Unlocking the Secrets of Australia’s Climate: A Comprehensive Guide to Temperature Maps
Related Articles: Unlocking the Secrets of Australia’s Climate: A Comprehensive Guide to Temperature Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unlocking the Secrets of Australia’s Climate: A Comprehensive Guide to Temperature Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unlocking the Secrets of Australia’s Climate: A Comprehensive Guide to Temperature Maps

Australia, the world’s smallest continent, boasts a remarkable diversity of landscapes and climates. From the scorching deserts of the interior to the lush rainforests of the east coast, the continent experiences a vast range of temperatures throughout the year. Understanding this temperature variation is crucial for a multitude of reasons, from planning travel itineraries and outdoor activities to making informed decisions about agriculture and infrastructure development.
Navigating the Australian Temperature Landscape: A Visual Guide
Temperature maps provide a visually compelling and insightful representation of Australia’s thermal landscape. These maps, often generated by meteorological agencies like the Bureau of Meteorology (BOM), depict temperature variations across the country at a specific point in time or over a given period. They employ a color scale, typically ranging from cool blue tones for lower temperatures to warm reds and oranges for higher temperatures.
Understanding the Significance of Temperature Maps
Temperature maps serve as invaluable tools for various stakeholders:
- Travelers: Planning a trip to Australia? Temperature maps help you anticipate the weather conditions at your destination, enabling you to pack accordingly and choose activities best suited to the expected temperatures.
- Farmers and Agriculturalists: Farmers rely on temperature maps to understand the suitability of different crops in various regions. This information aids in optimizing planting schedules, irrigation practices, and pest management strategies.
- Infrastructure Developers: Engineers and urban planners use temperature maps to assess the impact of climate on infrastructure projects. This includes factors like heat stress on materials, potential for extreme weather events, and the need for climate-resilient designs.
- Scientists and Researchers: Temperature maps provide valuable data for climate scientists studying long-term trends, understanding the impact of climate change, and predicting future climate scenarios.
- Emergency Management Agencies: Temperature maps aid in forecasting extreme weather events like heatwaves and bushfires, enabling proactive measures for public safety and resource allocation.
Factors Influencing Australia’s Temperature Distribution
Australia’s diverse temperature patterns result from a complex interplay of several factors:
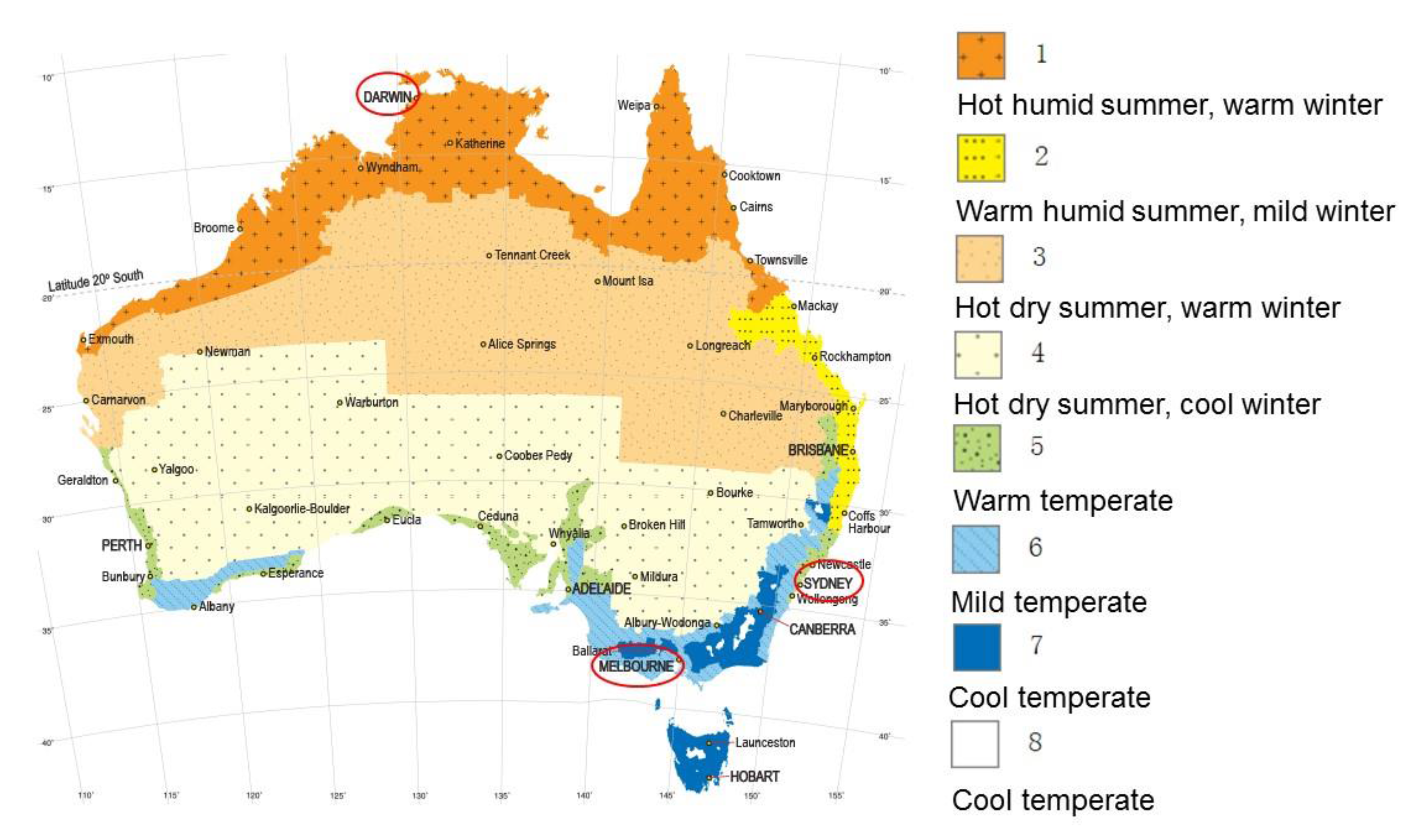
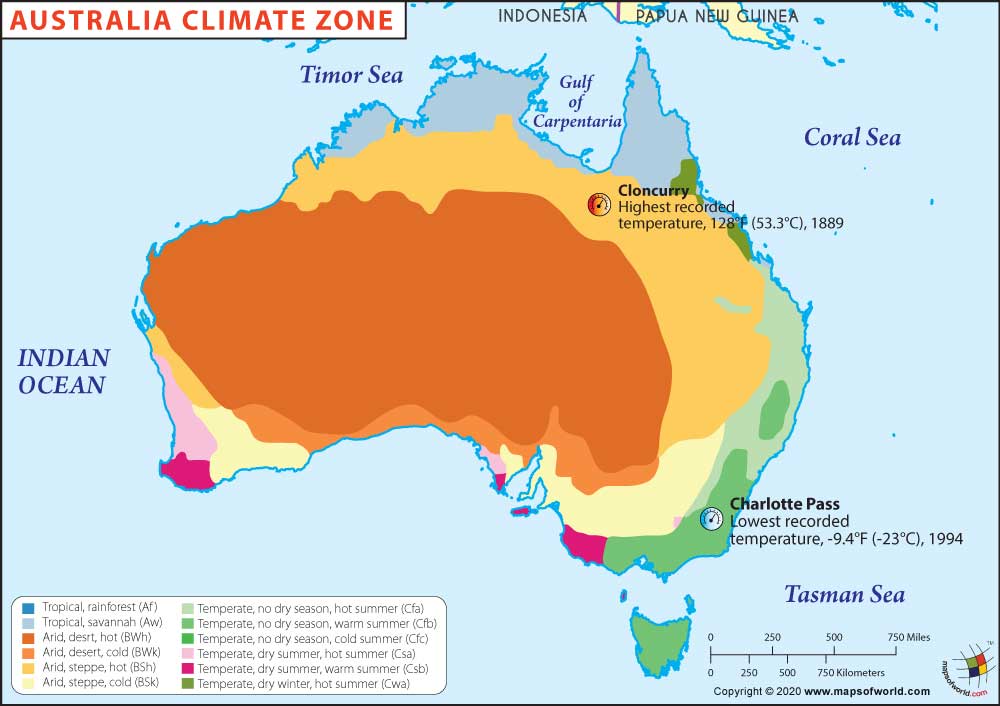
- Latitude: The continent’s vast latitudinal extent, stretching from tropical to temperate zones, contributes significantly to the variation in temperature. Northern Australia experiences a tropical climate with consistently high temperatures, while southern regions exhibit a more temperate climate with distinct seasonal variations.
