A Snapshot of a Turbulent Era: Examining the 1937 Map of Europe
Related Articles: A Snapshot of a Turbulent Era: Examining the 1937 Map of Europe
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Snapshot of a Turbulent Era: Examining the 1937 Map of Europe. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Snapshot of a Turbulent Era: Examining the 1937 Map of Europe
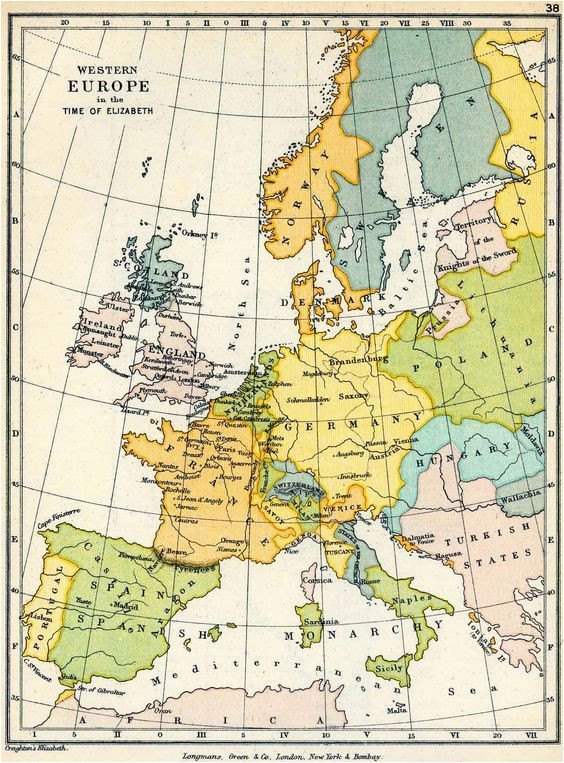
The 1937 map of Europe offers a fascinating glimpse into a period of immense political and social upheaval. The continent, scarred by the First World War and teetering on the brink of another, presented a complex tapestry of nations, each with its own unique history, aspirations, and anxieties. Examining this map provides a valuable window into the geopolitical landscape of the time, allowing us to understand the forces at play and the events that would shape the future of Europe.
The Shifting Sands of Borders:
The 1937 map reflects the aftermath of the First World War, showcasing the redrawing of borders and the rise of new nations. The collapse of the Austro-Hungarian and Ottoman Empires led to the creation of Czechoslovakia, Yugoslavia, and Poland, among others. These newly formed states, often fragile and struggling with internal divisions, were navigating their place in the world, seeking stability and recognition on the international stage.
However, the peace was precarious. The Treaty of Versailles, which had officially ended the war, imposed harsh penalties on Germany, leading to resentment and a desire for revenge. This simmering discontent fueled the rise of extremist ideologies, particularly Nazism, which promised to restore Germany’s lost glory and reclaim its rightful place in Europe.
The Shadow of Fascism:
The 1937 map also reveals the growing influence of fascist regimes in Europe. Benito Mussolini’s Italy, having conquered Ethiopia in 1935, had established itself as a major power in the Mediterranean. Meanwhile, Adolf Hitler’s Nazi Germany was rapidly consolidating its power, annexing Austria in 1938 and threatening the independence of Czechoslovakia. This expansionist policy, driven by nationalist ambitions and a desire to overturn the Treaty of Versailles, cast a dark shadow over the continent, signaling the growing possibility of another devastating conflict.
The Rise of Soviet Power:
The Soviet Union, under the leadership of Joseph Stalin, was undergoing a period of rapid industrialization and military expansion. The 1937 map reflects the growing influence of the USSR, particularly in Eastern Europe, where it sought to establish a sphere of influence and secure its borders. This ideological rivalry with the West, combined with the expansionist ambitions of Nazi Germany, created a volatile geopolitical situation, further increasing the risk of war.
