Europe in 1810: A Continent in Flux
Related Articles: Europe in 1810: A Continent in Flux
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Europe in 1810: A Continent in Flux. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Europe in 1810: A Continent in Flux

The year 1810 presents a Europe in the midst of significant transformation. The Napoleonic Wars, a period of intense conflict that had begun in 1803, were at their peak, shaping the political landscape of the continent in profound ways. This era witnessed the rise and fall of empires, the redrawing of borders, and the emergence of new ideologies that would profoundly impact the future of Europe.
The Rise of Napoleon and the French Empire
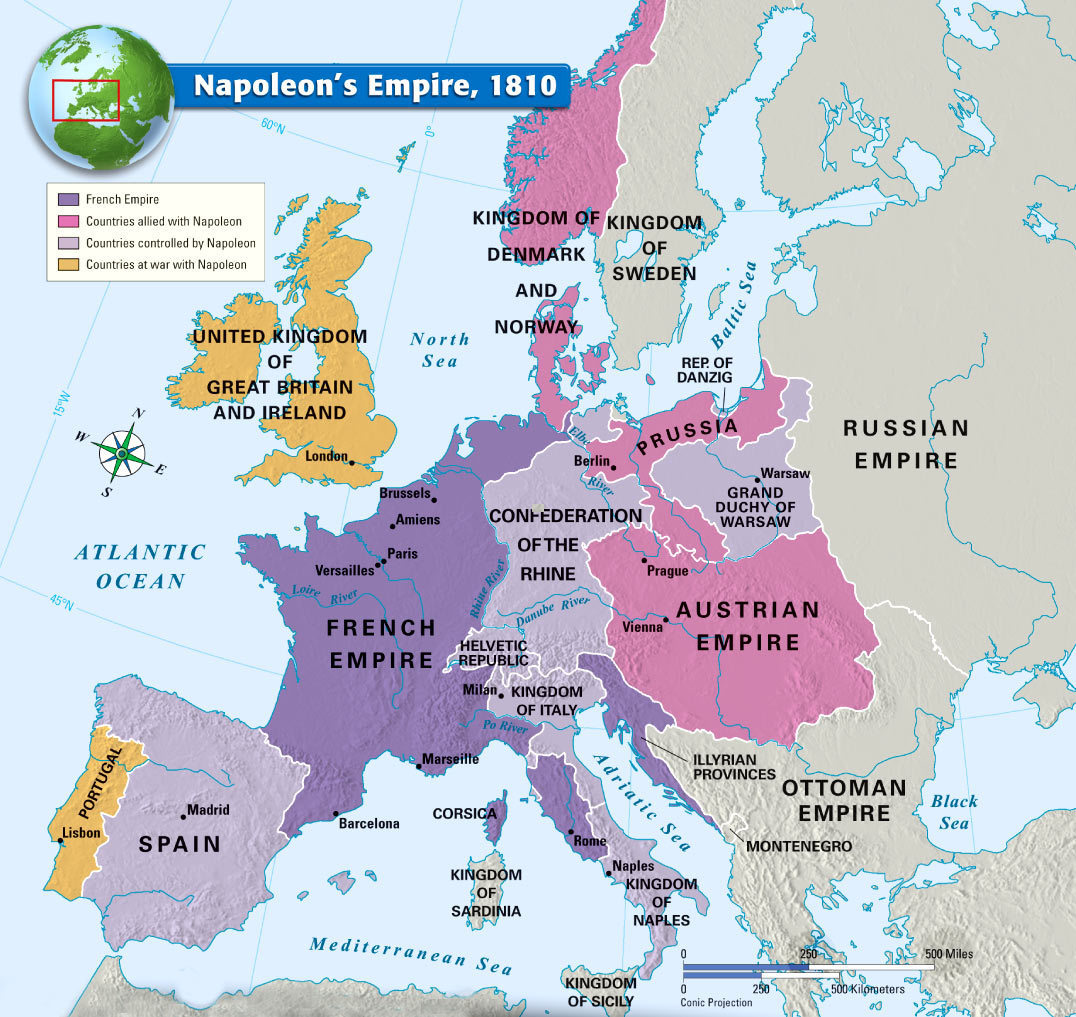
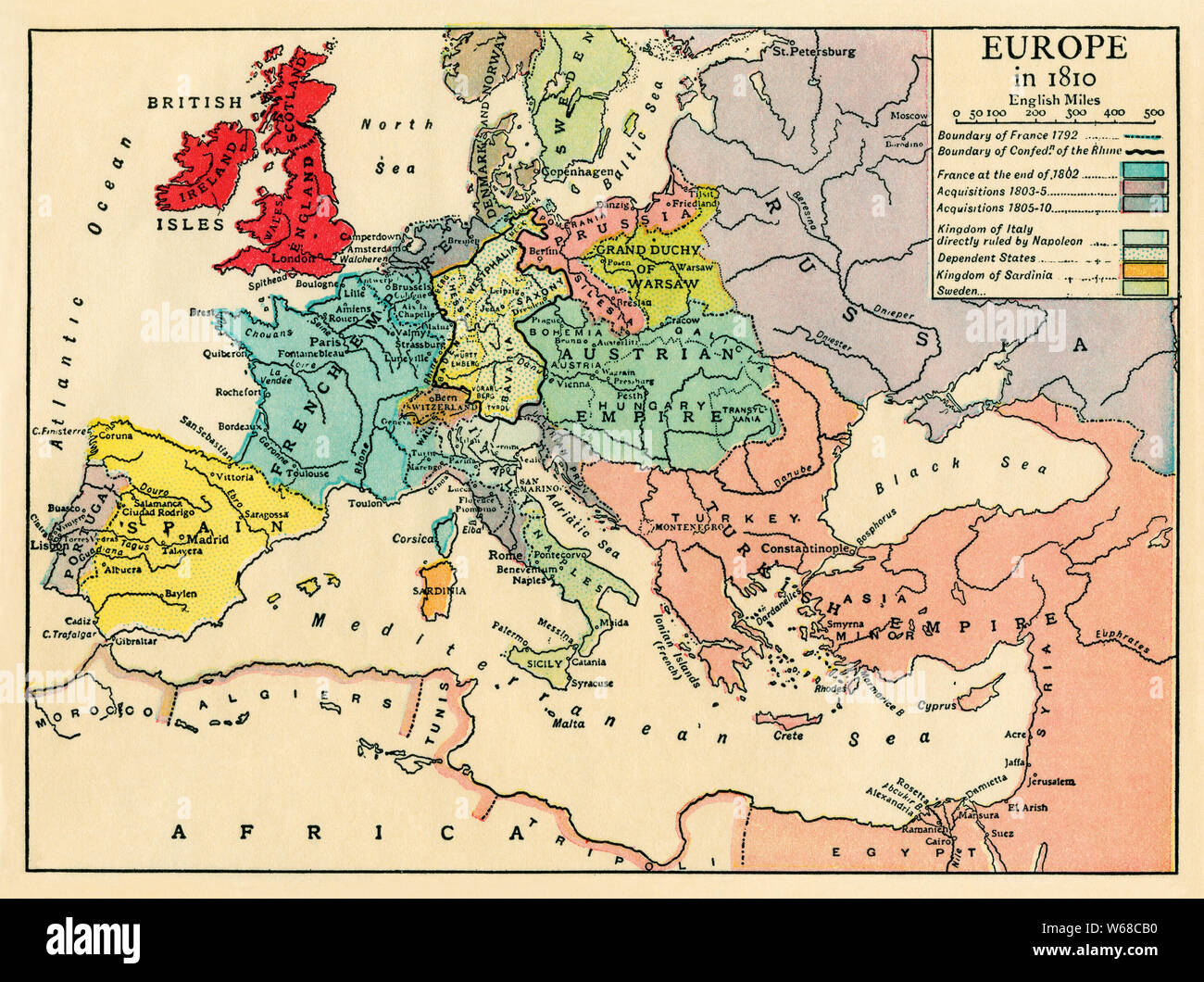
Napoleon Bonaparte, the ambitious and charismatic French general, had ascended to power in 1799, establishing himself as First Consul and effectively ruling France. His military prowess led to a series of victories against various European coalitions, culminating in the creation of a vast French Empire. By 1810, Napoleon’s influence stretched across much of continental Europe, encompassing territories like Spain, Italy, the Netherlands, and parts of Germany.