- Altitude: Higher elevations experience cooler temperatures due to thinner air and reduced atmospheric pressure. This is evident in the mountainous regions of the Great Dividing Range, where temperatures are significantly lower than in the surrounding lowlands.
- Ocean Currents: The influence of ocean currents, such as the East Australian Current, plays a crucial role in moderating coastal temperatures. Warm currents bring warmer waters to the eastern coast, resulting in warmer temperatures compared to the western coast, which is influenced by cooler currents.
- Continentality: Australia’s vast size and its location far from major ocean influences contribute to its continental climate. This results in large diurnal temperature variations, with significant differences between daytime and nighttime temperatures, particularly in the interior.
- Topography: The presence of mountain ranges and other topographic features can create microclimates with distinct temperature variations. For instance, rain shadows on the eastern side of mountain ranges can lead to drier and warmer conditions compared to the windward side.
Deciphering the Language of Temperature Maps: Key Elements
Temperature maps often include various components to provide a comprehensive understanding of the data:
- Temperature Scale: The map typically employs a color scale to represent temperature ranges. The specific scale may vary depending on the source, but generally, cooler temperatures are represented by blues and greens, while warmer temperatures are shown in reds and oranges.
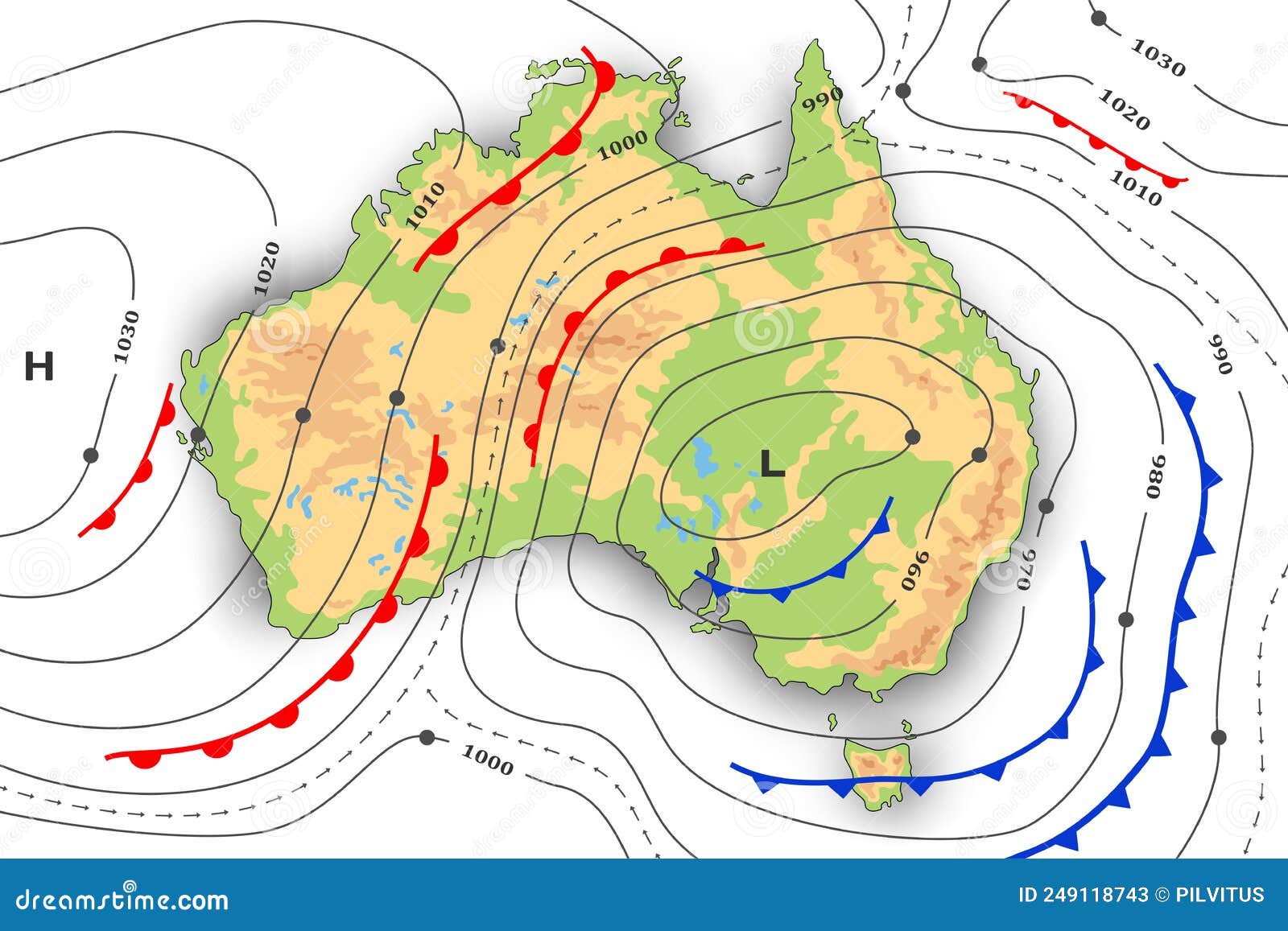
- Isotherms: These are lines connecting points of equal temperature. Isotherms provide a visual representation of temperature gradients and help identify areas with similar temperature conditions.
