Unlocking the Secrets of the Sky: A Deep Dive into Weather Radar Maps
Related Articles: Unlocking the Secrets of the Sky: A Deep Dive into Weather Radar Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unlocking the Secrets of the Sky: A Deep Dive into Weather Radar Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unlocking the Secrets of the Sky: A Deep Dive into Weather Radar Maps
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unlocking the Secrets of the Sky: A Deep Dive into Weather Radar Maps
- 3.1 Understanding the Basics: How Weather Radar Works
- 3.2 Deciphering the Colors: A Visual Guide to Precipitation
- 3.3 The Importance of Weather Radar Maps: A Multifaceted Tool
- 3.4 Navigating the Weather Underground Radar Map: A Detailed Exploration
- 3.5 Frequently Asked Questions about Weather Underground Radar Maps
- 3.6 Tips for Effectively Utilizing Weather Underground Radar Maps
- 3.7 Conclusion: Weather Underground Radar Maps – A Vital Tool for Weather Awareness
- 4 Closure
Unlocking the Secrets of the Sky: A Deep Dive into Weather Radar Maps
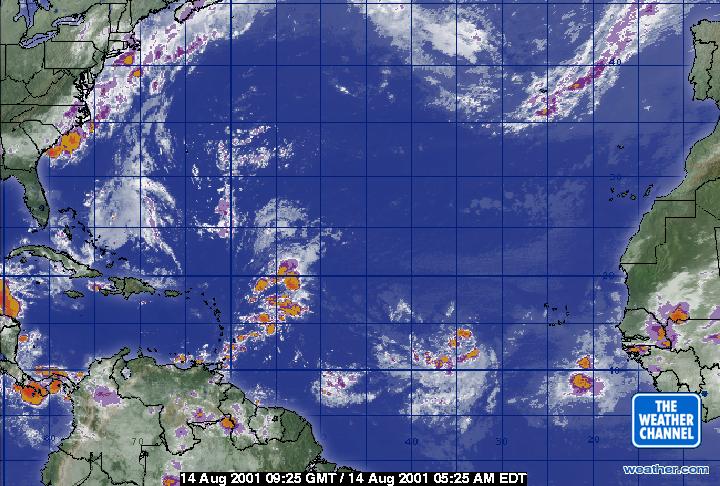
The sky, a vast and ever-changing canvas, holds a multitude of weather phenomena, from gentle breezes to raging storms. Understanding these atmospheric events is crucial for safety, planning, and a myriad of other activities. A powerful tool in this endeavor is the weather radar map, a visual representation of precipitation and other weather conditions, providing valuable insights into the present and future state of the atmosphere.
Understanding the Basics: How Weather Radar Works
Weather radar, a vital tool for meteorologists and the public alike, utilizes electromagnetic waves to detect precipitation and other atmospheric phenomena. The process involves transmitting radio waves into the atmosphere and analyzing the reflected signals. These signals, known as echoes, reveal the presence, intensity, and movement of precipitation.
The Core Components:
- Transmitter: Emits radio waves, typically in the microwave frequency range, into the atmosphere.
- Antenna: Focuses the radio waves into a beam, directing them towards the target area.
- Receiver: Detects the reflected radio waves, or echoes, returning from the atmosphere.
- Processor: Analyzes the echoes, converting them into meaningful information, such as precipitation intensity and movement.
The Science Behind the Echoes:
The strength of the reflected signal, or echo, depends on the size and composition of the precipitation particles. Larger particles, like hailstones, reflect more strongly than smaller particles, like drizzle. The Doppler effect, the change in frequency of a wave due to the relative motion of the source and observer, provides information about the speed and direction of precipitation movement.
Deciphering the Colors: A Visual Guide to Precipitation
Weather radar maps are often presented as a color-coded display, with each color representing a different intensity of precipitation. This color scale allows for quick and intuitive interpretation of the data.
- Green: Light precipitation, such as drizzle or light rain.
- Yellow: Moderate precipitation, such as moderate rain or snow.
- Orange: Heavy precipitation, such as heavy rain or snow.
- Red: Very heavy precipitation, such as torrential rain or a blizzard.
