Unpacking the Tapestry: A Comprehensive Guide to Southern European Geography
Related Articles: Unpacking the Tapestry: A Comprehensive Guide to Southern European Geography
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unpacking the Tapestry: A Comprehensive Guide to Southern European Geography. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unpacking the Tapestry: A Comprehensive Guide to Southern European Geography
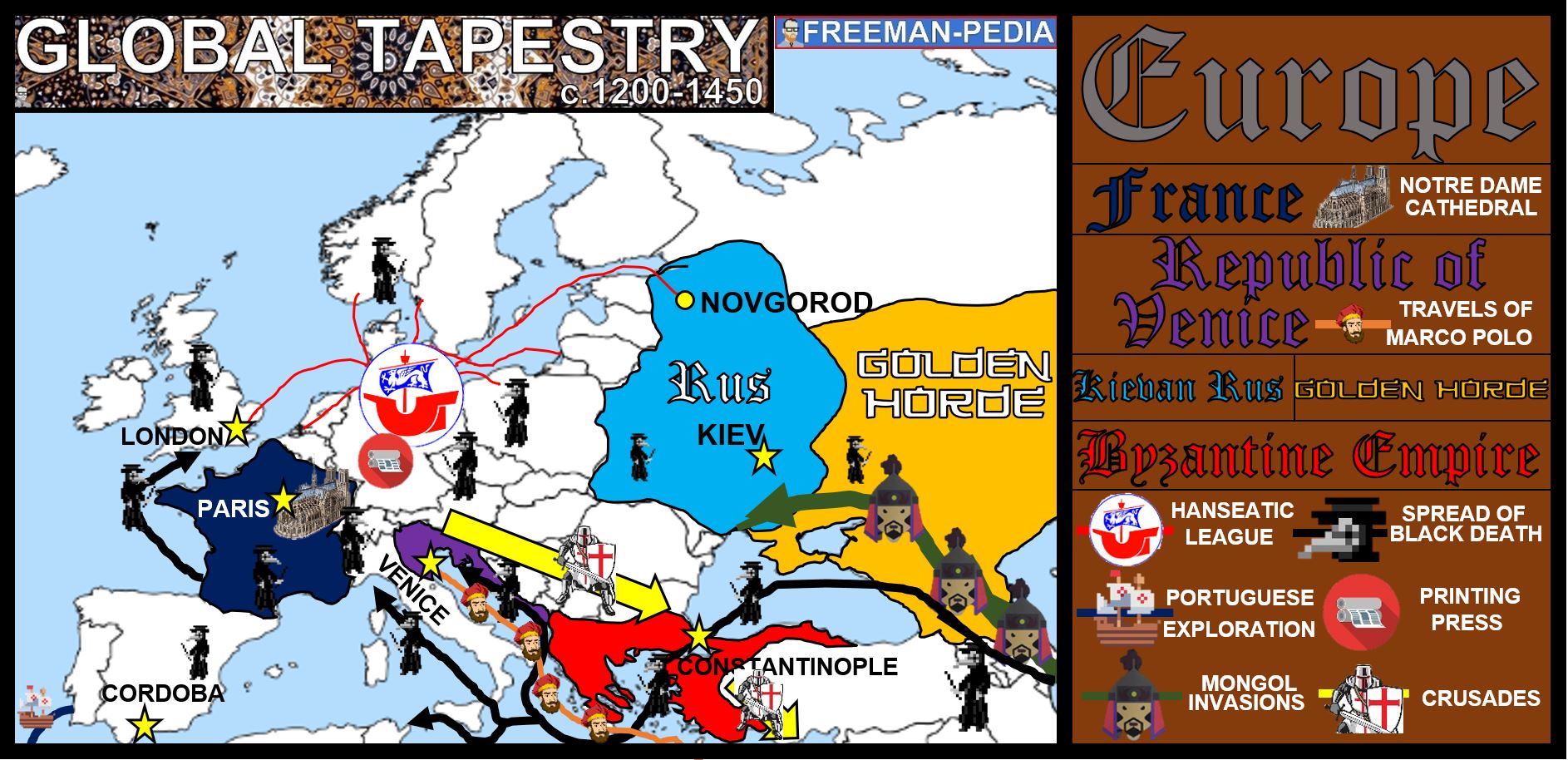
Southern Europe, a region brimming with history, culture, and breathtaking landscapes, encompasses a diverse array of countries that have shaped the course of human civilization. Understanding the geographical layout of this region is essential for appreciating its unique character, its historical significance, and its contemporary challenges. This article delves into the map of Southern Europe, providing a comprehensive exploration of its constituent countries, their geographical features, and the factors that contribute to their interconnectedness.
