Fort Laramie: A Historical Crossroads on the Map
Related Articles: Fort Laramie: A Historical Crossroads on the Map
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Fort Laramie: A Historical Crossroads on the Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Fort Laramie: A Historical Crossroads on the Map
Fort Laramie, a name synonymous with the American West, holds a prominent place in the annals of history. Situated in the heart of the Great Plains, this historic outpost served as a crucial nexus for trade, exploration, and military operations during the 19th century. Understanding the significance of Fort Laramie requires delving into its geographical location, its historical evolution, and its lasting impact on the landscape and culture of the American West.
Geographical Context:
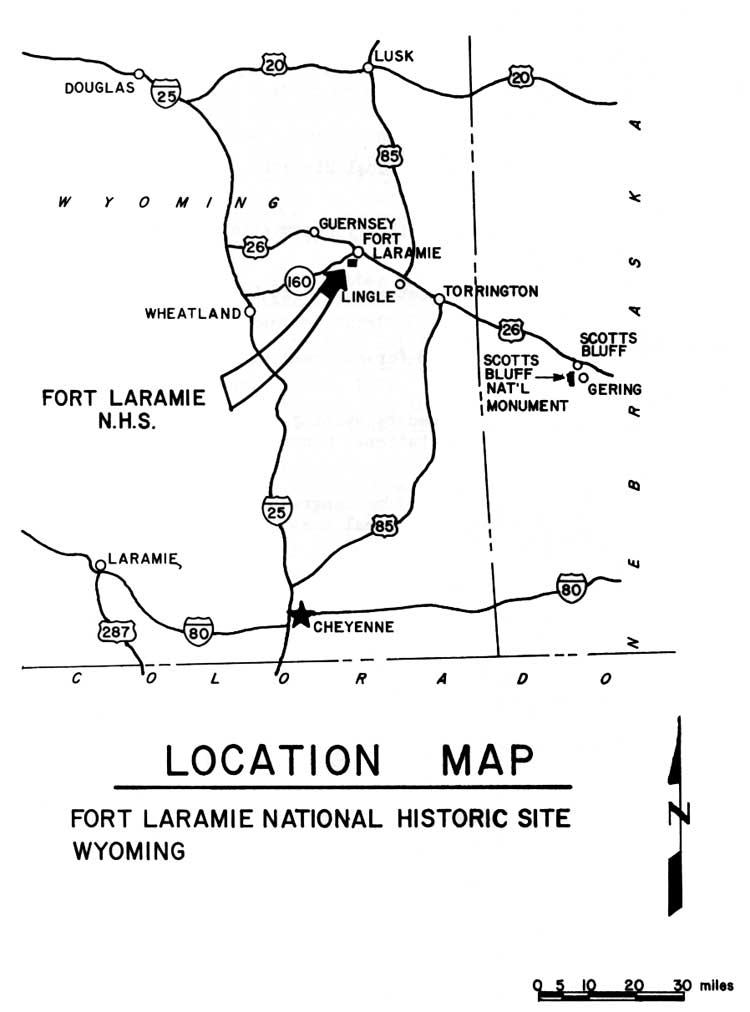
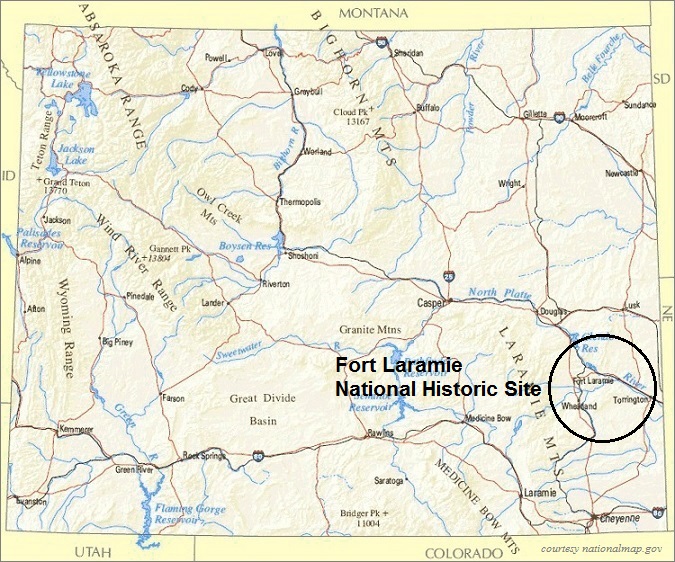
Fort Laramie’s strategic location on the Laramie River, in present-day Wyoming, played a pivotal role in its historical importance. Situated on the eastern edge of the Rocky Mountains, the fort controlled a vital access point to the vast western territories. It lay along the famed Oregon Trail, a major route for westward expansion and the transportation of goods and people. This strategic position ensured Fort Laramie’s role as a hub for trade, military operations, and cultural exchange.
