The World of Carthage: A Maritime Power’s Reach
Related Articles: The World of Carthage: A Maritime Power’s Reach
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The World of Carthage: A Maritime Power’s Reach. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The World of Carthage: A Maritime Power’s Reach

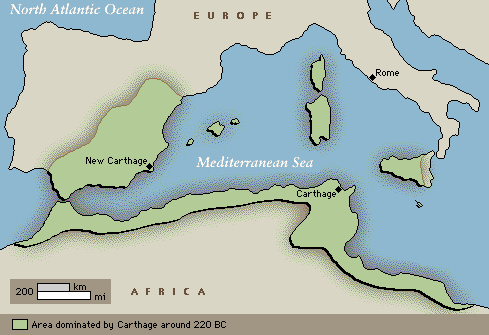
Carthage, a Phoenician city-state that flourished in North Africa from the 8th century BC to the 3rd century BC, wielded immense power and influence throughout the Mediterranean world. Its strategic location on the coast of Tunisia provided access to vital trade routes and resources, making it a formidable naval and commercial force. While the city’s physical boundaries were relatively limited, its sphere of influence extended far beyond its walls, spanning a vast network of colonies, trading posts, and alliances across the Mediterranean.
Mapping Carthage’s Influence
Understanding Carthage’s world map is crucial for grasping its historical significance. It reveals the city’s strategic positioning, economic prowess, and political ambitions. Here’s a breakdown of the key elements that define Carthage’s reach:
1. The Core Territory:
- The City of Carthage: Situated on a peninsula in present-day Tunisia, Carthage served as the political, economic, and cultural heart of the empire. Its strategic location on the Mediterranean coast provided easy access to the sea, facilitating trade and naval expansion.
- The Hinterland: Extending inland from the city, Carthage controlled a vast agricultural hinterland, providing vital resources like grain, olive oil, and livestock. This area served as a crucial source of wealth and manpower for the city-state.
2. The Colonial Network:
- Western Mediterranean: Carthage established numerous colonies along the coasts of North Africa, Spain, and Sicily. These colonies served as strategic outposts for trade, military control, and resource extraction. They also provided a vital buffer against rival powers like Rome.
- Eastern Mediterranean: While less prominent than its western expansion, Carthage also established colonies and trading posts in the Eastern Mediterranean, including Cyprus, Sardinia, and the Balearic Islands. This expansion allowed the city to access additional resources and markets.
3. The Trade Routes:
- Seaborne Trade: Carthage’s maritime dominance allowed it to establish extensive trade routes throughout the Mediterranean Sea. Its ships carried goods like grain, olive oil, wine, textiles, metals, and slaves across the basin, connecting various cultures and economies.
- Land-based Trade: Carthage also maintained land-based trade routes, connecting its hinterland to its colonies and trading partners. These routes facilitated the movement of goods, people, and ideas across the Mediterranean region.
4. Alliances and Rivalries:
- Phoenician Cities: Carthage maintained close ties with other Phoenician cities, particularly Tyre and Sidon, sharing cultural and commercial links. These alliances provided strategic advantages and access to vital resources.
- Greek Cities: Carthage engaged in both trade and conflict with Greek cities, establishing alliances and competing for control of strategic territories. This dynamic relationship shaped the political landscape of the Mediterranean.
- Roman Republic: The rise of Rome posed the most significant threat to Carthage. The two powers clashed repeatedly over territorial disputes, ultimately culminating in the Punic Wars, which resulted in the destruction of Carthage in 146 BC.
Understanding the Importance of Carthage’s World Map
Carthage’s world map offers invaluable insights into the dynamics of the ancient Mediterranean world. It highlights the city’s:
- Economic Power: Carthage’s vast network of colonies and trade routes allowed it to control vital resources and markets, making it one of the wealthiest and most powerful entities in the Mediterranean.
- Naval Dominance: Carthage’s mastery of seafaring technology and its powerful navy enabled it to control key sea lanes and project its power across the Mediterranean.
