Exploring the Humboldt Current: A Vital Force in the Pacific Ocean
Related Articles: Exploring the Humboldt Current: A Vital Force in the Pacific Ocean
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Exploring the Humboldt Current: A Vital Force in the Pacific Ocean. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Exploring the Humboldt Current: A Vital Force in the Pacific Ocean

The Humboldt Current, a cold, nutrient-rich current that flows northward along the western coast of South America, is a vital ecosystem and a significant contributor to the global oceanographic system. Its influence extends far beyond its physical boundaries, impacting climate, marine life, and human societies. This article delves into the intricacies of the Humboldt Current, its impact on the surrounding environment, and its significance for both ecological balance and human livelihoods.
Understanding the Humboldt Current:
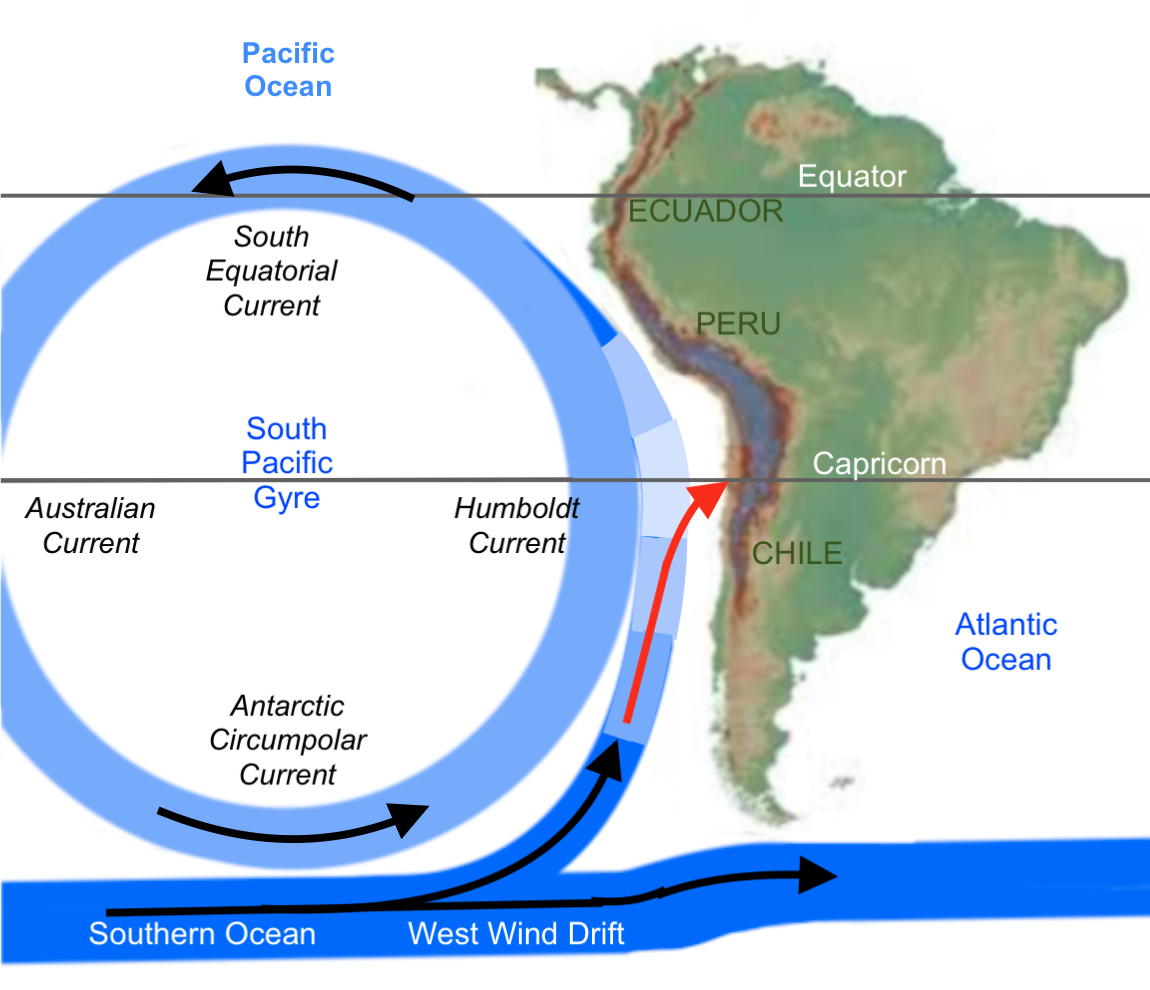
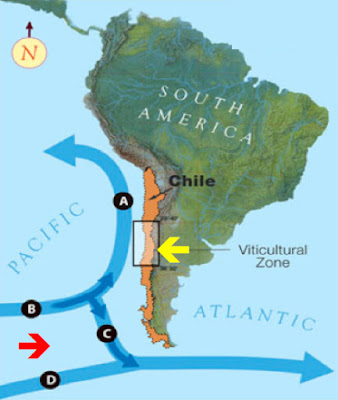
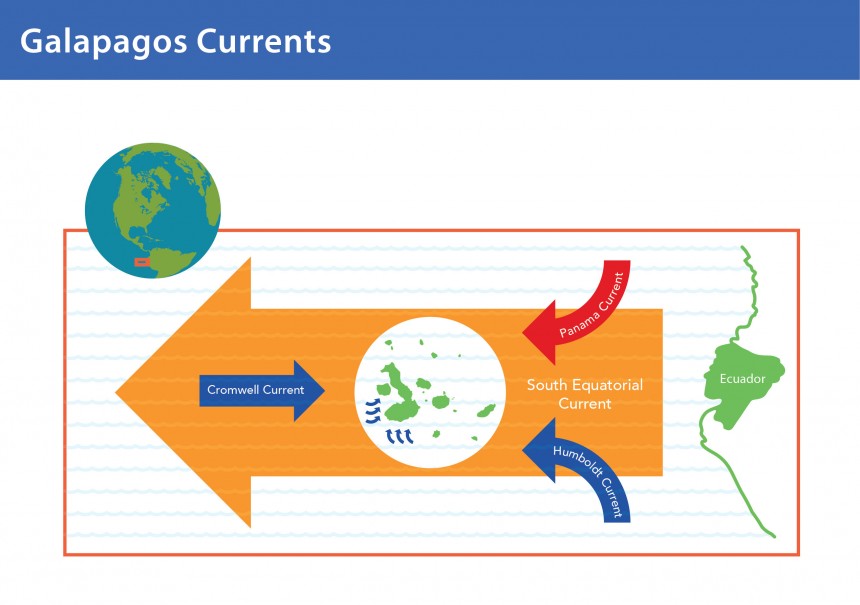
The Humboldt Current, also known as the Peru Current, originates in the Antarctic Circumpolar Current and flows northward along the western coast of South America, reaching as far north as the equator. This current is characterized by its cold, nutrient-rich waters, a result of upwelling, a process where deep, nutrient-rich water is brought to the surface.
The Mechanics of Upwelling:
Upwelling is driven by a combination of factors:
- Prevailing Winds: The prevailing winds along the South American coast push surface water westward, creating a void that is filled by cold, nutrient-rich water from the depths.
- Coriolis Effect: The Earth’s rotation deflects moving objects, including water, to the right in the Southern Hemisphere. This effect further contributes to the westward movement of surface water, facilitating upwelling.
- Oceanographic Conditions: The shape of the South American coastline and the presence of the Andes Mountains contribute to the formation of the Humboldt Current and its upwelling.
The Significance of Upwelling:
Upwelling brings essential nutrients, including nitrates, phosphates, and silicates, to the surface waters, fueling a rich ecosystem. This nutrient-rich water supports a diverse and abundant marine life, including:
- Phytoplankton: These microscopic algae form the base of the marine food web, consuming nutrients and converting sunlight into energy.
- Zooplankton: These small animals feed on phytoplankton and are, in turn, consumed by larger organisms.
- Fish: The Humboldt Current is renowned for its abundant fish populations, including anchovies, sardines, and tuna, attracting significant commercial fisheries.
