Troubleshooting Network Drive Mapping Issues in Windows 10
Related Articles: Troubleshooting Network Drive Mapping Issues in Windows 10
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Troubleshooting Network Drive Mapping Issues in Windows 10. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Troubleshooting Network Drive Mapping Issues in Windows 10

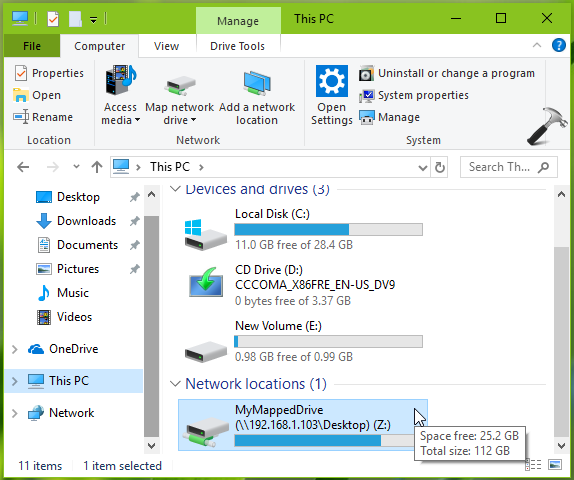
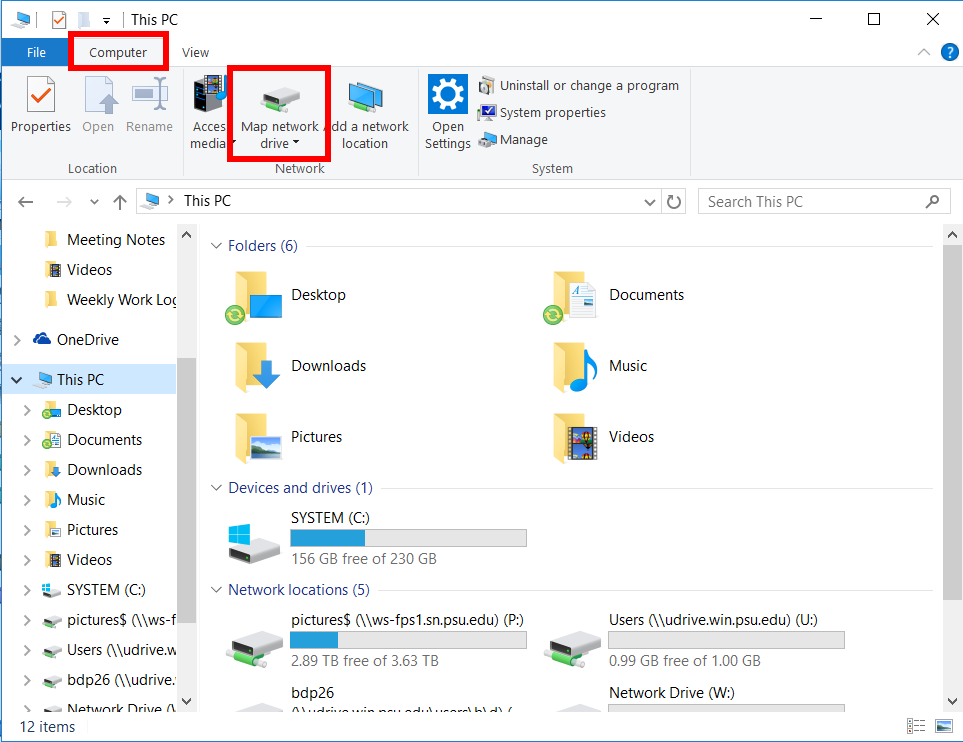
Connecting to shared resources on a network is a fundamental aspect of many modern work environments. Windows 10 offers a seamless way to access these resources through the "Map Network Drive" feature, allowing users to treat remote folders as if they were local drives. However, encountering issues while attempting to map a network drive can be frustrating and hinder productivity. This article provides a comprehensive guide to troubleshooting common problems that prevent successful network drive mapping in Windows 10.
Understanding the Problem:
Before delving into troubleshooting steps, it’s crucial to understand the underlying reasons why network drive mapping might fail. The most common culprits include:
- Incorrect Credentials: The most frequent reason for mapping failures is incorrect username or password.
- Network Connectivity Issues: A faulty network connection, either between your computer and the server hosting the shared resource or within the network itself, can prevent successful mapping.
- Firewall Blockage: Firewalls, both on your computer and the server, may block network access to the shared resource.
- Permission Restrictions: The user account may lack the necessary permissions to access the shared folder on the server.
- Server Issues: The server hosting the shared resource might be experiencing technical difficulties or be unavailable.
- Incorrect Path or Drive Letter: Mistakes in specifying the correct network path or drive letter can lead to mapping errors.
Troubleshooting Steps:
1. Verify Network Connectivity:
- Ping the Server: Open the Command Prompt (cmd) and type "ping [server IP address]" or "ping [server name]". A successful response indicates network connectivity.