- Cultural Influence: Through trade and diplomacy, Carthage spread its cultural influence across the region, contributing to the development of art, architecture, and technology.
- Strategic Significance: Carthage’s position as a major power in the Mediterranean shaped the geopolitical landscape of the ancient world, influencing the rise and fall of other empires.
- Historical Lessons: Studying Carthage’s world map provides valuable lessons about the importance of strategic positioning, economic power, and the dynamics of trade and diplomacy in shaping the course of history.
FAQs about Carthage’s World Map
1. What were the main factors that contributed to Carthage’s success as a maritime power?
Carthage’s success as a maritime power stemmed from a combination of factors, including:
- Strategic Location: Its position on the North African coast provided access to vital trade routes and resources.
- Naval Technology: Carthage developed advanced shipbuilding techniques and naval tactics, enabling it to build powerful fleets.
- Trade Network: Its extensive network of colonies and trade routes allowed it to control vital resources and markets.
- Economic Strength: Carthage’s wealth derived from trade and resource extraction, funding its naval expansion and military capabilities.
2. How did Carthage’s relationship with other civilizations shape its world map?
Carthage’s relationship with other civilizations was characterized by a mix of cooperation and conflict.
- Phoenician Cities: Carthage maintained close ties with other Phoenician cities, sharing cultural and commercial links.
- Greek Cities: Carthage engaged in both trade and conflict with Greek cities, establishing alliances and competing for control of strategic territories.
- Roman Republic: The rise of Rome posed the most significant threat to Carthage, leading to the Punic Wars.
3. What are some of the key differences between Carthage’s world map and that of its rivals, such as the Roman Republic?
Carthage’s world map differed from that of its rivals in several key aspects:
- Naval Dominance: Carthage relied heavily on its naval power for expansion and control of trade routes, whereas Rome focused on land-based conquest.
- Colonial Expansion: Carthage established a vast network of colonies across the Mediterranean, while Rome primarily focused on expanding its territory through direct conquest.
- Trade Focus: Carthage’s economy was heavily reliant on trade, while Rome’s economy was more focused on agriculture and resource extraction.
4. What can we learn from studying Carthage’s world map today?
Studying Carthage’s world map provides valuable insights into the dynamics of the ancient Mediterranean world. It highlights the importance of:
- Strategic Positioning: Carthage’s strategic location facilitated its rise to power.
- Economic Power: Control over trade and resources is essential for maintaining influence.
- Naval Dominance: Sea power can be a vital tool for projecting influence and controlling key trade routes.
- Diplomacy and Alliances: Building strong alliances and maintaining diplomatic relations can be crucial for survival and success.
Tips for Studying Carthage’s World Map
- Use a variety of sources: Consult maps, historical texts, archaeological evidence, and scholarly articles to gain a comprehensive understanding of Carthage’s world map.
- Focus on key locations: Identify and understand the significance of Carthage’s core territory, colonies, trading posts, and alliances.
- Analyze trade routes: Trace the flow of goods and people across the Mediterranean, understanding the economic and cultural connections that Carthage forged.
- Compare and contrast: Compare Carthage’s world map with those of its rivals, identifying key differences and similarities in their strategic approaches.
- Connect to broader historical context: Place Carthage’s world map within the larger context of the ancient Mediterranean world, understanding its role in shaping the course of history.
Conclusion
Carthage’s world map stands as a testament to the city’s remarkable influence on the ancient Mediterranean world. Its strategic location, naval dominance, and economic prowess allowed it to establish a vast network of colonies and trade routes, shaping the course of history and leaving an indelible mark on the region. Studying Carthage’s world map provides valuable insights into the dynamics of ancient civilizations, highlighting the importance of strategic positioning, economic power, and the intricate interplay of trade, diplomacy, and conflict in shaping the geopolitical landscape of the ancient world.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The World of Carthage: A Maritime Power’s Reach. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