A Fragmented Europe
Despite Napoleon’s dominance, Europe in 1810 was far from unified. The French Empire coexisted with a patchwork of independent states, each with its own political structure and alliances. The United Kingdom, under the reign of King George III, remained a powerful force, resisting Napoleon’s ambitions and challenging his control of the seas. Austria, Prussia, and Russia, though weakened by the Napoleonic Wars, still held significant power and posed potential threats to Napoleon’s authority.
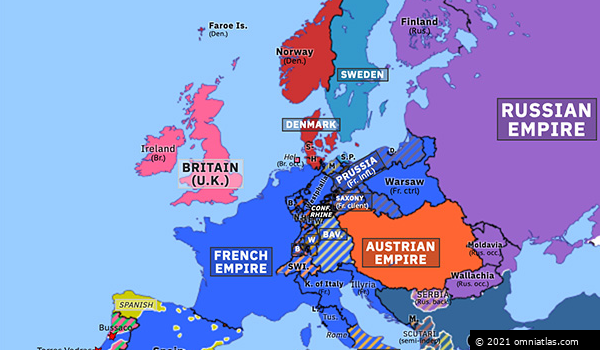
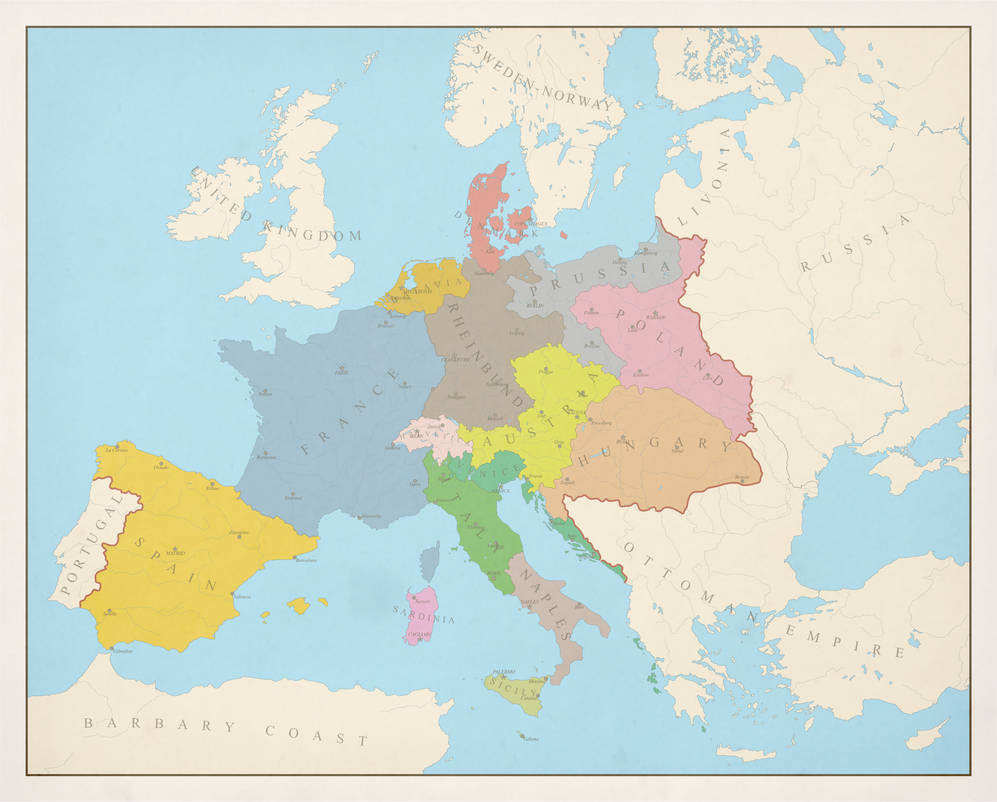
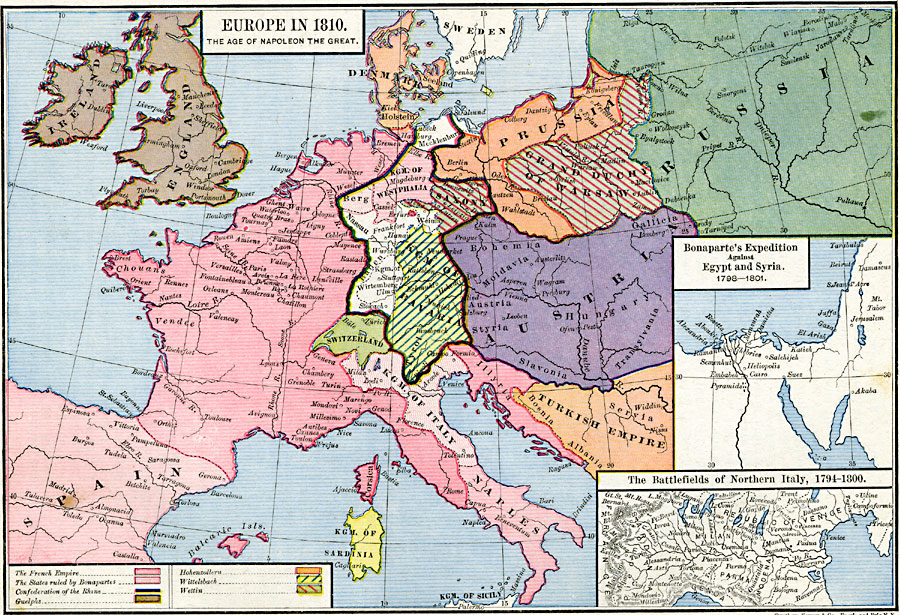
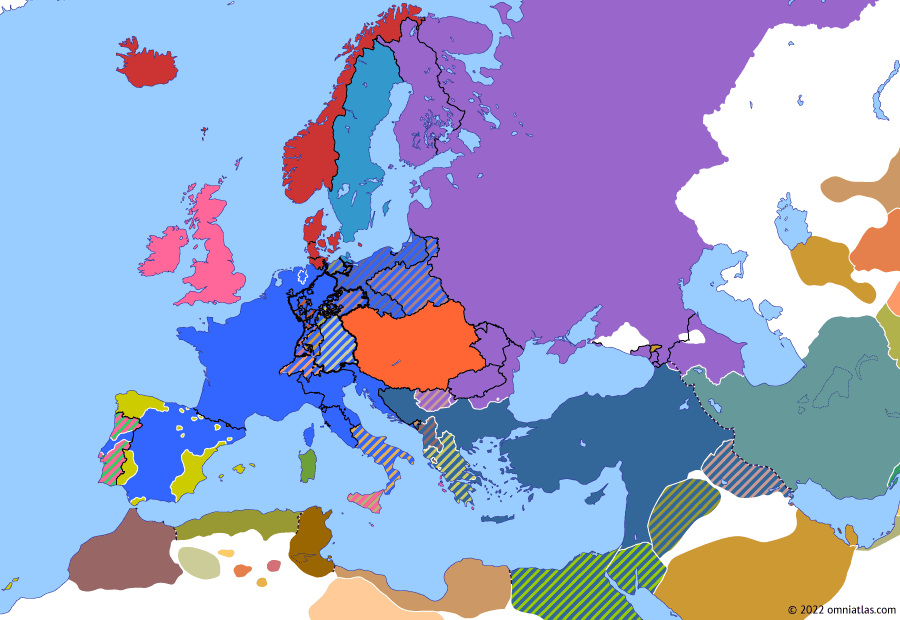
The Map of Europe in 1810
The map of Europe in 1810 reflects the complex geopolitical situation of the time. It showcases the vast expanse of the French Empire, with its core territories in France and its satellite kingdoms spread across the continent. The map also reveals the intricate web of alliances and rivalries that defined European politics.
Key Features of the Map:
- The French Empire: The French Empire, encompassing France, Italy, the Netherlands, and parts of Germany, dominated the map, highlighting Napoleon’s territorial ambitions.
- The United Kingdom: The United Kingdom, isolated from continental Europe, remained a powerful force, challenging Napoleon’s naval supremacy.
- The Austrian Empire: The Austrian Empire, centered in Vienna, controlled territories in Central Europe, including Bohemia, Hungary, and parts of Italy.
- The Kingdom of Prussia: The Kingdom of Prussia, centered in Berlin, held territories in northern Germany, maintaining its own power despite setbacks in the Napoleonic Wars.
- The Russian Empire: The Russian Empire, stretching across vast territories in Eastern Europe and Asia, remained a potential threat to Napoleon’s ambitions.
- The Ottoman Empire: The Ottoman Empire, centered in Constantinople, controlled territories in the Balkans and the Middle East, holding a significant presence in the Eastern Mediterranean.
