The Königsberg Bridge Problem: A Journey into the Origins of Graph Theory
Related Articles: The Königsberg Bridge Problem: A Journey into the Origins of Graph Theory
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Königsberg Bridge Problem: A Journey into the Origins of Graph Theory. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Königsberg Bridge Problem: A Journey into the Origins of Graph Theory

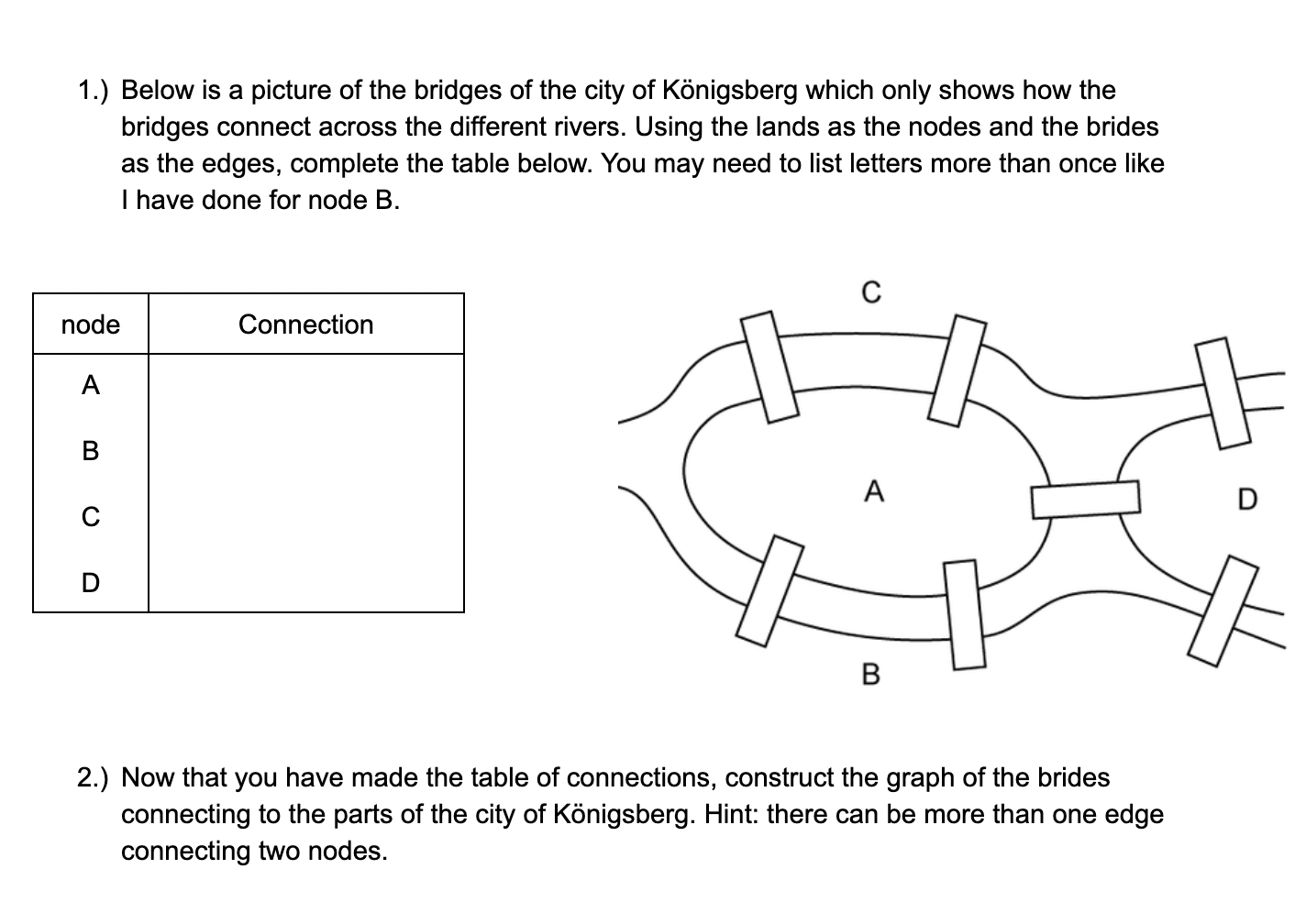
The Königsberg Bridge Problem, a seemingly simple puzzle about seven bridges connecting four landmasses in the Prussian city of Königsberg (now Kaliningrad, Russia), became a pivotal moment in the development of modern mathematics. This seemingly trivial problem, which captivated mathematicians in the 18th century, paved the way for the birth of graph theory, a branch of mathematics that has revolutionized our understanding of networks, relationships, and complex systems.