Defining Southern Europe: A Geographical and Cultural Landscape
Southern Europe, also known as the Mediterranean region, lacks a universally agreed upon definition. However, the term typically refers to countries located on the southern edge of Europe, bordering the Mediterranean Sea. While this definition encompasses the Iberian Peninsula, the Italian Peninsula, the Balkan Peninsula, and the islands of the Mediterranean, it leaves room for interpretation, particularly when considering countries like Cyprus and Malta.
The Countries of Southern Europe: A Diverse Mosaic
Southern Europe is home to a diverse array of countries, each with its own unique history, culture, and geographical features. The region’s diverse landscape encompasses mountainous terrain, fertile plains, and picturesque coastlines, contributing to the varied economies and lifestyles of its inhabitants.
1. Iberian Peninsula:
- Spain: The largest country in Southern Europe, Spain boasts a diverse landscape ranging from the Pyrenees Mountains to the fertile plains of Andalusia. Its rich history, vibrant culture, and stunning coastline attract millions of tourists annually.
- Portugal: Located on the western edge of the Iberian Peninsula, Portugal is renowned for its beautiful beaches, historic cities, and rich maritime heritage. Its strategic location on the Atlantic Ocean has historically played a significant role in its economic development.
2. Italian Peninsula:
- Italy: With its iconic landmarks, rich history, and delicious cuisine, Italy is a major player in Southern Europe. Its diverse landscape encompasses the Alps, the Apennines, and the fertile plains of the Po Valley.
- San Marino: Located within Italy, San Marino is an independent microstate known for its medieval architecture and its status as one of the oldest republics in the world.
- Vatican City: Also located within Italy, Vatican City is an independent city-state and the smallest country in the world, serving as the headquarters of the Catholic Church.
3. Balkan Peninsula:
- Greece: Known for its ancient ruins, stunning islands, and vibrant culture, Greece is a cornerstone of Southern Europe. Its diverse landscape includes mountainous terrain, fertile valleys, and the Aegean Sea.
- Albania: Situated on the eastern coast of the Adriatic Sea, Albania is a country of diverse landscapes, from rugged mountains to coastal plains. Its rich history and cultural heritage are increasingly attracting visitors.
- Bosnia and Herzegovina: This landlocked country is known for its diverse ethnic groups, its rich history, and its stunning natural beauty. Its landscape encompasses mountainous terrain, fertile valleys, and the Neretva River.
- Bulgaria: Located on the eastern edge of the Balkan Peninsula, Bulgaria is a country of diverse landscapes, ranging from the Rhodope Mountains to the Black Sea coast. Its rich history and cultural heritage are reflected in its numerous ancient ruins and historical sites.
- Croatia: Situated on the Adriatic coast, Croatia is known for its stunning coastline, its picturesque islands, and its rich history. Its diverse landscape includes mountains, valleys, and the Adriatic Sea.
- Cyprus: Located on an island in the eastern Mediterranean Sea, Cyprus is a country with a rich history and a diverse culture. Its landscape encompasses mountainous terrain, fertile plains, and the Mediterranean Sea.
- Kosovo: Located in the western Balkan Peninsula, Kosovo is a young country with a rich history and a diverse culture. Its landscape encompasses mountainous terrain, fertile valleys, and the Ibar River.
- Montenegro: Located on the Adriatic coast, Montenegro is a country of stunning natural beauty, with its rugged mountains, picturesque lakes, and pristine coastline.
- North Macedonia: Located in the central Balkan Peninsula, North Macedonia is a country with a rich history and a diverse culture. Its landscape encompasses mountainous terrain, fertile valleys, and the Vardar River.
- Romania: Situated in southeastern Europe, Romania is a country with a diverse landscape, ranging from the Carpathian Mountains to the Danube Delta. Its rich history and cultural heritage are reflected in its numerous ancient ruins and historical sites.