- Purple: Extremely heavy precipitation, often associated with severe thunderstorms or hail.
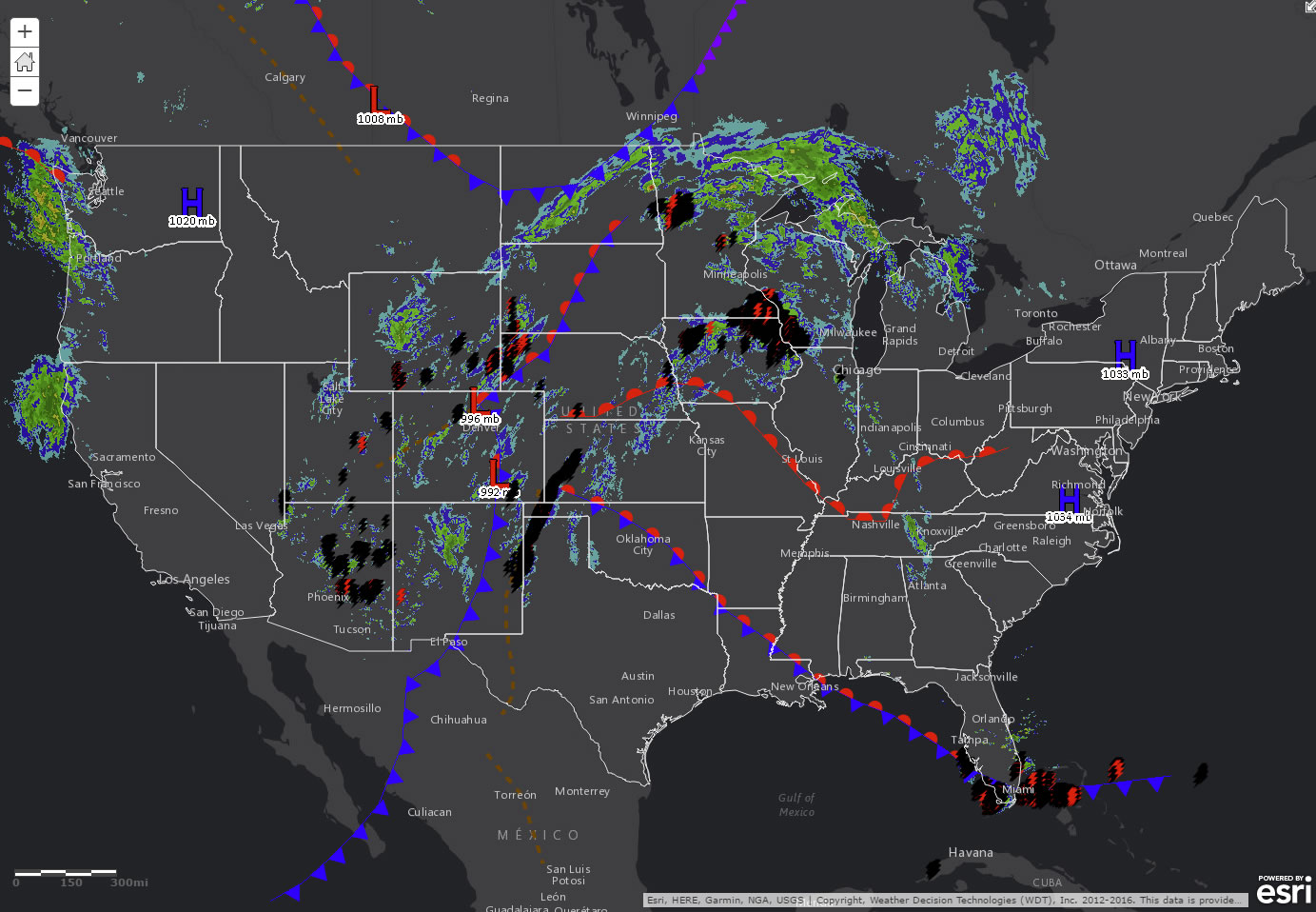
Beyond precipitation intensity, radar maps can also depict other weather phenomena:
- Storm cells: Areas of concentrated precipitation, often associated with thunderstorms.