The Problem:
Königsberg, a city built on the Pregel River, was renowned for its seven bridges connecting four landmasses: two islands and two mainland sections. The city’s residents, eager to explore their surroundings, often wondered if it was possible to walk through the city, crossing each bridge exactly once and returning to the starting point. This seemingly simple question, posed by the Swiss mathematician Leonhard Euler in 1736, became a mathematical enigma that defied solution for decades.
Euler’s Breakthrough:
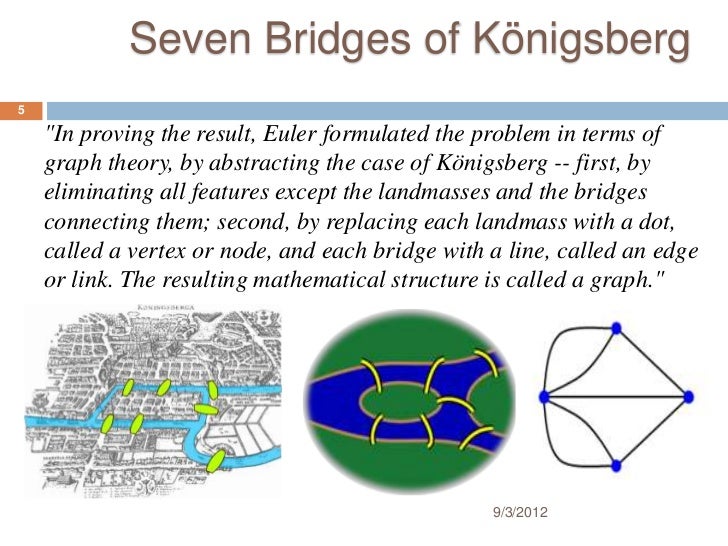
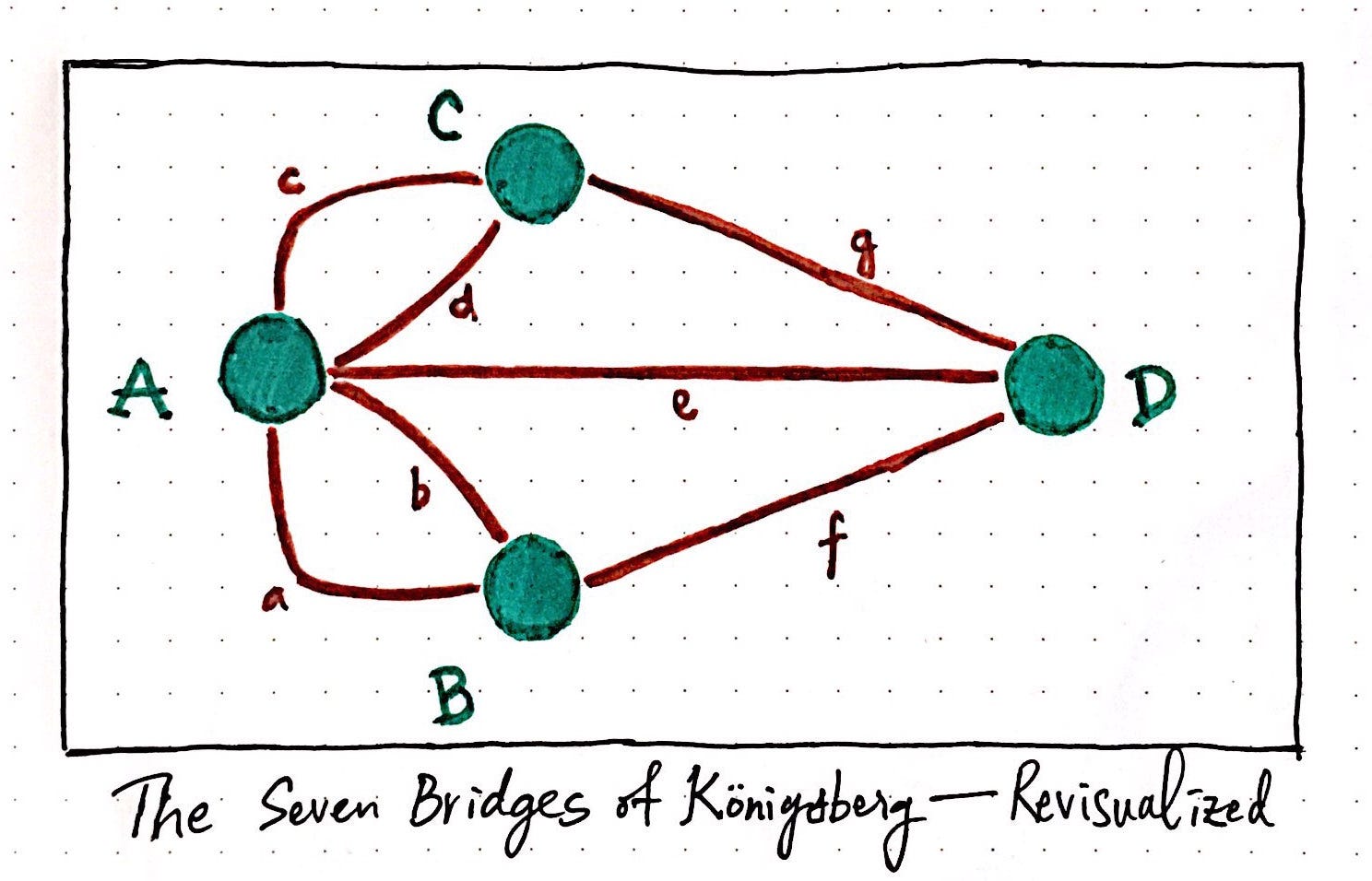
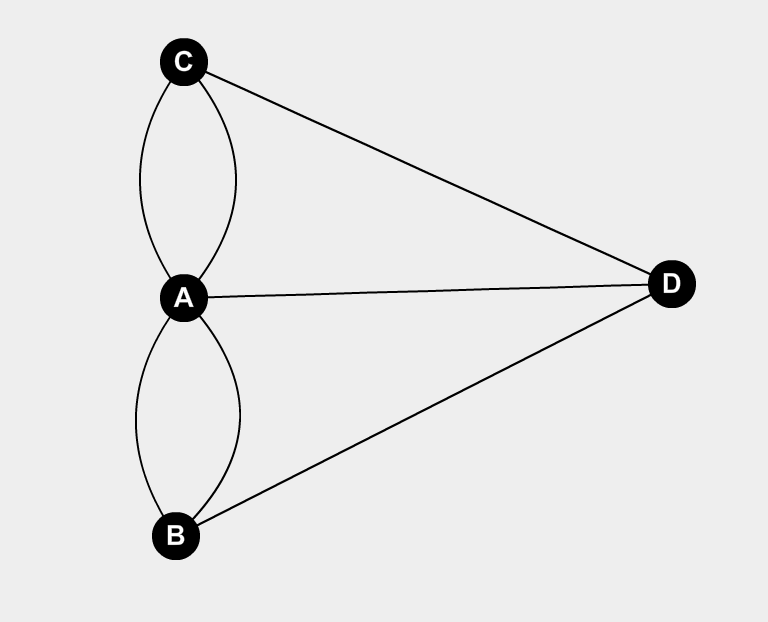
Euler, a pioneer in the field of mathematics, approached the problem with a novel perspective. Instead of focusing on the specific arrangement of bridges and landmasses, he abstracted the problem, representing each landmass as a point (vertex) and each bridge as a line connecting two points (edge). This simplified representation, now known as a graph, allowed Euler to analyze the problem without being bogged down by unnecessary details.
