Unraveling the Tapestry of Ancient Attica: A Journey Through History on a Map
Related Articles: Unraveling the Tapestry of Ancient Attica: A Journey Through History on a Map
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Tapestry of Ancient Attica: A Journey Through History on a Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unraveling the Tapestry of Ancient Attica: A Journey Through History on a Map
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unraveling the Tapestry of Ancient Attica: A Journey Through History on a Map
- 3.1 The Geographical Heart of Ancient Attica: A Foundation for Civilization
- 3.2 The Ancient Map of Attica: A Window into a Bygone Era
- 3.3 The Significance of Attica: A Cradle of Civilization
- 3.4 FAQs: Unraveling the Mysteries of Ancient Attica
- 3.5 Tips for Exploring the Ancient Map of Attica
- 3.6 Conclusion: A Legacy That Endures
- 4 Closure
Unraveling the Tapestry of Ancient Attica: A Journey Through History on a Map

The region of Attica, nestled in the heart of ancient Greece, holds a unique position in history. Its landscape, a tapestry woven with fertile plains, rugged mountains, and a coastline kissed by the Aegean Sea, nurtured a civilization that would leave an indelible mark on the world. This article explores the significance of Attica through its ancient map, revealing the intricate connection between geography, culture, and the rise of one of the most influential civilizations in antiquity.
The Geographical Heart of Ancient Attica: A Foundation for Civilization
Attica’s geography played a pivotal role in shaping its history. The region, bordered by the Saronic Gulf to the south and the mountains of Parnes and Penteli to the north, possessed a diverse landscape that provided both challenges and opportunities.
The Fertile Plain of Athens: The heart of Attica was the plain of Athens, a fertile expanse that supported agriculture and fostered the growth of settlements. This area, crisscrossed by rivers and streams, provided ample resources for sustenance and economic activity.
The Rugged Mountains: The mountains surrounding the plain, while posing challenges for travel and communication, also offered strategic advantages. They provided natural defenses against invaders and served as a source of valuable resources, including marble and silver.