- Temperature Anomalies: These indicate deviations from the average temperature for a particular period. Positive anomalies represent warmer-than-average conditions, while negative anomalies indicate cooler-than-average temperatures.
- Legend: The map legend provides a key to interpreting the color scale and other symbols used on the map.
- Time Period: Temperature maps typically represent data for a specific point in time or over a defined period. This information is essential for understanding the context of the data and making accurate interpretations.
Utilizing Temperature Maps for Informed Decision-Making
Temperature maps offer a wealth of information that can inform decision-making in various sectors:
- Tourism and Recreation: Travelers can use temperature maps to plan trips, choose appropriate activities, and pack suitable clothing for their destinations.
- Agriculture and Horticulture: Farmers can use temperature maps to select suitable crops, optimize planting schedules, and manage irrigation and pest control strategies.
- Urban Planning and Infrastructure Development: Temperature maps help urban planners design climate-resilient cities, considering factors like heat stress, urban heat islands, and potential for extreme weather events.
- Climate Change Adaptation and Mitigation: Scientists and policymakers can use temperature maps to monitor climate change impacts, identify areas vulnerable to extreme weather events, and develop strategies for adaptation and mitigation.
FAQs about Australia’s Temperature Maps
1. Where can I access temperature maps for Australia?
The Bureau of Meteorology (BOM) is the primary source for Australian temperature maps. Their website provides access to real-time weather data, historical records, and various maps and charts, including temperature maps. Other sources include the Australian Government’s Climate Change website and various academic institutions.
2. What are the typical temperature ranges in different regions of Australia?
Australia experiences a wide range of temperatures depending on the region and season. The northern tropics typically experience hot and humid conditions with average temperatures above 30°C (86°F) during summer. Southern Australia experiences a more temperate climate with average temperatures ranging from 10°C (50°F) in winter to 25°C (77°F) in summer.
3. How do temperature maps help in understanding climate change impacts?
Temperature maps provide valuable data for monitoring long-term temperature trends and identifying changes in climate patterns. By comparing historical temperature data with current data, scientists can assess the rate and magnitude of temperature increases, indicating the impact of climate change.
4. What are the potential implications of rising temperatures in Australia?
Rising temperatures in Australia can have significant implications, including increased heat stress, more frequent and intense heatwaves, altered agricultural productivity, water scarcity, and increased risk of bushfires.
5. How can I use temperature maps to plan a trip to Australia?
Temperature maps help you anticipate the weather conditions at your destination, enabling you to pack appropriate clothing, choose activities suited to the expected temperatures, and plan your itinerary accordingly.
Tips for Utilizing Temperature Maps Effectively
- Check the source and date of the data: Ensure the data is current and from a reliable source.
- Pay attention to the scale and units: Understand the temperature scale used on the map and the units of measurement.
- Consider the time period: Analyze the data for the specific time period you are interested in, whether it’s a specific date or a longer period.
- Look for patterns and trends: Observe temperature variations across different regions and over time to identify patterns and trends.
- Combine with other data sources: Use temperature maps in conjunction with other weather data, such as rainfall maps, wind maps, and humidity maps, for a more comprehensive understanding of the climate.
Conclusion
Temperature maps offer a powerful tool for understanding and visualizing the diverse temperature landscape of Australia. They provide valuable insights for travelers, farmers, infrastructure developers, scientists, and policymakers, enabling informed decision-making in various sectors. By leveraging the information gleaned from temperature maps, we can better adapt to the challenges and opportunities presented by Australia’s dynamic climate.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unlocking the Secrets of Australia’s Climate: A Comprehensive Guide to Temperature Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
