Unveiling Africa’s Diverse Tapestry: A Comprehensive Look at the Vegetation Map
Related Articles: Unveiling Africa’s Diverse Tapestry: A Comprehensive Look at the Vegetation Map
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling Africa’s Diverse Tapestry: A Comprehensive Look at the Vegetation Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling Africa’s Diverse Tapestry: A Comprehensive Look at the Vegetation Map
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling Africa’s Diverse Tapestry: A Comprehensive Look at the Vegetation Map
- 3.1 A Visual Journey Through Africa’s Botanical Diversity
- 3.2 Beyond the Map: Understanding the Dynamics of African Vegetation
- 3.3 The Importance of the African Vegetation Map
- 3.4 FAQs about the African Vegetation Map
- 3.5 Tips for Understanding and Utilizing the African Vegetation Map
- 3.6 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Unveiling Africa’s Diverse Tapestry: A Comprehensive Look at the Vegetation Map
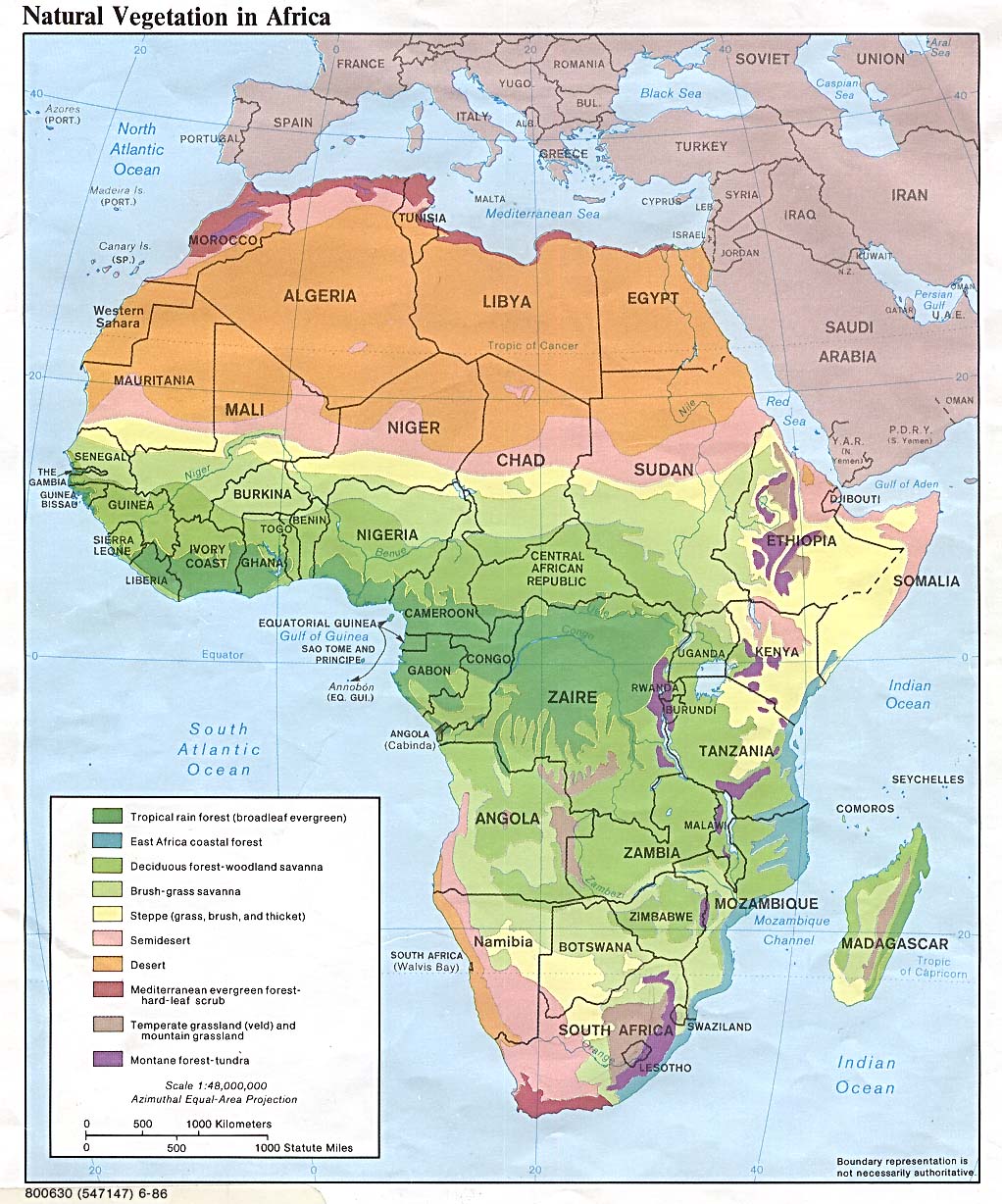
Africa, the second-largest continent, boasts an astounding array of landscapes, each with its own unique flora. This diversity is intricately woven into the continent’s tapestry, shaping its ecosystems, influencing human societies, and holding vital clues to understanding global climate change. The African vegetation map, a visual representation of this intricate botanical mosaic, serves as a crucial tool for researchers, policymakers, and conservationists alike.
A Visual Journey Through Africa’s Botanical Diversity
The African vegetation map provides a comprehensive overview of the continent’s diverse plant life, categorized into distinct vegetation zones based on factors such as rainfall, temperature, soil type, and elevation. These zones, ranging from lush rainforests to arid deserts, showcase the adaptability and resilience of life in the face of varying environmental conditions.
1. Tropical Rainforests:
- Location: Primarily found in the Congo Basin, along the Guinea Coast, and in parts of Madagascar.
- Characteristics: Characterized by high rainfall, warm temperatures, and dense vegetation, including towering trees, epiphytes, and a rich understory.