Historical Evolution:
Fort Laramie’s history is intricately woven with the evolution of the American West. Its origins can be traced back to 1834 when the American Fur Company established a trading post on the site. This post, known as Fort William, served as a key trading center for Native American tribes and fur traders.
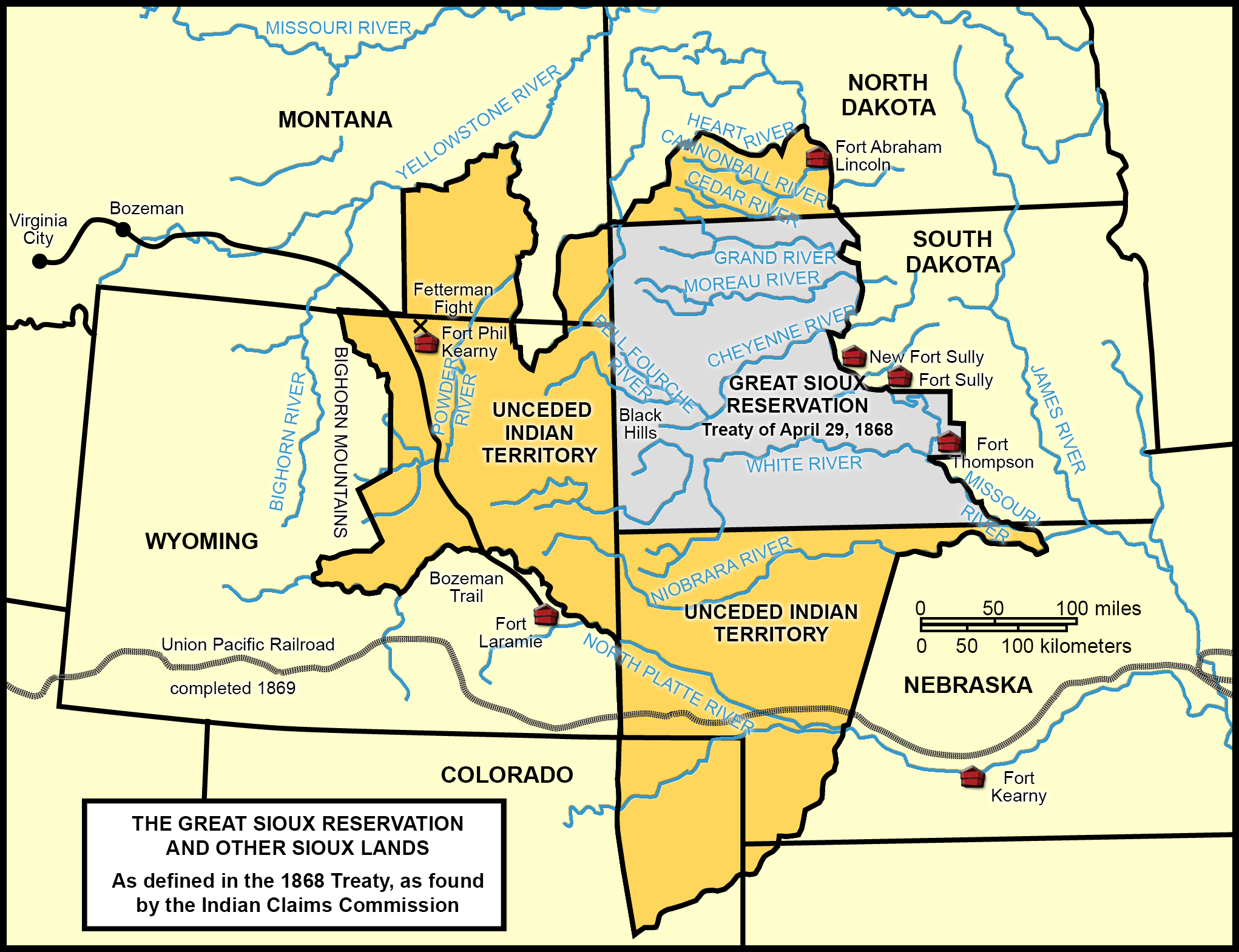
In 1849, the U.S. Army took control of the fort, renaming it Fort Laramie. The army’s presence transformed the fort into a military stronghold, serving as a base for protecting westward expansion and maintaining peace on the frontier. The fort’s importance increased during the Indian Wars of the 1860s and 1870s, as it played a critical role in military operations and negotiations with various Native American tribes.