The Solution:
Through his analysis, Euler discovered that the possibility of traversing all bridges exactly once depended on the degree of each vertex, which represents the number of bridges connected to a landmass. He realized that a path traversing all bridges exactly once could only exist if all vertices had an even degree, meaning an even number of bridges connected to each landmass.
In the case of Königsberg, however, the problem presented an obstacle. Each of the four landmasses had an odd number of bridges connected to them. Therefore, Euler concluded that it was impossible to traverse all bridges exactly once and return to the starting point.
The Significance of Euler’s Solution:
Euler’s solution to the Königsberg Bridge Problem marked a significant turning point in the history of mathematics. It introduced the concept of graph theory, a powerful tool for representing and analyzing networks and relationships. This new field proved instrumental in understanding complex systems in various domains, including:
- Computer Science: Graph theory plays a crucial role in algorithms for network routing, data analysis, and search engine optimization.
- Social Sciences: Sociologists use graph theory to analyze social networks, understanding the flow of information and influence within communities.
- Biology: Graph theory is used to model biological networks, such as protein-protein interactions and gene regulatory networks.
- Engineering: Engineers use graph theory for optimizing network flow, designing efficient transportation systems, and analyzing the stability of structures.
Beyond the Königsberg Bridges:
The Königsberg Bridge Problem, while seemingly simple, opened the door to a vast and complex world of mathematical exploration. It demonstrated the power of abstraction in solving complex problems and laid the foundation for a new branch of mathematics that has had a profound impact on various fields.
FAQs about the Königsberg Bridge Problem:
1. What is a graph in mathematics?
A graph is a mathematical structure consisting of vertices (points) and edges (lines) that connect them. It is a visual representation of relationships between objects.
2. What is the degree of a vertex?
The degree of a vertex in a graph is the number of edges connected to it.
3. What are the necessary conditions for a graph to be traversable?
A graph can be traversed by crossing each edge exactly once and returning to the starting point if and only if:
* The graph is connected (all vertices are reachable from each other).
* All vertices have an even degree.4. How did Euler’s solution to the Königsberg Bridge Problem contribute to the development of graph theory?
Euler’s solution introduced the concept of a graph as a tool for analyzing networks. His work laid the foundation for graph theory, which has become a fundamental tool in various fields.
5. Are there real-world applications of graph theory?
Yes, graph theory has numerous applications in various fields, including computer science, social sciences, biology, and engineering.
Tips for Understanding the Königsberg Bridge Problem:
- Visualize the problem: Draw a simple diagram representing the landmasses and bridges of Königsberg.
- Simplify the problem: Abstract the problem by representing landmasses as vertices and bridges as edges.
- Focus on the degrees of vertices: Understand the relationship between the degree of a vertex and the possibility of traversing a graph.
- Explore real-world applications: Look for examples of how graph theory is used in different fields.
Conclusion:
The Königsberg Bridge Problem, though seemingly trivial, has had a profound impact on the development of mathematics. It led to the birth of graph theory, a powerful tool for understanding networks and relationships. This simple puzzle, born from a curious observation in a Prussian city, has become a cornerstone of modern mathematics, influencing various fields and shaping our understanding of complex systems.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Königsberg Bridge Problem: A Journey into the Origins of Graph Theory. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!