- Key Species: Mahogany, ebony, rubber trees, and numerous species of palms.
- Ecological Significance: Act as carbon sinks, support biodiversity, and provide essential resources for local communities.
2. Montane Forests:
- Location: Found on high-altitude slopes, particularly in the Eastern African highlands and the Atlas Mountains.
- Characteristics: Cooler temperatures, increased rainfall, and diverse vegetation ranging from coniferous forests to bamboo thickets.
- Key Species: Cedar, juniper, bamboo, and various endemic species.
- Ecological Significance: Contribute to water regulation, support unique biodiversity, and provide habitat for endangered species.
3. Savannas:
- Location: Cover vast areas of sub-Saharan Africa, characterized by a distinct dry season.
- Characteristics: Dominated by grasses with scattered trees, including acacia, baobab, and termite mounds.
- Key Species: Elephants, giraffes, zebras, lions, and numerous herbivores.
- Ecological Significance: Support large herds of grazing animals, play a crucial role in nutrient cycling, and are vulnerable to human activities.
4. Deserts and Semi-Deserts:
- Location: Found in northern and southern Africa, including the Sahara, Namib, and Kalahari.
- Characteristics: Extremely low rainfall, high temperatures, and sparse vegetation adapted to arid conditions.
- Key Species: Cacti, succulents, desert grasses, and specialized animals like camels and scorpions.
- Ecological Significance: Play a vital role in regulating regional climates, support unique biodiversity, and face increasing pressures from desertification.
5. Mediterranean Woodlands and Shrublands:
- Location: Primarily found along the northern coast of Africa, with a Mediterranean climate.
- Characteristics: Characterized by dry, hot summers and wet, mild winters, supporting drought-tolerant trees and shrubs.
- Key Species: Olive trees, cork oaks, and various shrubs adapted to the Mediterranean climate.
- Ecological Significance: Provide important resources for local communities, support unique biodiversity, and face challenges from urbanization and agricultural expansion.
