exploring the 1900 Map
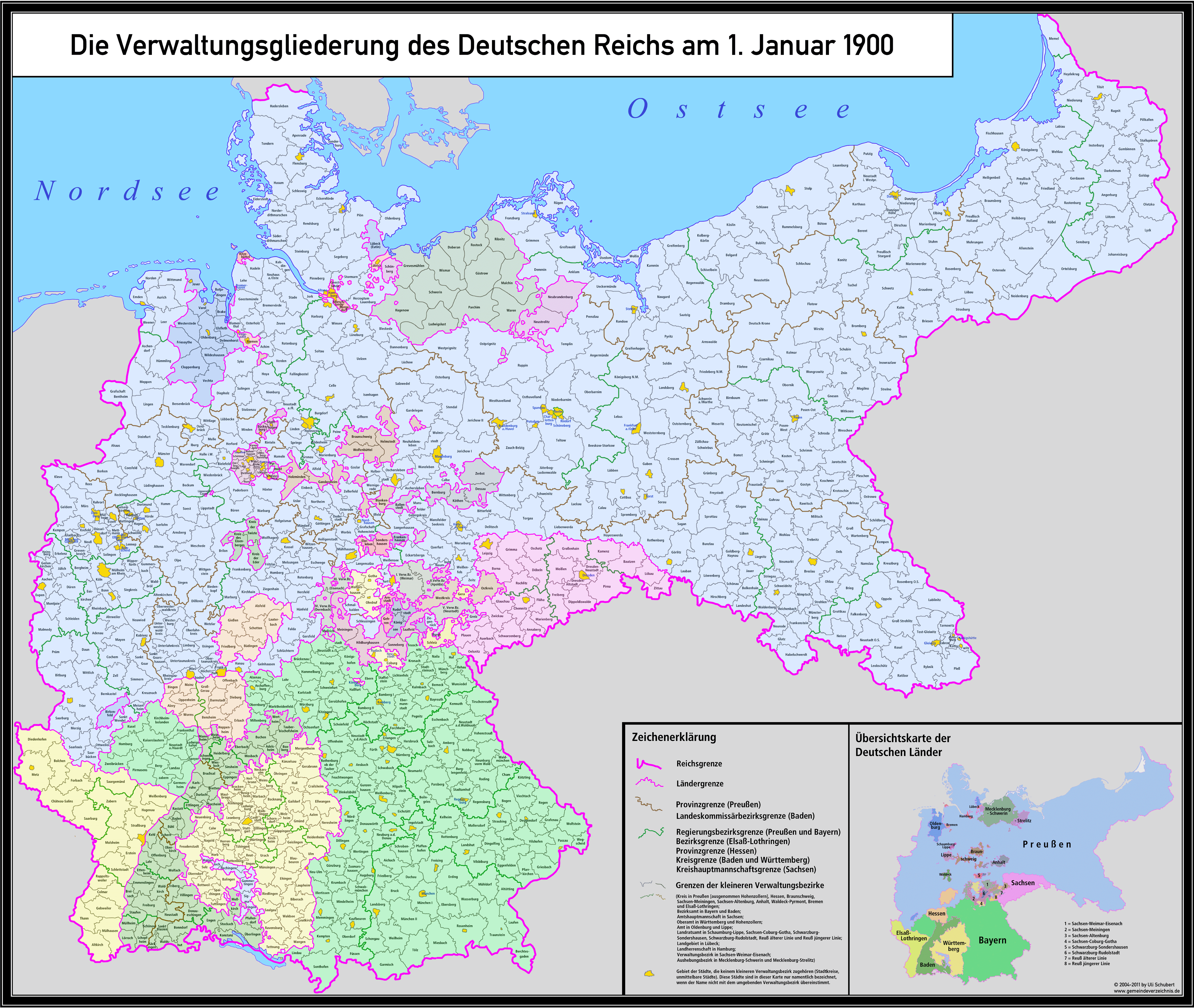
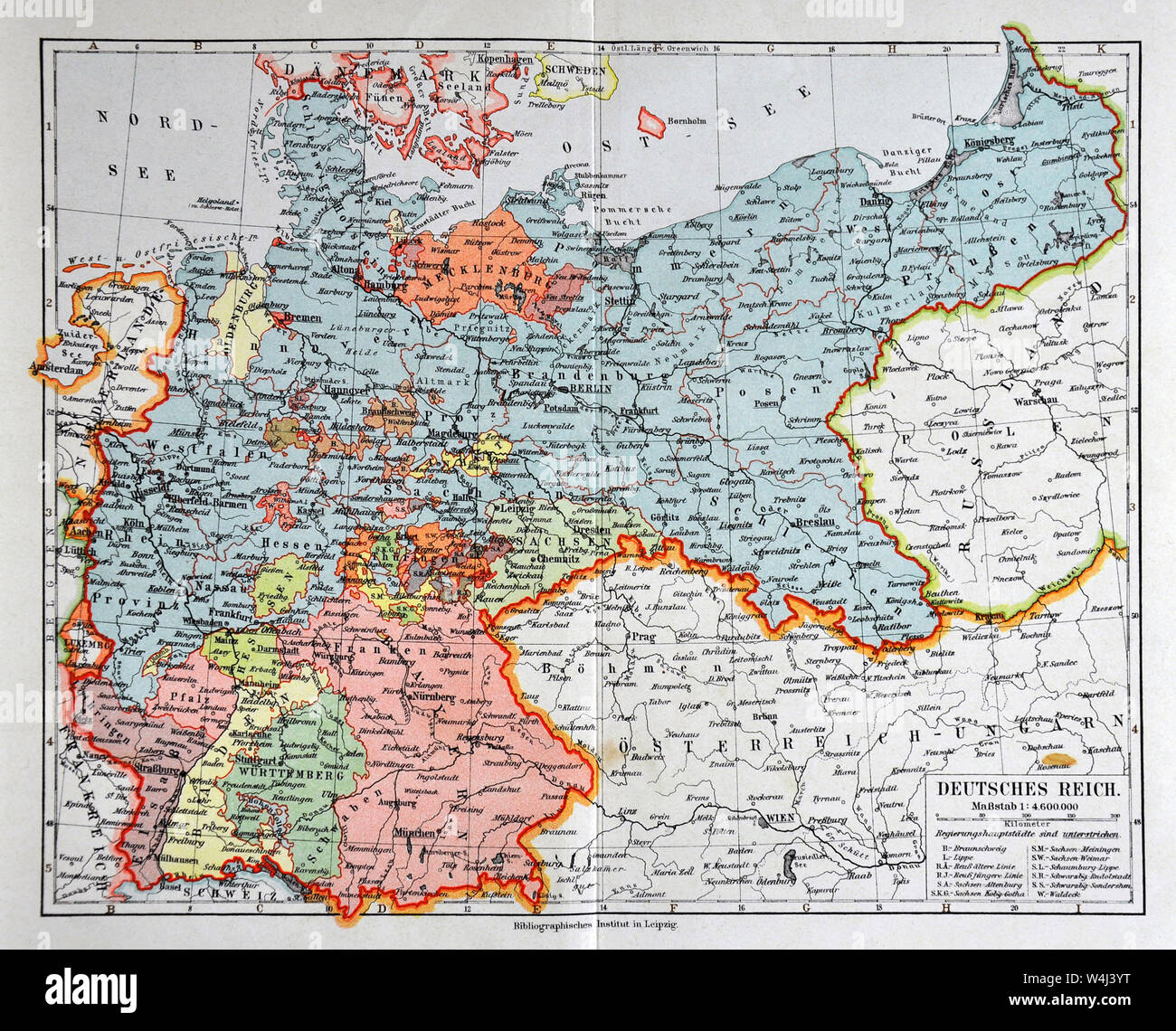
The year 1900 marked a pivotal moment in German history. Having emerged from a period of unification and rapid industrialization, the German Empire stood as a powerful force in Europe, its territorial boundaries reflecting a complex web of political, economic, and cultural influences. Studying the 1900 map of Germany offers a unique window into this era, illuminating the nation’s geographical scope, its political structure, and the dynamic forces that shaped its destiny.
A Nation United: The German Empire in 1900
The 1900 map reveals a Germany significantly different from its modern-day counterpart. It depicts a unified nation, encompassing a vast territory stretching from the North Sea in the north to the Alps in the south, and from the Netherlands in the west to the Russian Empire in the east. This vast expanse encompassed a diverse array of regions, each with its own distinct history, culture, and identity.