The Aegean Coastline: Attica’s coastline, with its numerous harbors and inlets, facilitated maritime trade and communication. This access to the sea allowed the region to connect with other civilizations and participate in the burgeoning trade networks of the ancient world.
A Strategic Crossroads: The geographic location of Attica placed it at a crossroads between the Aegean Sea and the mainland of Greece. This strategic position made the region a natural hub for trade and cultural exchange, fostering its development as a center of power and influence.
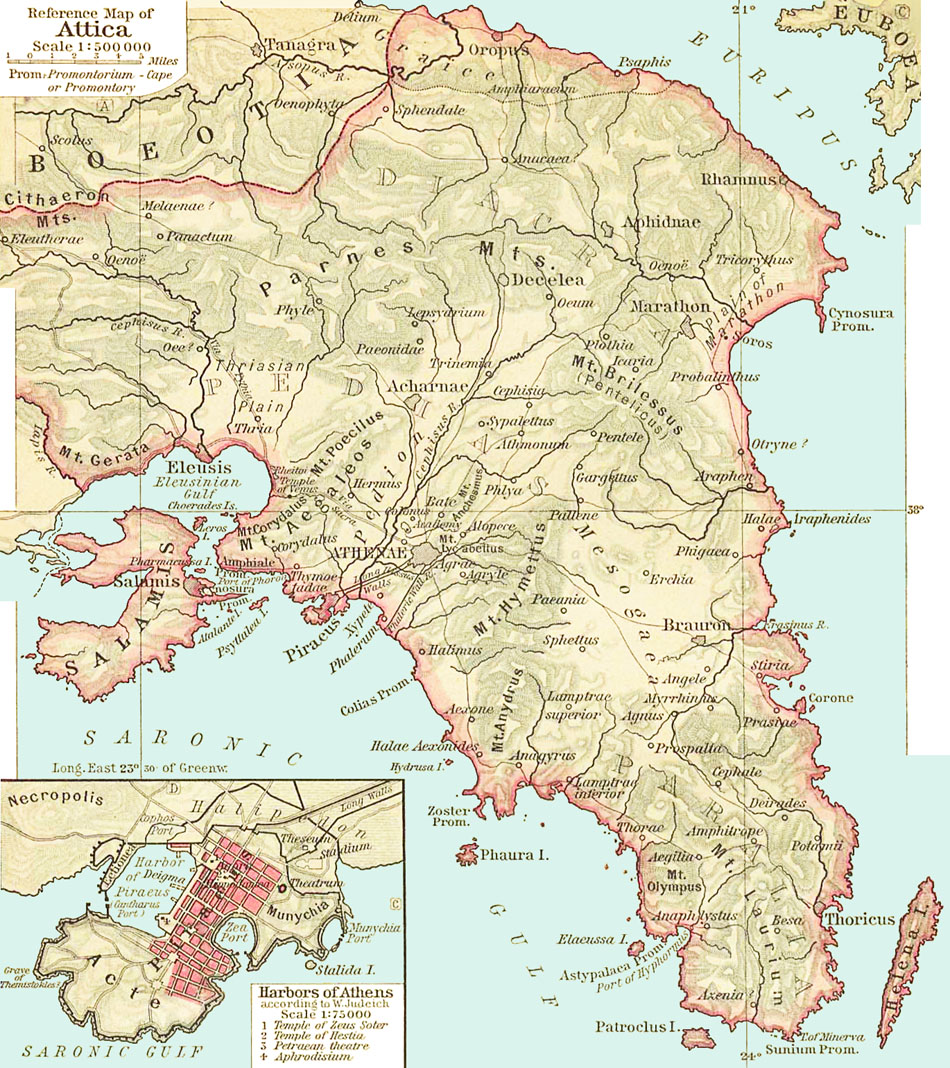
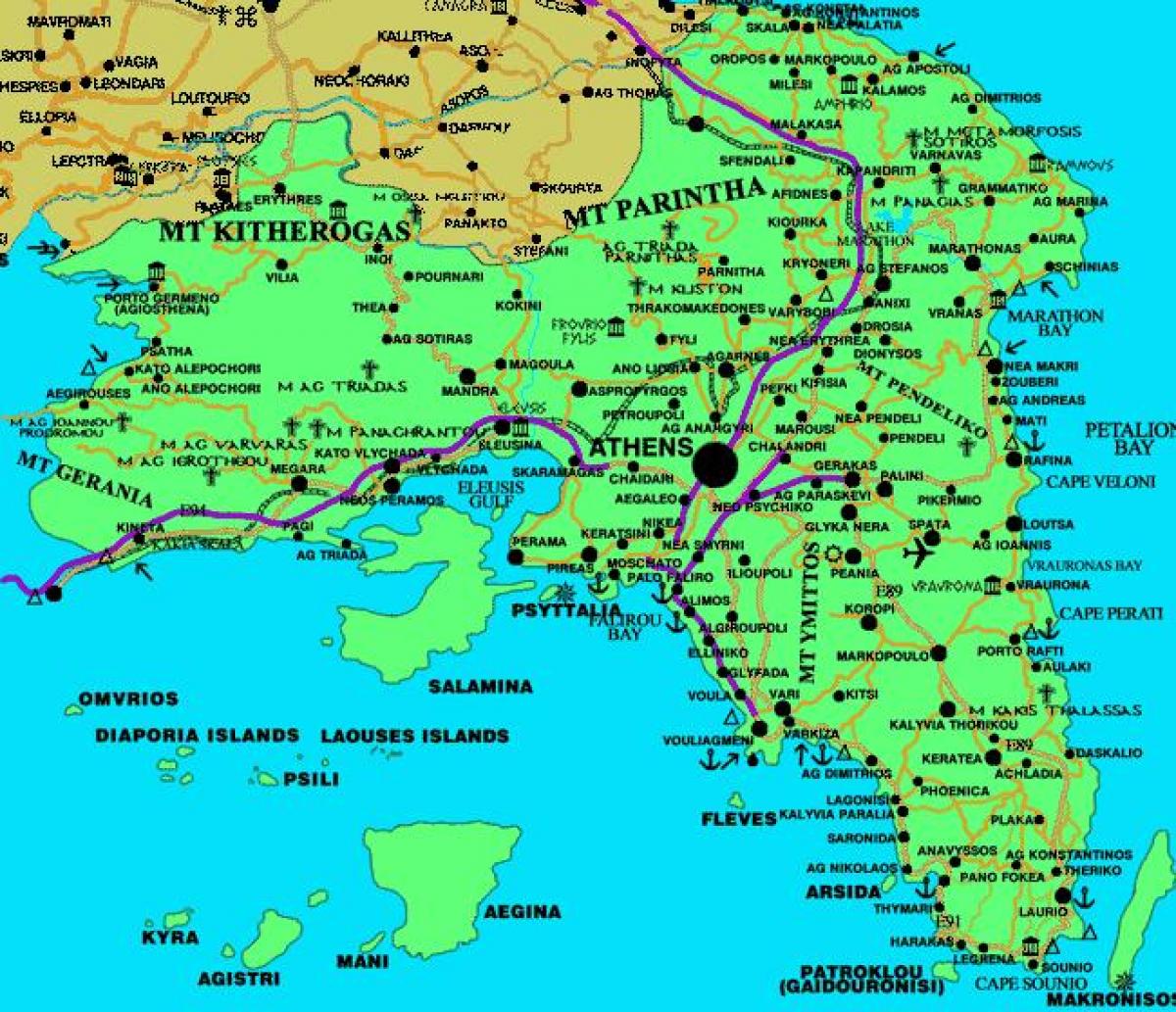
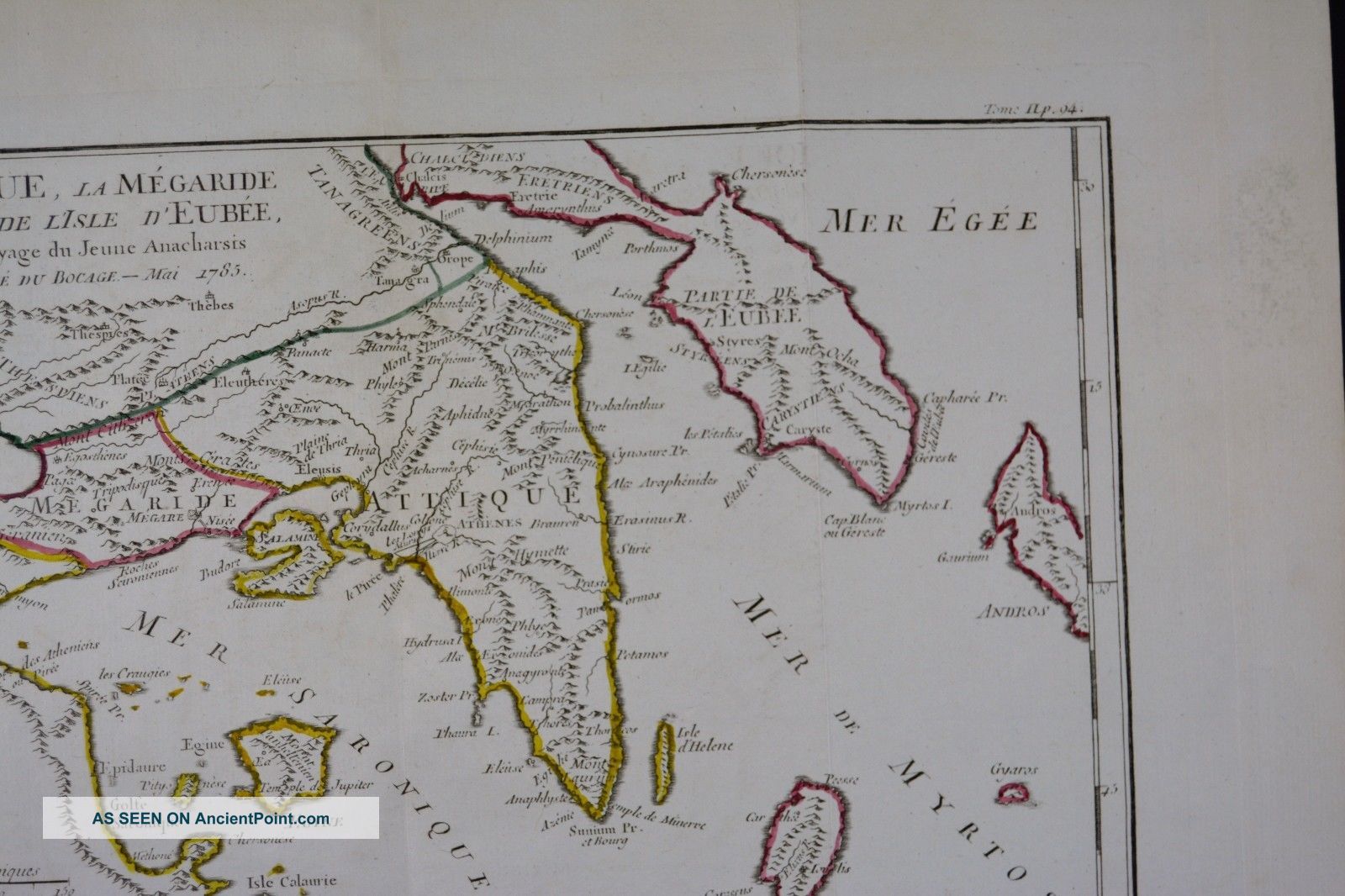
The Ancient Map of Attica: A Window into a Bygone Era
The ancient map of Attica, meticulously reconstructed through archaeological evidence and historical texts, provides a compelling glimpse into the region’s past. It reveals the location of key cities, settlements, and geographical features that shaped the lives of the ancient Athenians.