6. Mangrove Forests:
- Location: Found along the coastlines of Africa, particularly in estuaries and deltas.
- Characteristics: Salt-tolerant trees adapted to tidal conditions, creating unique ecosystems.
- Key Species: Mangrove trees, various fish species, and shorebirds.
- Ecological Significance: Protect coastlines from erosion, provide breeding grounds for fish and other marine life, and are threatened by pollution and coastal development.
Beyond the Map: Understanding the Dynamics of African Vegetation
The African vegetation map is more than just a static representation. It reflects the dynamic interplay of various factors, including:
- Climate Change: Rising temperatures and shifting rainfall patterns are altering vegetation zones, leading to the expansion of deserts and the encroachment of savannas into forest areas.
- Human Activities: Deforestation, agricultural expansion, urbanization, and overgrazing are significantly impacting vegetation patterns, leading to habitat loss and biodiversity decline.
- Soil Degradation: Erosion, nutrient depletion, and salinization are affecting soil fertility, impacting vegetation health and productivity.
- Wildlife Interactions: The distribution and abundance of wildlife, particularly herbivores, play a crucial role in shaping vegetation structure and influencing plant diversity.
The Importance of the African Vegetation Map
Understanding the complexities of the African vegetation map is essential for:
- Conservation Efforts: Identifying areas of high biodiversity and prioritizing conservation actions to protect threatened species and ecosystems.
- Sustainable Development: Developing land management strategies that minimize environmental impacts and promote sustainable resource use.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Assessing the role of vegetation in carbon sequestration and understanding how climate change is impacting vegetation patterns.
- Food Security: Supporting sustainable agricultural practices that enhance food production while preserving biodiversity.
FAQs about the African Vegetation Map
Q: What is the primary purpose of the African vegetation map?
A: The African vegetation map provides a visual representation of the continent’s diverse plant life, categorizing it into distinct vegetation zones based on rainfall, temperature, soil type, and elevation. This map serves as a crucial tool for researchers, policymakers, and conservationists to understand the distribution and dynamics of Africa’s ecosystems.
Q: How does the African vegetation map contribute to conservation efforts?
A: The map helps identify areas of high biodiversity and prioritize conservation actions by highlighting unique ecosystems and vulnerable species. It also allows for the monitoring of changes in vegetation patterns over time, providing valuable data for conservation strategies.
Q: How is the African vegetation map impacted by climate change?
A: Climate change is altering vegetation zones, leading to the expansion of deserts and the encroachment of savannas into forest areas. The map provides insights into these shifts, enabling researchers to understand the impacts of climate change on ecosystems and biodiversity.
Q: What are the challenges faced by African vegetation?
A: African vegetation faces numerous challenges, including deforestation, agricultural expansion, urbanization, overgrazing, soil degradation, and climate change. These factors are leading to habitat loss, biodiversity decline, and ecosystem degradation.
Q: How can we use the African vegetation map to promote sustainable development?
A: The map helps inform sustainable land management practices, promoting resource use that minimizes environmental impacts and supports local communities. It also helps in identifying areas suitable for different land uses, balancing economic development with environmental conservation.
Tips for Understanding and Utilizing the African Vegetation Map
- Explore online resources: Numerous online platforms, such as the World Wildlife Fund (WWF) and the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), provide interactive maps and data on African vegetation.
- Consult scientific publications: Research papers and reports published by reputable organizations offer in-depth analyses of African vegetation patterns and their ecological significance.
- Engage with local communities: Local communities possess valuable knowledge about their surrounding ecosystems and can provide insights into the challenges and opportunities related to vegetation management.
- Support conservation initiatives: By supporting organizations working to protect African ecosystems, you can contribute to the preservation of biodiversity and the sustainable use of natural resources.
