Navigating the World: Understanding Longitude and Latitude
Related Articles: Navigating the World: Understanding Longitude and Latitude
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the World: Understanding Longitude and Latitude. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating the World: Understanding Longitude and Latitude
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating the World: Understanding Longitude and Latitude
- 3.1 Longitude: Measuring East to West
- 3.2 Latitude: Measuring North to South
- 3.3 The Power of Intersection: Pinpointing Locations
- 3.4 The Importance of Longitude and Latitude
- 3.5 Understanding the Grid: A Visual Representation
- 3.6 FAQ: Exploring the Nuances of Longitude and Latitude
- 3.7 Tips for Working with Longitude and Latitude
- 3.8 Conclusion: A Universal Language for Our World
- 4 Closure
Navigating the World: Understanding Longitude and Latitude

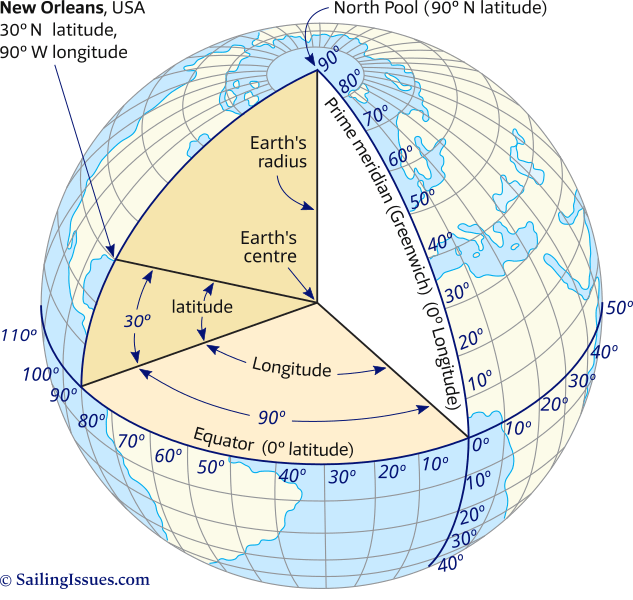
The Earth, a vast sphere spinning in space, is a complex entity. To comprehend its intricate geography and navigate its diverse landscapes, we rely on a system of coordinates: longitude and latitude. These invisible lines, intersecting at precise points, provide a framework for pinpointing locations on our planet with unparalleled accuracy.
Longitude: Measuring East to West
Imagine a series of lines, like the rungs of a ladder, running vertically from the North Pole to the South Pole. These lines are lines of longitude, also known as meridians. They measure the angular distance east or west of a reference point, the Prime Meridian.
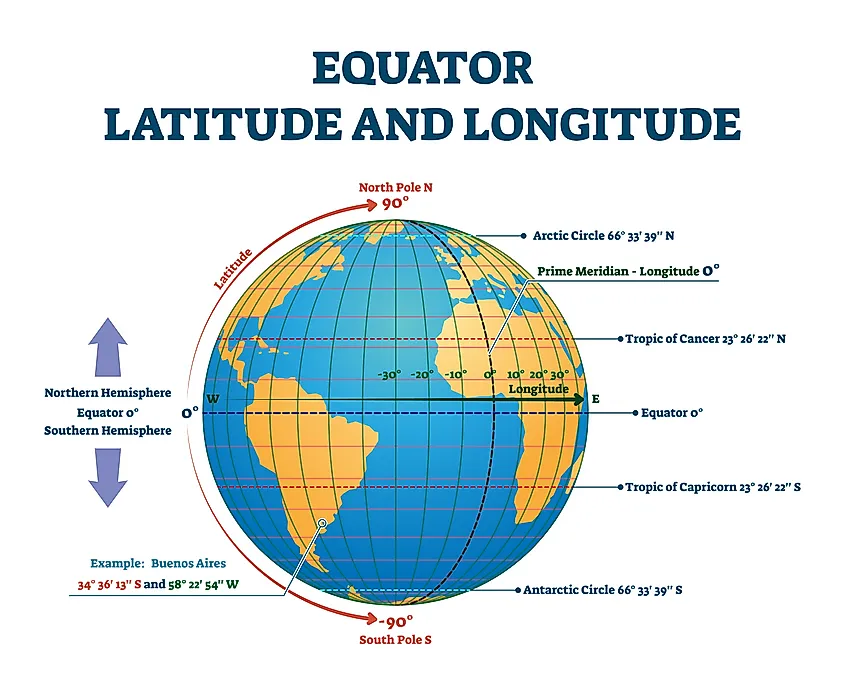
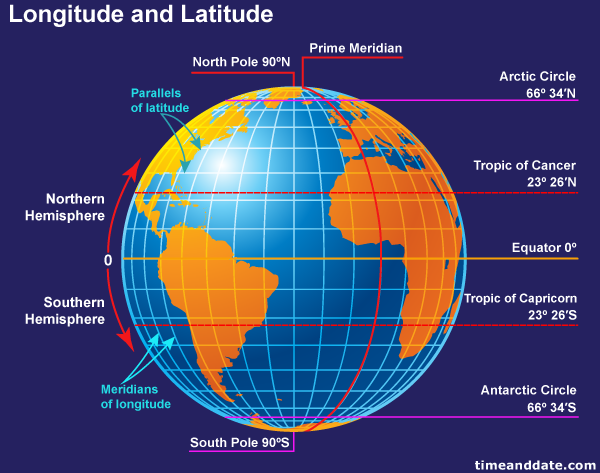
The Prime Meridian, designated as 0° longitude, runs through Greenwich, England. Each meridian east of the Prime Meridian is assigned a positive value, while meridians west of it are assigned negative values. As you move further east or west from the Prime Meridian, the longitude values increase, reaching a maximum of 180° at the International Date Line.