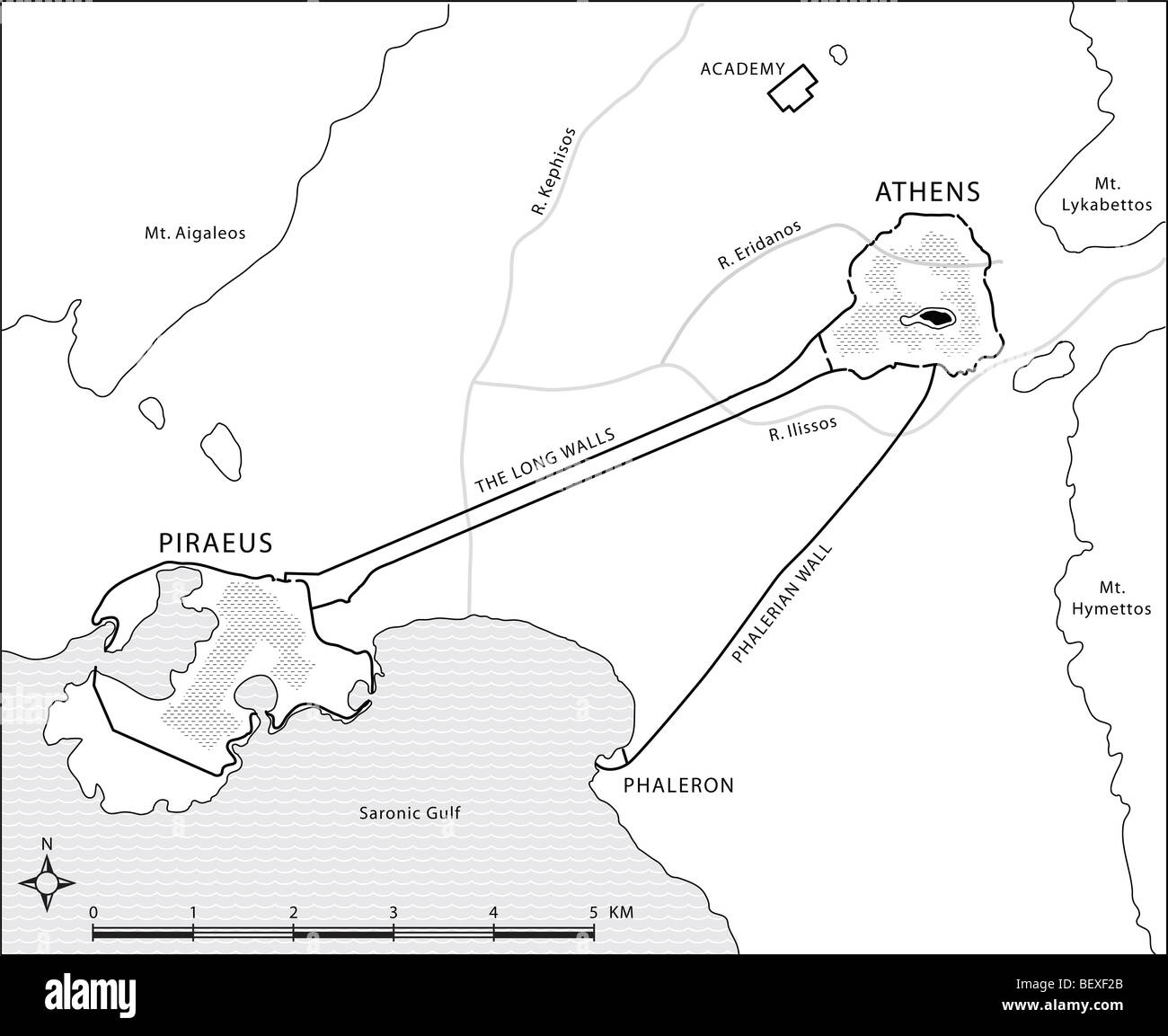
Athens: The Heart of Attica: The map highlights the city of Athens, the political and cultural center of Attica. Its strategic location on the plain, close to the harbor of Piraeus, facilitated trade and communication, contributing to its rise as a major city-state.