Conclusion
The African vegetation map is a powerful tool for understanding the continent’s rich biodiversity and the complex interplay of factors shaping its ecosystems. It serves as a vital resource for conservation efforts, sustainable development initiatives, and climate change research. By harnessing the knowledge embedded in this map, we can work towards preserving Africa’s unique flora and ensuring the well-being of its diverse ecosystems for generations to come.

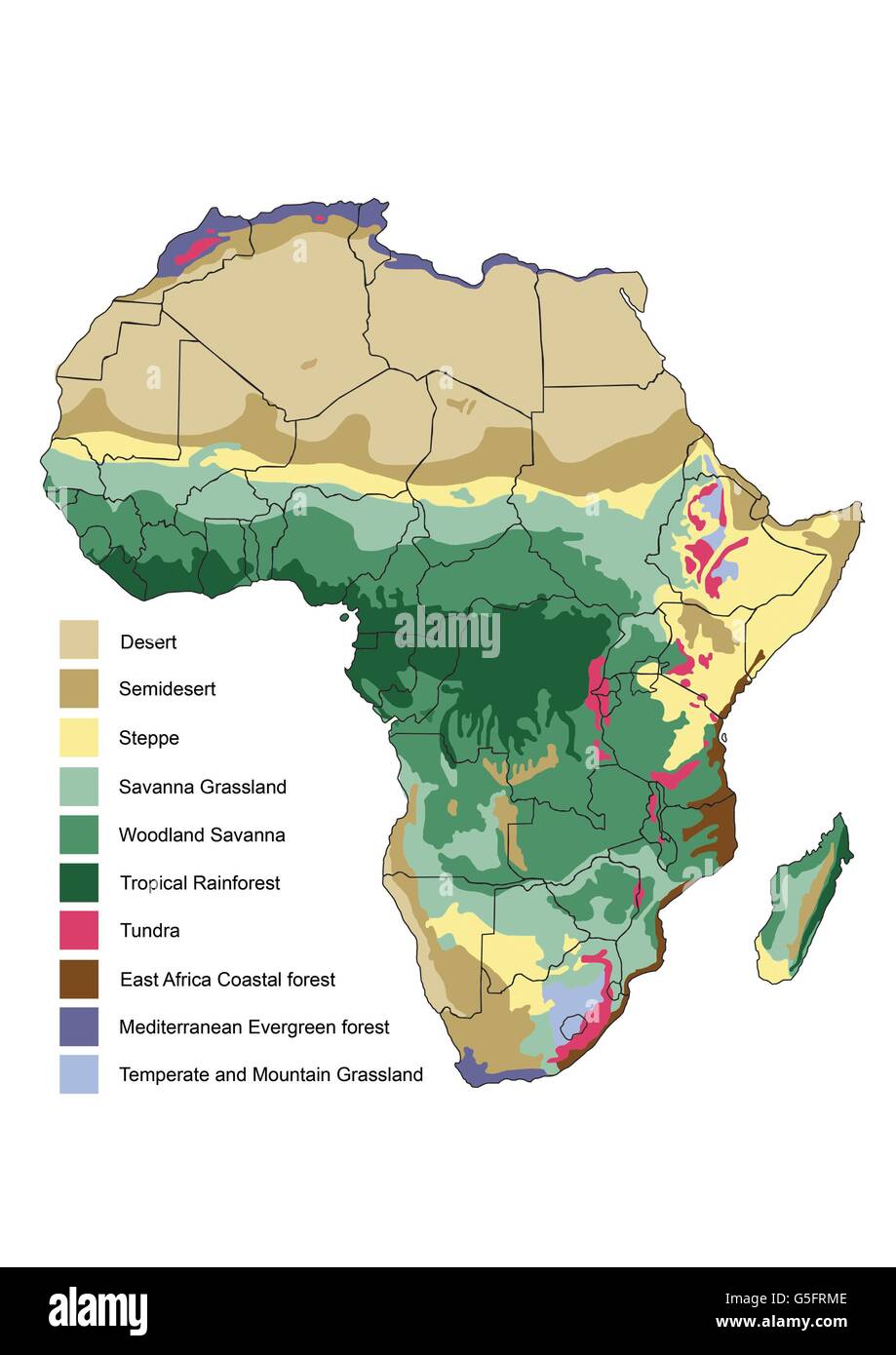

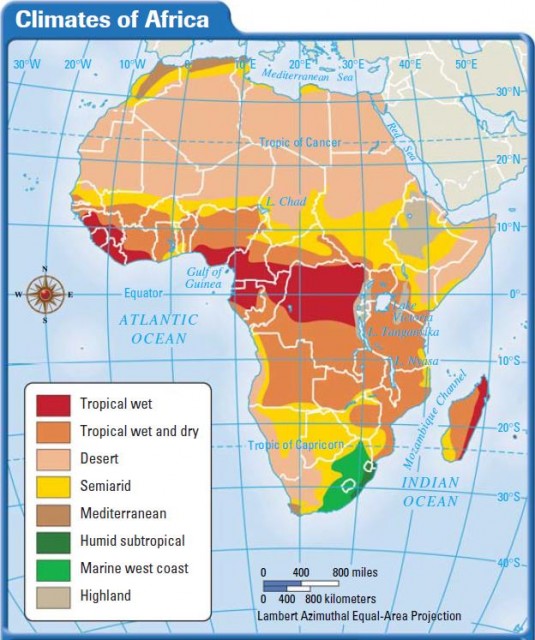

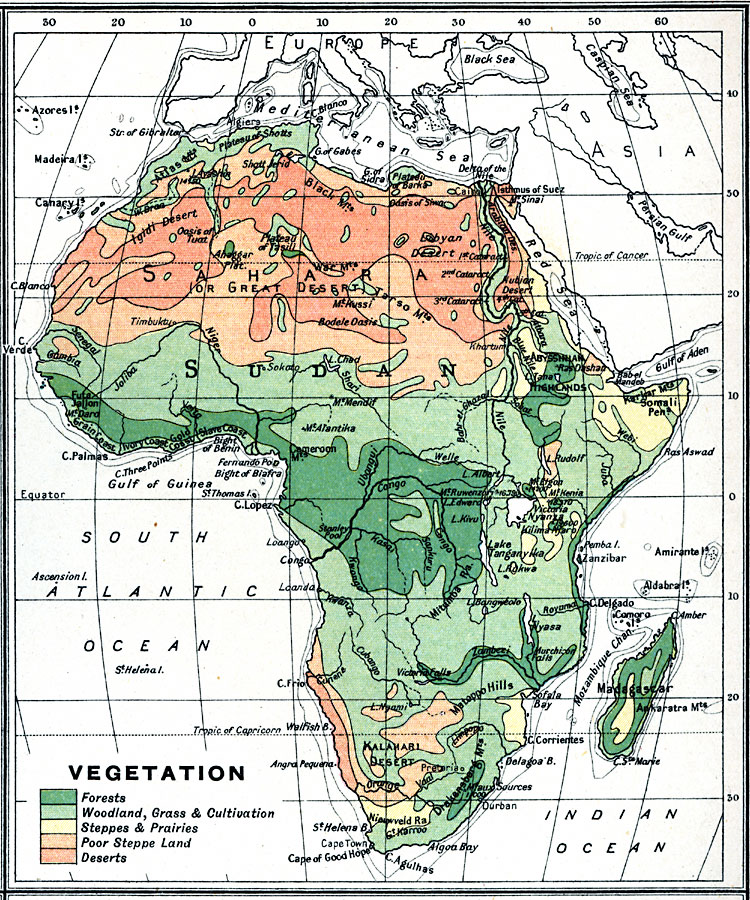
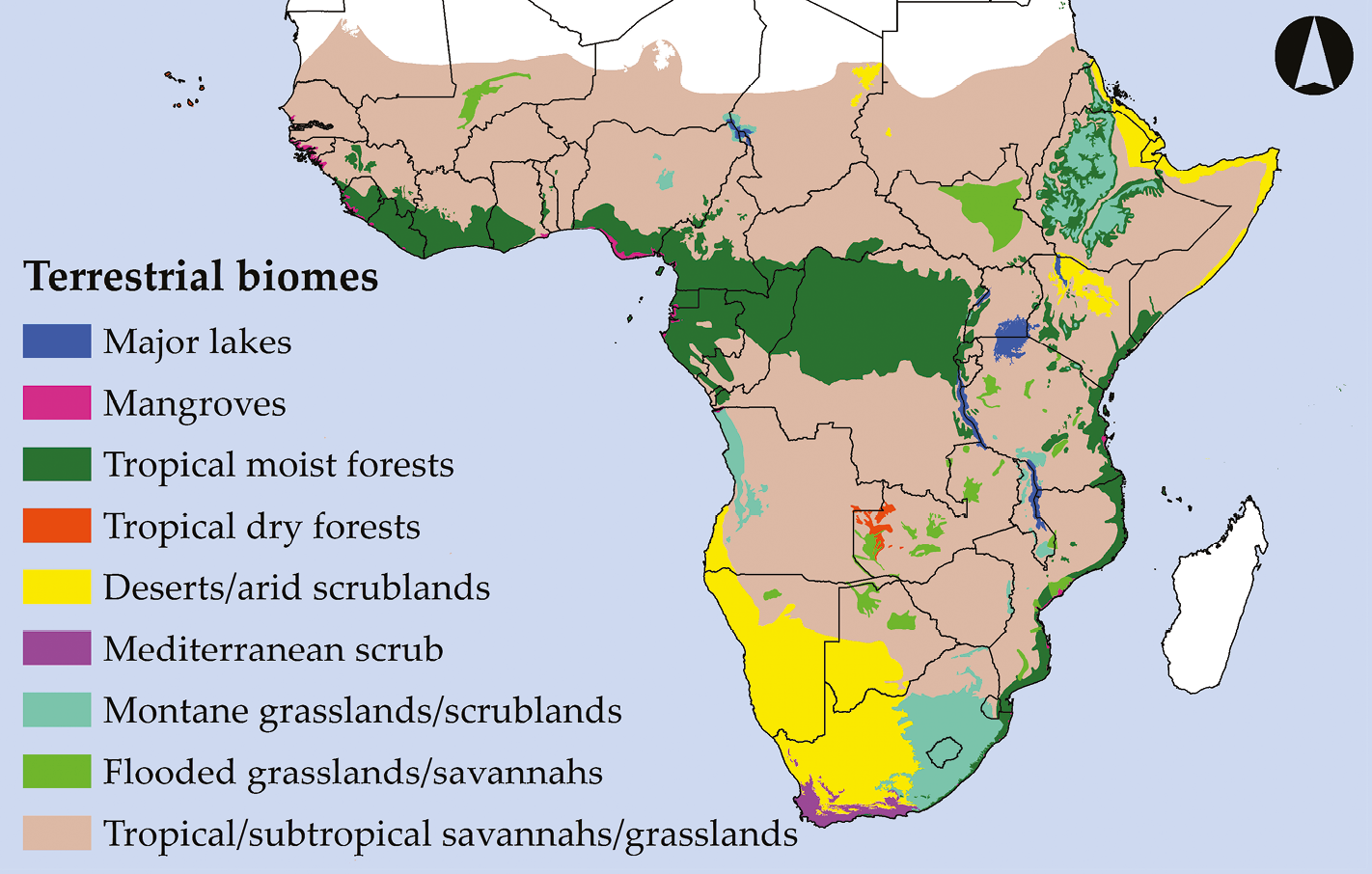