- Wind shear: Changes in wind speed or direction, which can pose risks to aviation.
- Hail: Large, solid precipitation particles, often associated with severe thunderstorms.
- Tornadoes: Rotating columns of air, a highly dangerous weather phenomenon.
The Importance of Weather Radar Maps: A Multifaceted Tool
Weather radar maps serve a diverse range of purposes, providing valuable information for:
- Public Safety: Early warnings of severe weather events, such as tornadoes, thunderstorms, and heavy precipitation, allowing for timely evacuation and safety measures.
- Aviation: Guidance for pilots, helping them navigate around hazardous weather conditions, ensuring safe and efficient flights.
- Agriculture: Assessing the amount and distribution of rainfall, crucial for irrigation planning and crop management.
- Hydrology: Monitoring precipitation levels and identifying potential flooding risks, aiding in flood prediction and mitigation efforts.
- Emergency Management: Providing vital information for disaster response teams, enabling efficient allocation of resources and coordination of rescue operations.
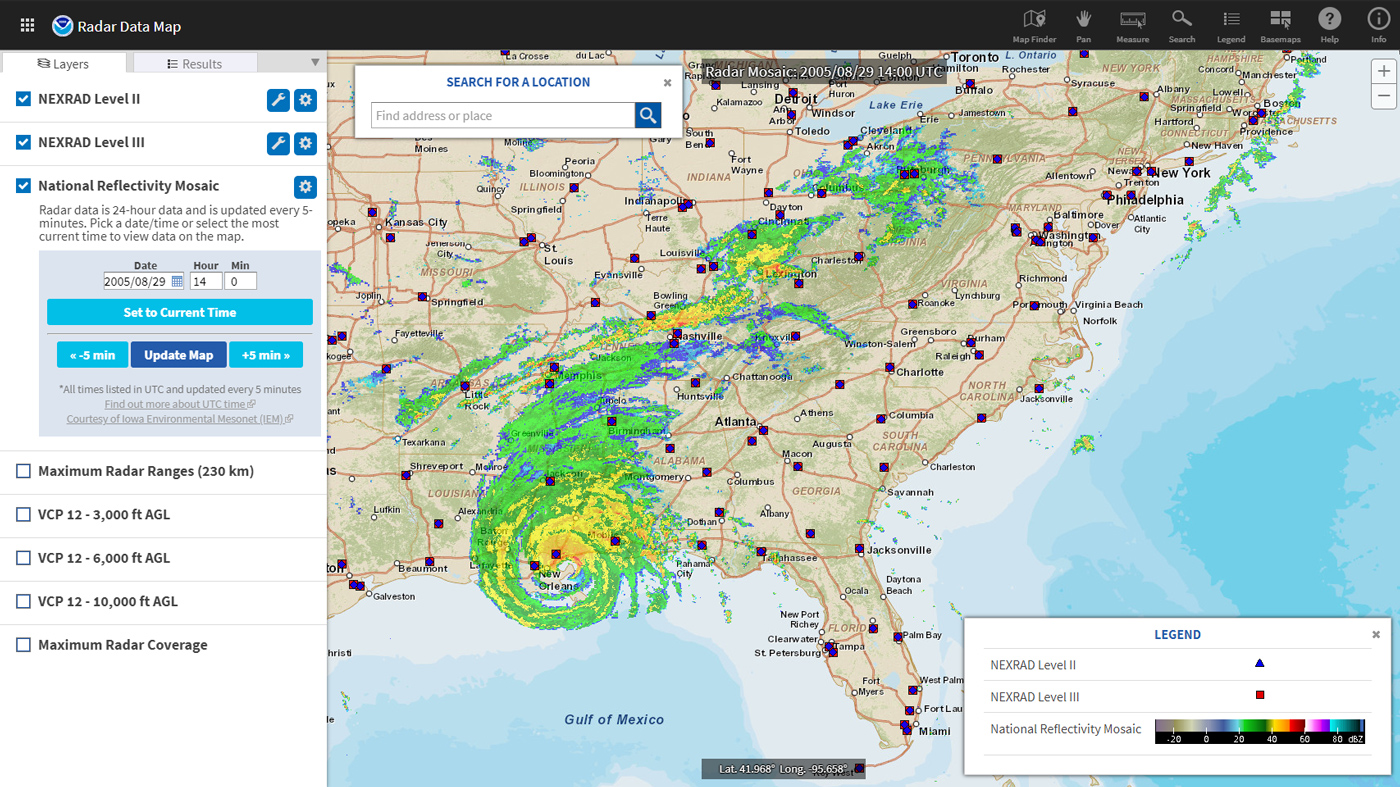
Navigating the Weather Underground Radar Map: A Detailed Exploration
The Weather Underground, a prominent source of weather information, provides a comprehensive radar map interface, offering a wealth of data and features.