- Serbia: Located in the central Balkan Peninsula, Serbia is a country with a rich history and a diverse culture. Its landscape encompasses mountainous terrain, fertile valleys, and the Danube River.
- Slovenia: Located in central Europe, Slovenia is a country with a diverse landscape, ranging from the Alps to the Adriatic coast. Its rich history and cultural heritage are reflected in its numerous castles, churches, and historical sites.
4. Islands of the Mediterranean:
- Malta: Located in the central Mediterranean Sea, Malta is an island nation with a rich history and a diverse culture. Its landscape encompasses limestone cliffs, sandy beaches, and the Mediterranean Sea.
- Cyprus: Located on an island in the eastern Mediterranean Sea, Cyprus is a country with a rich history and a diverse culture. Its landscape encompasses mountainous terrain, fertile plains, and the Mediterranean Sea.
Geographical Features and Their Impact:
The geographical features of Southern Europe have played a significant role in shaping its history, culture, and economy.
- The Mediterranean Sea: This vast body of water has historically served as a vital trade route, connecting Southern Europe with Africa, Asia, and the Middle East. The sea’s warm waters and sunny climate have also made the region a popular destination for tourism.
- Mountains: The mountainous terrain of Southern Europe has created diverse microclimates and ecological niches, contributing to the region’s rich biodiversity. Mountains have also served as natural barriers, influencing the development of distinct cultures and languages.
- Rivers: The region’s major rivers, such as the Danube, Po, and Ebro, have played a vital role in transportation, agriculture, and economic development.
- Coastlines: The extensive coastlines of Southern Europe have attracted human settlements for centuries, providing access to resources, trade routes, and opportunities for fishing and agriculture.
Interconnectedness and Challenges:
Southern Europe is a region of interconnectedness, with countries sharing common historical, cultural, and economic ties. The region’s shared heritage, its proximity to one another, and its reliance on the Mediterranean Sea have created a strong sense of community.
However, Southern Europe also faces a number of challenges, including:
- Economic disparities: The region’s economies vary widely, with some countries experiencing greater levels of economic development than others.
- Political instability: The Balkan Peninsula has been plagued by political instability and conflict in recent decades, posing challenges to regional integration and economic development.
- Climate change: The region is particularly vulnerable to the effects of climate change, with rising sea levels, more frequent droughts, and extreme weather events posing threats to its environment, agriculture, and tourism industries.
FAQs about the Map of Southern Europe:
1. What countries are considered part of Southern Europe?
The definition of Southern Europe is not universally agreed upon, but it typically includes countries located on the southern edge of Europe, bordering the Mediterranean Sea. This includes the Iberian Peninsula, the Italian Peninsula, the Balkan Peninsula, and the islands of the Mediterranean, such as Cyprus and Malta.
2. What are the major geographical features of Southern Europe?
Southern Europe is characterized by a diverse landscape, including mountainous terrain, fertile plains, and picturesque coastlines. The Mediterranean Sea, major rivers, and extensive coastlines have played a significant role in shaping the region’s history, culture, and economy.
3. What are the challenges facing Southern Europe?
Southern Europe faces a number of challenges, including economic disparities, political instability, and the effects of climate change.
4. What is the significance of the map of Southern Europe?
The map of Southern Europe provides a visual representation of the region’s geographical features, its constituent countries, and the factors that contribute to their interconnectedness. Understanding the region’s geography is essential for appreciating its unique character, its historical significance, and its contemporary challenges.
Tips for Using the Map of Southern Europe:
- Identify the major geographical features: Locate the Mediterranean Sea, major rivers, mountain ranges, and coastlines.
- Explore the individual countries: Learn about the location, size, and key geographical features of each country.
- Analyze the relationships between countries: Consider how proximity, shared borders, and common geographical features have influenced the relationships between countries.
- Understand the impact of geography on history and culture: Examine how the region’s geographical features have shaped its history, culture, and economy.
Conclusion:
The map of Southern Europe is a valuable tool for understanding the region’s complex geography, its diverse countries, and the factors that contribute to their interconnectedness. By exploring the region’s geographical features, its historical development, and its contemporary challenges, we gain a deeper appreciation for the rich tapestry of Southern Europe, its unique character, and its enduring importance in the world.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unpacking the Tapestry: A Comprehensive Guide to Southern European Geography. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!