The Political Landscape: Kingdoms, Duchies, and Free Cities
While unified under the leadership of the Kaiser, the German Empire was not a monolithic entity. It was a complex federation of 26 states, each with varying degrees of autonomy. Kingdoms like Prussia, Bavaria, and Saxony held significant political weight, alongside smaller duchies, grand duchies, and free cities. This intricate patchwork of states reflected the delicate balance of power within the Empire, showcasing the historical and cultural diversity that shaped the nation’s political landscape.
Territorial Acquisitions and the Rise of Imperialism
The 1900 map also reveals the impact of German imperialism. Through a series of wars and diplomatic maneuvers, the German Empire had expanded its territories beyond the borders of the German Confederation, gaining control of significant overseas colonies in Africa, Asia, and Oceania. These acquisitions, driven by the desire for economic resources, strategic advantage, and national prestige, transformed Germany into a global power, but also sowed the seeds of future conflict.
Economic Powerhouse: The Industrial Revolution and Urbanization
The 1900 map reflects the dramatic economic transformation that swept through Germany during the late 19th century. The Industrial Revolution had spurred rapid urbanization, with cities like Berlin, Hamburg, and Cologne becoming bustling centers of commerce, manufacturing, and innovation. The map reveals the dense network of railroads and waterways that connected these urban hubs, facilitating trade and communication across the Empire.
Cultural Crossroads: A Tapestry of Identities
The 1900 map provides a glimpse into the cultural tapestry of Imperial Germany. It highlights the diverse ethnicities, languages, and traditions that coexisted within its borders. From the German-speaking majority to the significant populations of Poles, Czechs, and Danes, the map underscores the multicultural nature of the Empire, a complexity that would later contribute to internal tensions.
The Legacy of the 1900 Map: A Window into the Past
The 1900 map serves as a valuable tool for understanding the historical context of Germany in the early 20th century. It illuminates the nation’s political, economic, and cultural realities, revealing the forces that shaped its trajectory. By studying the map, we gain insight into the complex dynamics that led to the outbreak of World War I, the rise of nationalism, and the eventual downfall of the German Empire.
FAQs about the 1900 Map of Germany
1. What were the largest states within the German Empire in 1900?
The largest states in terms of population and territory were Prussia, Bavaria, Saxony, Württemberg, and Baden. Prussia, with its powerful military and industrial base, dominated the political landscape.
2. What were the major cities in Germany in 1900?
Major cities included Berlin (the capital), Hamburg, Munich, Cologne, Leipzig, Frankfurt, Dresden, and Bremen. These cities were centers of commerce, industry, and culture.
3. What were the main industries in Germany in 1900?
Germany was a leading industrial power, with major industries including coal mining, iron and steel production, shipbuilding, textiles, and chemicals.
4. What were the major political parties in Germany in 1900?
The major political parties were the Social Democratic Party (SPD), the Conservative Party, the National Liberal Party, and the Center Party. The SPD, representing the interests of the working class, was the largest party.
5. What were the major social issues in Germany in 1900?
Major social issues included poverty, inequality, and the rise of socialist movements. The rapid industrialization and urbanization led to social tensions and calls for reform.
6. What were the major cultural developments in Germany in 1900?
Germany experienced a flourishing of cultural life, with notable figures in literature, music, art, and philosophy. The period saw the emergence of movements like Naturalism and Expressionism, which challenged traditional artistic norms.
7. What were the major foreign policy issues facing Germany in 1900?
Germany’s foreign policy was characterized by a desire for expansion and a growing rivalry with Britain, France, and Russia. The scramble for colonies in Africa and the growing naval arms race heightened tensions between the great powers.
Tips for Studying the 1900 Map of Germany
1. Focus on the key territorial features: Pay attention to the borders of the various states, the major cities, and the location of important industrial centers.
2. Consider the political structure: Examine the distribution of power between the various states and the role of the Kaiser.
3. Analyze the economic landscape: Identify the major industries and transportation networks that shaped the German economy.
4. Explore the cultural diversity: Observe the distribution of ethnicities, languages, and cultural traditions within the Empire.
5. Connect the map to historical events: Use the map to understand the context of major events like the unification of Germany, the Industrial Revolution, and the rise of imperialism.