- Marine Mammals: The abundance of fish supports a variety of marine mammals, such as seals, sea lions, dolphins, and whales.
- Seabirds: The region is a haven for seabirds, with vast colonies of guano-producing birds, like pelicans and boobies, relying on the rich ecosystem for food.
The Humboldt Current and Climate:
The Humboldt Current plays a crucial role in regulating the climate of the South American Pacific coast. Its cold waters moderate the coastal temperatures, creating a relatively cool and arid climate in the region. This climate is conducive to the development of unique ecosystems, such as the Atacama Desert, the driest desert on Earth.
Ecological Importance of the Humboldt Current:
The Humboldt Current ecosystem is a vibrant and productive region, supporting a diverse range of species and contributing significantly to the global marine biodiversity. The upwelling process ensures a constant supply of nutrients, fueling the food web and sustaining a rich ecosystem. The current’s influence extends far beyond its immediate boundaries, impacting the distribution and abundance of marine life throughout the Pacific Ocean.
Human Impact and Sustainability:
The Humboldt Current has been a crucial resource for human populations for centuries, providing food, economic opportunities, and cultural significance. However, human activities, including overfishing, pollution, and climate change, pose significant threats to the delicate balance of this ecosystem.
- Overfishing: The high abundance of fish in the Humboldt Current has attracted extensive commercial fisheries. Overfishing can deplete fish stocks, disrupting the food web and impacting the entire ecosystem.
- Pollution: Coastal development, industrial activities, and agricultural runoff can introduce pollutants into the ocean, harming marine life and disrupting the delicate balance of the ecosystem.
- Climate Change: Rising sea temperatures, changes in wind patterns, and ocean acidification due to climate change can disrupt the upwelling process, impacting the productivity and stability of the Humboldt Current ecosystem.
Conservation Efforts:
Recognizing the importance of the Humboldt Current and the threats it faces, various conservation efforts are underway to protect this vital ecosystem:
- Sustainable Fishing Practices: Implementing fishing quotas, establishing marine protected areas, and promoting sustainable fishing methods are crucial for ensuring the long-term health of fish stocks.
- Pollution Control: Reducing industrial emissions, managing agricultural runoff, and promoting responsible waste disposal are essential for mitigating pollution in the Humboldt Current.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Reducing greenhouse gas emissions through renewable energy sources and energy efficiency is essential for mitigating the impacts of climate change on the Humboldt Current ecosystem.
FAQs About the Humboldt Current:
Q: What is the significance of the Humboldt Current for human societies?
A: The Humboldt Current is a vital resource for human societies, providing food, economic opportunities, and cultural significance. It supports extensive commercial fisheries, contributes to tourism, and influences the climate of the surrounding region.
Q: What are the main threats to the Humboldt Current ecosystem?
A: Overfishing, pollution, and climate change pose significant threats to the Humboldt Current ecosystem, potentially disrupting the delicate balance of the ecosystem and impacting the livelihoods of people who depend on it.
Q: What are some ways to protect the Humboldt Current?
A: Conservation efforts include promoting sustainable fishing practices, controlling pollution, and mitigating climate change. These measures aim to ensure the long-term health and productivity of this vital ecosystem.
Tips for Further Exploration:
- Visit the Humboldt Current region: Witness the diverse marine life and experience the unique culture of the region.
- Support sustainable seafood: Choose seafood from sustainable sources to help protect fish stocks and the health of the Humboldt Current.
- Learn about conservation efforts: Stay informed about the challenges and opportunities related to the Humboldt Current and support organizations working to protect this vital ecosystem.
Conclusion:
The Humboldt Current is a remarkable oceanographic phenomenon, playing a crucial role in shaping the Pacific Ocean’s ecosystem and influencing the climate of the South American coast. Understanding its intricacies, appreciating its importance, and addressing the threats it faces are crucial for ensuring the long-term health of this vital ecosystem and the well-being of the people who depend on it. By implementing sustainable practices, mitigating pollution, and addressing climate change, we can work towards safeguarding the Humboldt Current for future generations.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Exploring the Humboldt Current: A Vital Force in the Pacific Ocean. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