Longitude plays a crucial role in determining time zones. Since the Earth rotates on its axis, different locations experience sunrise and sunset at varying times. Each 15° difference in longitude corresponds to a one-hour time difference. This principle is the foundation of global timekeeping.
Latitude: Measuring North to South
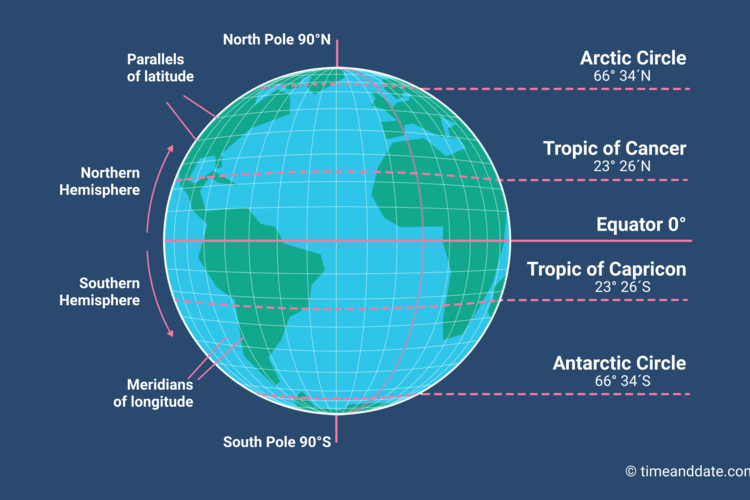
Now, picture a series of circles, parallel to the equator, encircling the Earth. These circles are lines of latitude, also known as parallels. They measure the angular distance north or south of the equator, which is designated as 0° latitude.
The equator is the largest of these circles, dividing the Earth into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. As you move further north or south from the equator, the latitude values increase, reaching 90° at the North and South Poles.
Latitude influences climate and weather patterns. Regions near the equator receive the most direct sunlight, leading to warmer temperatures. Conversely, locations at higher latitudes experience colder temperatures due to the angle of the sun’s rays.
The Power of Intersection: Pinpointing Locations
The true power of longitude and latitude lies in their intersection. When a line of longitude intersects a line of latitude, they pinpoint a specific location on Earth. This system, known as geographic coordinates, allows us to accurately define any point on the globe.
For example, the coordinates 40.7128° N, 74.0060° W represent the location of Times Square in New York City. This system provides a universal language for identifying locations, facilitating communication and collaboration across diverse geographical boundaries.
The Importance of Longitude and Latitude
Longitude and latitude are not mere abstract concepts; they are fundamental to our understanding and interaction with the world. Their applications are diverse and essential, impacting various aspects of our lives:
Navigation: GPS systems, essential for driving, flying, and maritime navigation, rely heavily on longitude and latitude. By triangulating signals from satellites, GPS devices determine precise locations, enabling accurate navigation and route planning.