The Deme System: The map also illustrates the intricate network of demes, smaller administrative units that encompassed Attica. These demes, each with its own identity and governing body, played a vital role in the political and social life of the region.
Sacred Sites and Temples: The map reveals the location of numerous sacred sites and temples dedicated to various gods and goddesses. These sites, often located on hilltops or in prominent locations, served as important centers of religious life and cultural identity.
The Landscape of Attica: The map depicts the varied landscape of Attica, from the fertile plain of Athens to the rugged mountains and the scenic coastline. This geographic diversity is reflected in the region’s cultural and economic activities.
The Significance of Attica: A Cradle of Civilization
The ancient map of Attica underscores the region’s significance as a cradle of civilization. Its strategic location, fertile land, and access to the sea fostered the development of a vibrant culture and a powerful city-state.
Athens: A Beacon of Culture and Learning: Athens, the capital of Attica, became renowned for its intellectual and artistic achievements. The city was home to renowned philosophers, playwrights, artists, and architects, who left an indelible mark on Western civilization.
The Athenian Democracy: Attica was also the birthplace of democracy, a political system that emphasized citizen participation and equality. The Athenian democracy, though imperfect, served as a model for later democratic systems and influenced the development of political thought throughout history.
The Legacy of Attica: The achievements of ancient Attica, from its artistic and intellectual contributions to its political innovations, have resonated throughout history. The region’s legacy continues to inspire and shape our understanding of civilization, culture, and democracy.
FAQs: Unraveling the Mysteries of Ancient Attica
Q: What were the main cities in ancient Attica?
A: The most prominent city in ancient Attica was Athens, the capital and the center of political, cultural, and economic life. Other important cities in the region included Piraeus, the main harbor of Athens, and Eleusis, a sacred site renowned for its Eleusinian Mysteries.
Q: What were the major industries in ancient Attica?
A: Agriculture was a key industry in Attica, with the fertile plain of Athens producing crops like wheat, barley, olives, and grapes. The region also had a thriving pottery industry, with Athenian pottery being highly prized throughout the ancient world. Mining, particularly for silver, was another important industry.
Q: What were the main religious beliefs of the people of Attica?
A: The people of Attica worshipped a pantheon of Greek gods and goddesses, including Zeus, Athena, Poseidon, and Apollo. Each god had specific domains and attributes, and their worship was integrated into the daily lives of the Athenians.
Q: How did the geography of Attica influence its history?
A: Attica’s geography played a crucial role in shaping its history. The fertile plain of Athens provided the foundation for agriculture and settlement, while the mountains offered natural defenses and resources. The coastline facilitated trade and communication, connecting Attica to other civilizations.
Q: What were the major achievements of ancient Attica?
A: Ancient Attica was renowned for its intellectual and artistic achievements, including the development of philosophy, drama, and sculpture. The region also gave birth to democracy, a political system that emphasized citizen participation and equality.
Tips for Exploring the Ancient Map of Attica
1. Use a Map with Detailed Labels: Look for a map that includes the names of major cities, settlements, mountains, rivers, and sacred sites. This will help you visualize the layout of Attica and understand the relationships between different locations.
2. Research Historical Context: To fully appreciate the ancient map of Attica, it’s essential to research the historical context. Read about the major events, civilizations, and cultural developments that took place in the region.
3. Visit Archaeological Sites: Visiting archaeological sites in Attica can bring the ancient map to life. Exploring the ruins of Athens, the Acropolis, and other ancient sites allows you to experience firsthand the physical remains of a bygone era.
4. Engage with Primary Sources: Reading ancient Greek texts, such as those by Herodotus, Thucydides, and Plato, can provide valuable insights into the lives and beliefs of the people of Attica.
5. Consider the Role of Geography: As you study the ancient map of Attica, pay attention to the role of geography in shaping the region’s history. Understand how the landscape influenced settlement patterns, trade routes, and the development of culture.
Conclusion: A Legacy That Endures
The ancient map of Attica serves as a testament to the enduring legacy of this region. It reveals the intricate connections between geography, culture, and the rise of one of the most influential civilizations in antiquity. From its fertile plains to its rugged mountains and its bustling harbors, Attica shaped a culture that left an indelible mark on the world. Its achievements in art, philosophy, and democracy continue to inspire and inform our understanding of civilization, culture, and the human spirit. The ancient map of Attica is not merely a historical artifact; it is a window into a world that continues to resonate with us today.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Tapestry of Ancient Attica: A Journey Through History on a Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