- Check Network Cable: Ensure the network cable is securely connected to both your computer and the network switch/router.
- Restart Network Devices: Restart your computer, router, and the server hosting the shared resource.
2. Verify Credentials:
- Double-Check Credentials: Ensure you are using the correct username and password for the shared resource.
- Test Credentials: Try logging into the server directly using the same credentials.
- Check for Account Lockouts: If you have entered incorrect credentials repeatedly, your account may be temporarily locked. Contact your network administrator to unlock it.
3. Address Firewall Issues:
- Check Windows Firewall Settings: In Windows Settings, navigate to "Windows Security" > "Firewall & network protection" and ensure that the firewall is not blocking access to the shared resource.
- Check Server Firewall: If the server has a firewall, ensure it allows access to the shared resource from your computer.
4. Verify Permissions:
- Check Share Permissions: On the server, right-click the shared folder, select "Properties," and navigate to the "Sharing" tab. Verify that your user account has the necessary permissions (read, write, or full control) to access the folder.
- Check Folder Permissions: Within the shared folder, right-click and select "Properties." Navigate to the "Security" tab and verify that your user account has the appropriate permissions.
5. Resolve Server Issues:
- Contact Network Administrator: If you suspect server issues, contact your network administrator to report the problem. They can diagnose and resolve any server-side problems.
6. Correct Path and Drive Letter:
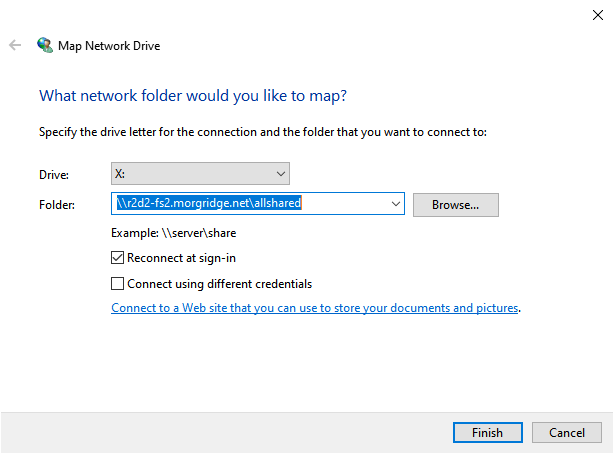
- Verify Network Path: Ensure the network path you are using is correct. Check for typos or incorrect formatting.
- Choose Available Drive Letter: Select a drive letter that is not currently in use on your computer.
7. Consider Advanced Troubleshooting:
- Check for Network Drive Mapping Errors: Use the "net use" command in the Command Prompt to check for any errors related to network drive mapping. The output will provide detailed information about the issue.
- Use Network Troubleshooter: Windows 10 has a built-in network troubleshooter. Access it by going to "Settings" > "Update & Security" > "Troubleshoot" and selecting "Network Adapter."
- Check for Malware: Malware can interfere with network connections and prevent network drive mapping. Run a full system scan with a reputable antivirus software.
8. Utilize Group Policy:
- Create a Group Policy Object (GPO): If you are managing multiple computers, you can use Group Policy to automatically map network drives for all users. This ensures consistent and efficient access to shared resources.
FAQs:
1. Why can’t I map a network drive to a specific drive letter?
The drive letter you are trying to use might already be assigned to another drive, or it might be reserved for a specific purpose. Try selecting a different drive letter.
2. What should I do if I see an error message about incorrect credentials?
Double-check the username and password you are using. If you are unsure, contact your network administrator for assistance.
3. How can I tell if my network connection is the problem?
Use the "ping" command in the Command Prompt to test connectivity to the server hosting the shared resource. If the ping fails, it indicates a network connectivity issue.
4. What are some common network drive mapping errors?
Common errors include "The network path was not found," "Access is denied," and "Error code 0x80070035." Each error message provides clues about the underlying cause of the problem.
5. Can I map a network drive to a specific folder instead of the entire drive?
Yes, you can map a network drive to a specific folder using the "Connect to a network drive" dialog box. In the "Folder" field, enter the complete path to the desired folder.
Tips:
- Use a consistent naming convention for network drives. This makes it easier to identify and manage shared resources.
- Regularly check and update network drive mappings. Ensure that the drive letter, network path, and credentials are still valid.
- Consider using a network drive mapping tool. These tools can simplify the process of mapping and managing network drives, especially in large organizations.
- Implement robust network security measures. This includes strong passwords, firewalls, and regular security updates to protect shared resources from unauthorized access.
Conclusion:
Mapping network drives in Windows 10 is a valuable feature that enables seamless access to shared resources. However, troubleshooting network drive mapping issues can be challenging. By systematically addressing common causes, such as incorrect credentials, network connectivity problems, firewall restrictions, and permission issues, you can effectively resolve most mapping problems. Remember to consult with your network administrator for assistance with complex or persistent issues. By following these steps and utilizing the provided tips, you can ensure smooth and reliable access to shared resources on your network.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Troubleshooting Network Drive Mapping Issues in Windows 10. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