Mapping: Maps, the visual representations of our world, are constructed using longitude and latitude. They provide a framework for organizing and presenting geographical information, allowing us to visualize and comprehend the Earth’s diverse landscapes and features.
Weather Forecasting: Weather patterns are influenced by latitude and longitude. By understanding the geographic location of weather phenomena, meteorologists can predict and track storms, temperature fluctuations, and other weather events, providing valuable information for public safety and preparedness.
Resource Management: Longitude and latitude play a crucial role in resource management. By mapping resource distribution, we can effectively monitor and manage natural resources, ensuring their sustainable use and conservation.
Scientific Research: Scientists use longitude and latitude to study and analyze various aspects of the Earth, including climate change, geological formations, and biodiversity. By understanding the spatial distribution of phenomena, researchers can gain valuable insights into the Earth’s intricate systems.
Understanding the Grid: A Visual Representation
To visualize the concept of longitude and latitude, imagine a grid superimposed on the Earth. The lines of longitude run vertically, like the lines on a graph paper, while the lines of latitude run horizontally. Each intersection represents a specific location on the globe.
This grid system, known as the geographic coordinate system, is a powerful tool for understanding and navigating our world. It provides a framework for organizing spatial information, allowing us to map, analyze, and manage the Earth’s resources effectively.
FAQ: Exploring the Nuances of Longitude and Latitude
1. What is the difference between latitude and longitude?
Latitude measures the angular distance north or south of the equator, while longitude measures the angular distance east or west of the Prime Meridian. Latitude lines are parallel circles, while longitude lines are meridians that converge at the poles.
2. How are longitude and latitude used in GPS systems?
GPS systems use a network of satellites orbiting Earth to determine precise locations. By triangulating signals from these satellites, GPS devices calculate the user’s latitude and longitude coordinates, providing accurate location information.
3. Why is the Prime Meridian located at Greenwich, England?
The Prime Meridian was established at Greenwich, England, in the late 19th century. This location was chosen due to the prominence of the Royal Observatory at Greenwich, which was a leading center of astronomical research at the time.
4. What is the International Date Line?
The International Date Line is an imaginary line that runs roughly along the 180° meridian. It marks the boundary between two calendar days. When crossing the International Date Line from east to west, the date is advanced by one day. Conversely, when crossing it from west to east, the date is moved back by one day.
5. How do longitude and latitude affect time zones?
Each 15° difference in longitude corresponds to a one-hour time difference. This is because the Earth rotates on its axis, and different locations experience sunrise and sunset at varying times. As a result, time zones are established based on longitude, with each zone representing a specific range of longitude values.
Tips for Working with Longitude and Latitude
1. Understanding Degrees, Minutes, and Seconds: Longitude and latitude are typically expressed in degrees (°), minutes (‘), and seconds ("). Each degree is divided into 60 minutes, and each minute is divided into 60 seconds.
2. Using Decimal Degrees: For digital applications, longitude and latitude are often expressed in decimal degrees. This format simplifies calculations and data processing.
3. Utilizing Online Tools: Numerous online tools and mapping platforms allow you to convert between different coordinate formats, search for locations using coordinates, and visualize geographic data.
4. Understanding the Relationship Between Longitude and Latitude: Remember that longitude lines converge at the poles, while latitude lines are parallel circles. This difference in geometry influences the distance between lines at different latitudes.
5. Applying Longitude and Latitude to Real-World Applications: Think about how longitude and latitude are used in various fields, such as navigation, mapping, weather forecasting, and resource management. This understanding will enhance your appreciation for the importance of this coordinate system.
Conclusion: A Universal Language for Our World
Longitude and latitude, a seemingly simple system of lines and angles, are essential tools for understanding and navigating our world. They provide a universal language for identifying locations, facilitating communication and collaboration across diverse geographical boundaries. From mapping the Earth’s landscapes to guiding our travels, longitude and latitude play a pivotal role in shaping our understanding and interaction with our planet. By appreciating the power and versatility of this coordinate system, we can unlock a deeper understanding of the world around us and navigate its complexities with greater precision and insight.
/Latitude-and-Longitude-58b9d1f35f9b58af5ca889f1.jpg)
![]()


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the World: Understanding Longitude and Latitude. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