Key Components:
- Interactive Map: Users can zoom in and out, pan across different regions, and explore specific areas of interest.
- Color Scale: Displays precipitation intensity with a clear color-coded scale, ranging from light to extremely heavy precipitation.
- Time Slider: Allows users to view radar data from past hours, providing a historical perspective on precipitation trends.
- Animation Feature: Provides a dynamic visualization of precipitation movement, highlighting the evolution of weather patterns.
- Overlay Options: Users can add overlays to the map, such as temperature, wind speed, and lightning strikes, providing a comprehensive view of weather conditions.
Additional Features:
- Radar Loop: Displays a continuous animation of radar data, showcasing the dynamic nature of precipitation movement.
- Storm Tracker: Identifies and tracks severe weather events, providing real-time updates on their location and intensity.
- Alerts: Provides timely warnings of severe weather events, including tornadoes, thunderstorms, and heavy precipitation.
Frequently Asked Questions about Weather Underground Radar Maps
Q: What is the refresh rate of the Weather Underground radar data?
A: The Weather Underground radar data is typically refreshed every few minutes, providing near real-time updates on weather conditions. The refresh rate may vary depending on the specific radar site and network connectivity.
Q: How accurate is the Weather Underground radar map?
A: The accuracy of the Weather Underground radar map depends on various factors, including the quality of the radar data, the density of radar stations, and the complexity of weather patterns. While the map provides a reliable representation of weather conditions, it is important to note that it is not a perfect predictor of the future.
Q: Can I access historical radar data on the Weather Underground website?
A: Yes, the Weather Underground website provides access to historical radar data, allowing users to review past precipitation patterns and track the evolution of weather events. The availability of historical data may vary depending on the specific region and time period.
Q: How can I use the Weather Underground radar map to prepare for severe weather?
A: The Weather Underground radar map can be a valuable tool for preparing for severe weather. By monitoring the map, you can identify potential threats, such as approaching thunderstorms or heavy precipitation. It is essential to stay informed about weather forecasts and warnings, and to take appropriate safety precautions when severe weather is anticipated.
Tips for Effectively Utilizing Weather Underground Radar Maps
- Regularly check the map: Stay informed about current weather conditions and potential threats by regularly checking the Weather Underground radar map.
- Focus on your location: Zoom in on your specific area of interest to gain a detailed view of local weather conditions.
- Pay attention to the color scale: Understand the different colors and their corresponding precipitation intensities to accurately interpret the data.
- Utilize the animation feature: Observe the movement of precipitation patterns to anticipate changes in weather conditions.
- Combine radar data with other sources: Integrate information from weather forecasts, warnings, and other sources to gain a comprehensive understanding of weather events.
Conclusion: Weather Underground Radar Maps – A Vital Tool for Weather Awareness
Weather Underground radar maps are a powerful tool for understanding and navigating the complexities of weather. By providing real-time visualizations of precipitation, wind, and other atmospheric phenomena, these maps empower individuals and organizations to make informed decisions about safety, planning, and preparedness. As technology continues to advance, the accuracy and sophistication of weather radar maps are expected to improve further, enhancing our ability to predict and respond to weather events. From navigating storms to planning outdoor activities, the Weather Underground radar map serves as an indispensable resource for staying informed and safe in a world increasingly influenced by the forces of nature.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unlocking the Secrets of the Sky: A Deep Dive into Weather Radar Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