Beyond Borders: The Social and Economic Landscape
The 1937 map of Europe is not just a representation of political boundaries, but also a reflection of the social and economic conditions prevailing at the time. The Great Depression, which had ravaged the world in the 1930s, continued to cast a long shadow over Europe. Unemployment was high, economies were struggling, and social unrest was widespread. This economic hardship contributed to the rise of extremist ideologies, as people sought scapegoats and promised solutions to their problems.
The Importance of Understanding the 1937 Map
Examining the 1937 map of Europe provides valuable insights into the events that led to the Second World War. It allows us to understand the geopolitical complexities of the time, the rise of authoritarian regimes, the tensions between nations, and the social and economic conditions that fueled conflict. By studying this historical snapshot, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the fragility of peace, the dangers of nationalism and extremism, and the importance of international cooperation in preventing future conflicts.
FAQs about the 1937 Map of Europe:
1. What were the major geopolitical changes that occurred in Europe between the First and Second World Wars?
The period between the two World Wars witnessed significant changes in the European geopolitical landscape. The collapse of empires, the rise of new nations, the spread of fascism, and the growing influence of the Soviet Union all contributed to a volatile and unpredictable environment.
2. What were the key factors that contributed to the rise of fascism in Europe?
The rise of fascism in Europe was a complex phenomenon with multiple contributing factors, including economic hardship, social unrest, political instability, and the desire for a strong leader. Fascism offered a simplistic solution to complex problems, promising national unity, economic recovery, and a return to traditional values.
3. How did the Treaty of Versailles contribute to the rise of tensions in Europe?
The Treaty of Versailles, which imposed harsh penalties on Germany after the First World War, created resentment and a desire for revenge among the German population. This discontent fueled the rise of extremist ideologies, particularly Nazism, which promised to overturn the treaty and restore Germany’s lost glory.
4. What was the role of the Soviet Union in the European geopolitical landscape of the 1930s?
The Soviet Union, under the leadership of Joseph Stalin, was undergoing a period of rapid industrialization and military expansion. It sought to establish a sphere of influence in Eastern Europe and secure its borders, creating a tense rivalry with the West.
5. How did the economic conditions of the 1930s contribute to the outbreak of the Second World War?
The Great Depression, which ravaged the world in the 1930s, had a profound impact on Europe. Unemployment was high, economies were struggling, and social unrest was widespread. This economic hardship contributed to the rise of extremist ideologies, as people sought scapegoats and promised solutions to their problems.
Tips for Understanding the 1937 Map of Europe:
1. Research the historical context: It is crucial to understand the events and trends that shaped the geopolitical landscape of 1937. Research the aftermath of the First World War, the rise of fascism, the Great Depression, and the growing influence of the Soviet Union.
2. Analyze the borders: Pay attention to the newly formed nations and the shifting borders. Consider the reasons for these changes and their impact on the political and social landscape.
3. Identify areas of tension: Look for regions where tensions were high and conflicts were likely to erupt. Consider the factors that contributed to these tensions, such as territorial disputes, ideological differences, or economic rivalries.
4. Examine the influence of major powers: Analyze the role of major powers, such as Germany, Italy, and the Soviet Union, in the geopolitical landscape. Consider their ambitions, their foreign policies, and their impact on the balance of power.
5. Connect the map to historical events: Use the map as a starting point to research specific historical events, such as the Anschluss (annexation of Austria by Germany), the Munich Agreement, or the outbreak of the Second World War.
Conclusion:
The 1937 map of Europe serves as a stark reminder of the fragility of peace and the dangers of unchecked nationalism and extremism. It highlights the complex geopolitical landscape of the time, the rise of authoritarian regimes, and the social and economic conditions that fueled conflict. By understanding the events and trends that shaped this period, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the importance of international cooperation, diplomacy, and the need to address the root causes of conflict. The lessons learned from this turbulent era remain relevant today, urging us to strive for a more peaceful and just world.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Snapshot of a Turbulent Era: Examining the 1937 Map of Europe. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