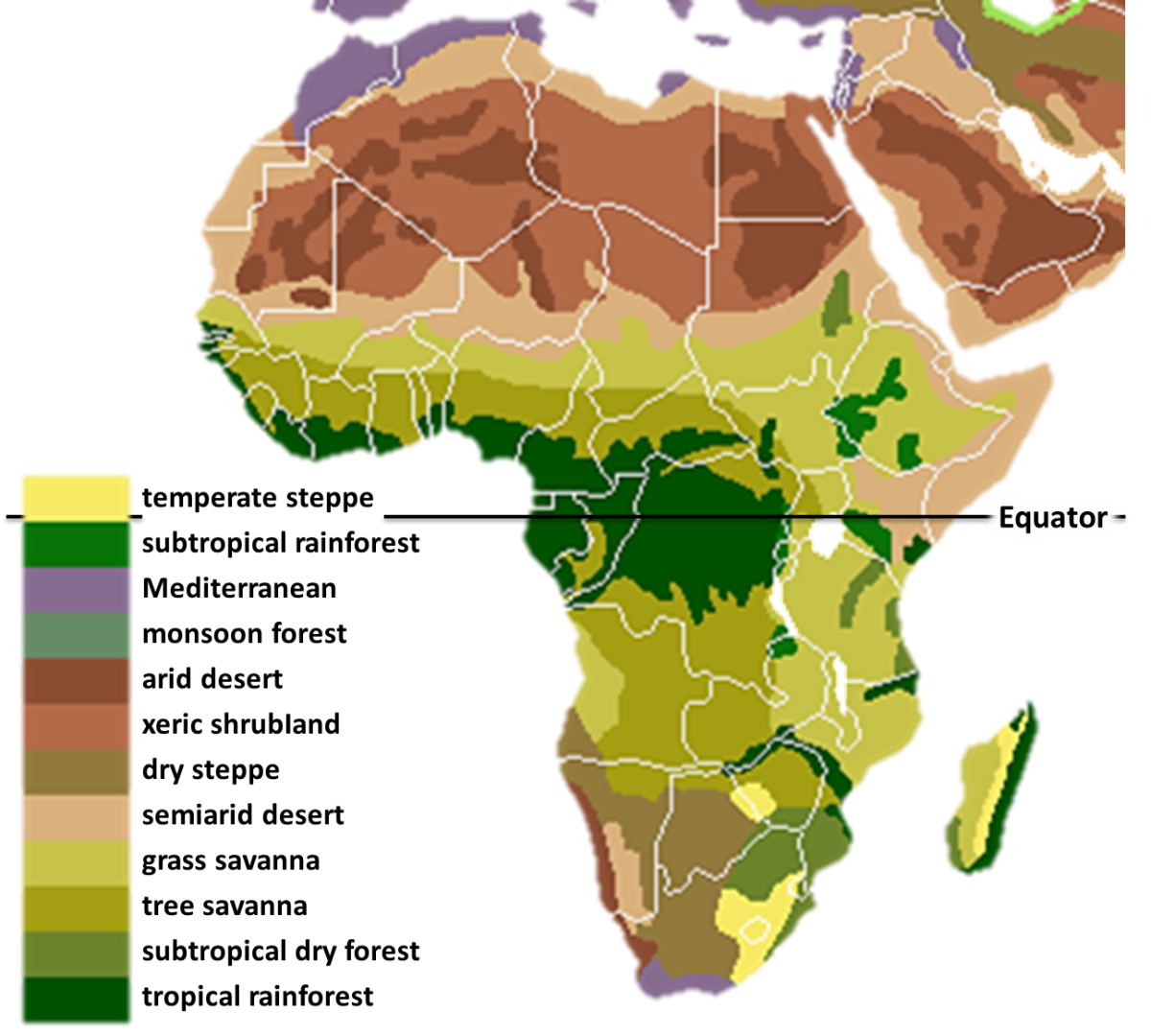
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling Africa’s Diverse Tapestry: A Comprehensive Look at the Vegetation Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