The Fort Laramie Treaty:
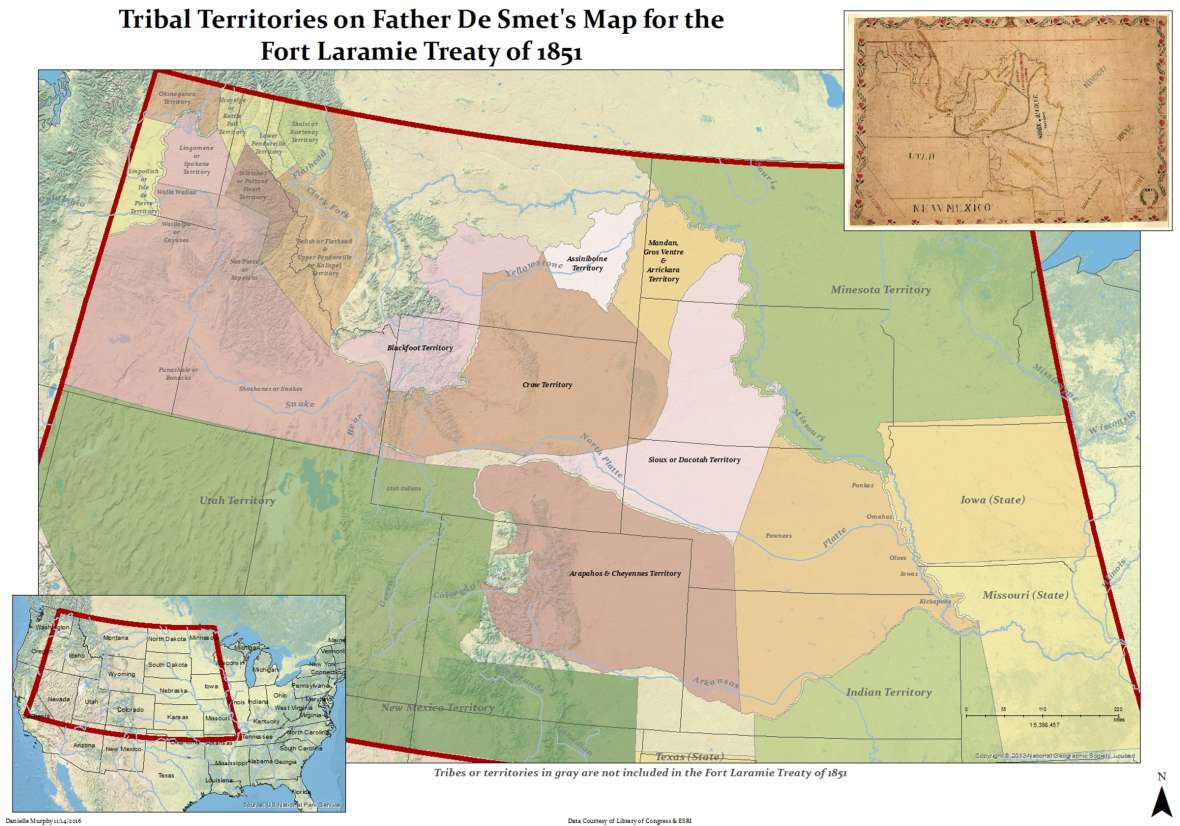
One of the most significant events in Fort Laramie’s history was the signing of the Fort Laramie Treaty in 1851. This treaty aimed to establish peace between the United States and several Native American tribes, including the Lakota, Cheyenne, Arapaho, and Crow. It defined tribal territories, established trade routes, and outlined provisions for peaceful coexistence. However, the treaty’s provisions were often violated, leading to further conflicts and tensions.