6. Compare the 1900 map to modern-day Germany: Analyze the changes in territorial boundaries, political structure, and economic development.
Conclusion
The 1900 map of Germany offers a powerful visual representation of a nation at a crossroads. It captures the dynamism of a newly unified empire, its economic prowess, and its complex political and social structures. By examining this historical artifact, we gain a deeper understanding of the forces that shaped Germany in the early 20th century, providing insights into the nation’s tumultuous past and its enduring legacy.
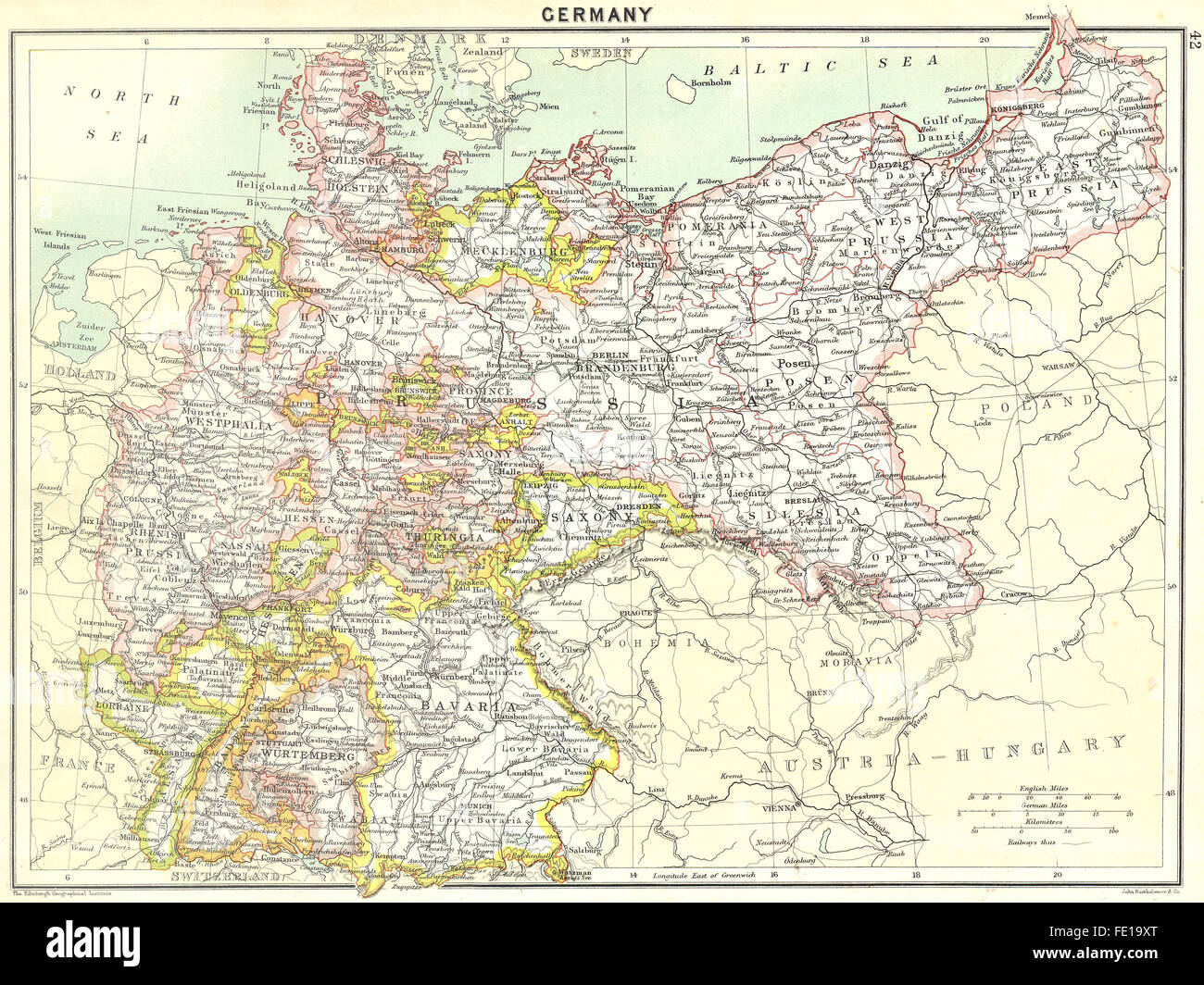


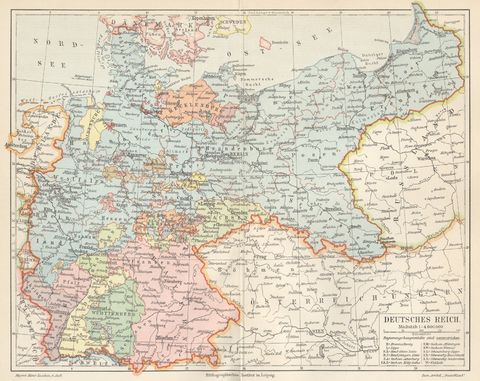


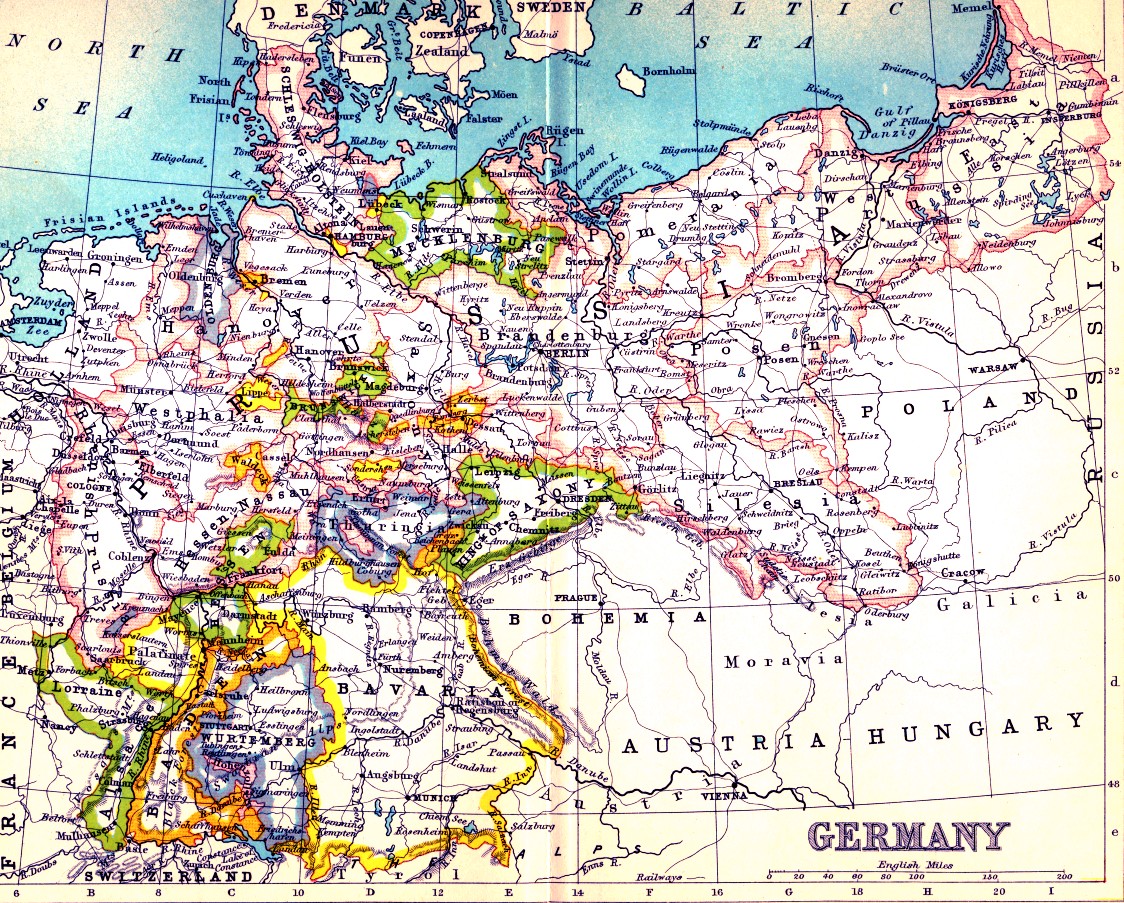
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Glimpse into Imperial Germany: Exploring the 1900 Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