The Significance of the Map
The map of Europe in 1810 is a powerful visual representation of the continent’s political and territorial configuration during a turbulent period. It highlights the rise of Napoleon and the French Empire, showcasing the impact of his military conquests on the European landscape. The map also reveals the intricate network of alliances and rivalries that defined the era, underscoring the complex dynamics of power that shaped the continent’s future.
The Legacy of the Map
The map of Europe in 1810 serves as a reminder of the fragility of political order and the constant flux of power dynamics. It underscores the importance of understanding historical context in analyzing current events and appreciating the long-term consequences of political decisions. The map also highlights the enduring impact of the Napoleonic Wars on the development of Europe, shaping the continent’s political landscape and influencing the course of its history.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Q1: What were the major political changes in Europe during the Napoleonic Wars?
A1: The Napoleonic Wars led to significant political changes in Europe, including:
- The rise of the French Empire under Napoleon Bonaparte, encompassing vast territories in continental Europe.
- The redrawing of borders, with many traditional kingdoms and principalities being dissolved or reorganized.
- The spread of French revolutionary ideals, challenging the existing political order and inspiring movements for change.
- The emergence of new ideologies, such as nationalism and liberalism, which would have a profound impact on European politics in the 19th century.
Q2: What were the major military battles of the Napoleonic Wars?
A2: The Napoleonic Wars witnessed a series of major military battles, including:
- The Battle of Austerlitz (1805), a decisive French victory over Austria and Russia.
- The Battle of Jena-Auerstedt (1806), a crushing French victory over Prussia.
- The Battle of Friedland (1807), a decisive French victory over Russia.
- The Battle of Trafalgar (1805), a British naval victory over the combined French and Spanish fleets.
- The Peninsular War (1808-1814), a protracted conflict between France and Spain, supported by Britain.
Q3: What were the main alliances during the Napoleonic Wars?
A3: The Napoleonic Wars were marked by a complex web of alliances, with shifting loyalties and changing coalitions. The main alliances included:
- The First Coalition (1792-1797): Austria, Prussia, Great Britain, Russia, and other European powers against France.
- The Second Coalition (1798-1802): Russia, Austria, Great Britain, and the Ottoman Empire against France.
- The Third Coalition (1805-1806): Russia, Austria, and Great Britain against France.
- The Fourth Coalition (1806-1807): Prussia, Russia, and Great Britain against France.
- The Fifth Coalition (1809): Austria and Great Britain against France.
- The Sixth Coalition (1812-1814): Russia, Prussia, Austria, Great Britain, and other European powers against France.
Q4: How did the Napoleonic Wars impact the development of nationalism in Europe?
A4: The Napoleonic Wars played a significant role in the development of nationalism in Europe. Napoleon’s conquests and the spread of French revolutionary ideals challenged the existing political order and inspired movements for national unity and self-determination. The wars also led to the formation of new national identities, as people from different regions and cultures began to identify themselves as part of a larger national community.
Tips for Studying the Map of Europe in 1810:
- Focus on the key territorial changes: Pay attention to the territories gained by the French Empire and the changes in the borders of other European states.
- Analyze the alliances and rivalries: Understand the complex web of alliances and rivalries that defined the political landscape of the time.
- Consider the impact of the Napoleonic Wars: Reflect on the long-term consequences of the Napoleonic Wars on the development of Europe.
- Compare the map with contemporary maps: Compare the map of Europe in 1810 with maps from earlier and later periods to understand the historical evolution of the continent’s political landscape.
- Use online resources: Explore online resources such as historical maps, articles, and books to gain a deeper understanding of the map of Europe in 1810.
Conclusion:
The map of Europe in 1810 offers a fascinating glimpse into a pivotal moment in European history. It captures the rise of Napoleon and the French Empire, the complex web of alliances and rivalries, and the profound impact of the Napoleonic Wars on the continent’s political landscape. By studying this map, we can gain a deeper understanding of the historical context of the time and appreciate the enduring influence of this period on the development of Europe.

![Central Europe 1810. Europe under Napoleon [2285 x 1883] European map](https://i.pinimg.com/736x/03/cf/15/03cf15666c3a27cc5ba763dc29cea566--maps-history-modern-history.jpg)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Europe in 1810: A Continent in Flux. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