Decline and Legacy:
By the late 19th century, the importance of Fort Laramie as a military outpost began to decline. The expansion of the railroad network and the eventual defeat of Native American resistance diminished the fort’s strategic value. In 1890, Fort Laramie was officially abandoned by the U.S. Army.
Despite its decline, Fort Laramie left an enduring legacy on the landscape and culture of the American West. It served as a focal point for trade, exploration, and military operations, shaping the westward expansion of the United States. The fort also witnessed significant cultural interactions between Native American tribes, fur traders, and settlers, leaving an indelible mark on the history of the region.
Fort Laramie Today:
Today, Fort Laramie stands as a National Historic Site, offering visitors a glimpse into its rich and complex history. The preserved ruins of the fort, along with its museum and interpretive exhibits, provide a window into the lives of those who once called this place home.
Exploring Fort Laramie: A Journey Through Time:
For those interested in experiencing the history of Fort Laramie firsthand, a visit to the site offers a unique and rewarding journey. Visitors can explore the fort’s ruins, including the original stockade, the officers’ quarters, and the trading post. The museum houses a collection of artifacts, photographs, and documents that shed light on the fort’s past.
The interpretive exhibits provide detailed information about the fort’s history, its role in westward expansion, and its impact on Native American culture. Visitors can also learn about the lives of the soldiers, traders, and Native Americans who once lived and worked at Fort Laramie.
Beyond the Fort: Exploring the Laramie River Valley:
The Laramie River Valley, where Fort Laramie is situated, offers a wealth of opportunities for outdoor recreation and exploration. Visitors can enjoy hiking, fishing, and camping in the surrounding area. The valley is also home to several other historical sites, including the Oregon Trail Ruts and the Register Cliff, which offers a glimpse into the lives of early pioneers.
FAQs about Fort Laramie:
1. What is the significance of Fort Laramie?
Fort Laramie played a crucial role in westward expansion, serving as a key trading post, military outpost, and focal point for cultural interactions between Native American tribes, fur traders, and settlers.
2. What is the Fort Laramie Treaty?
The Fort Laramie Treaty of 1851 aimed to establish peace between the United States and several Native American tribes, defining tribal territories, establishing trade routes, and outlining provisions for peaceful coexistence.
3. Why was Fort Laramie abandoned?
The importance of Fort Laramie as a military outpost declined with the expansion of the railroad network and the eventual defeat of Native American resistance. The fort was officially abandoned by the U.S. Army in 1890.
4. What can visitors see at Fort Laramie today?
Visitors can explore the fort’s ruins, including the original stockade, the officers’ quarters, and the trading post. The museum houses a collection of artifacts, photographs, and documents that shed light on the fort’s past.
5. What are some other historical sites in the Laramie River Valley?
The Laramie River Valley is home to several other historical sites, including the Oregon Trail Ruts and the Register Cliff.
Tips for Visiting Fort Laramie:
- Plan your visit: Allow ample time to explore the fort and its museum.
- Wear comfortable shoes: The fort is spread out over a large area and involves walking.
- Bring water and snacks: There are limited food and drink options available at the site.
- Check the website for special events and programs: The fort often hosts special events and programs throughout the year.
- Explore the surrounding area: The Laramie River Valley offers a wealth of opportunities for outdoor recreation and exploration.
Conclusion:
Fort Laramie stands as a powerful reminder of the complex history of the American West. Its strategic location, its role in westward expansion, and its impact on Native American culture make it a vital part of the nation’s heritage. Today, the fort serves as a National Historic Site, offering visitors a glimpse into the lives of those who shaped the American West. A visit to Fort Laramie is an opportunity to immerse oneself in history, to learn about the challenges and triumphs of those who came before, and to appreciate the enduring legacy of this historic outpost.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Fort Laramie: A Historical Crossroads on the Map. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
