Unveiling Data Patterns: A Comprehensive Guide to Heat Map Graphs
Related Articles: Unveiling Data Patterns: A Comprehensive Guide to Heat Map Graphs
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling Data Patterns: A Comprehensive Guide to Heat Map Graphs. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling Data Patterns: A Comprehensive Guide to Heat Map Graphs
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling Data Patterns: A Comprehensive Guide to Heat Map Graphs
- 3.1 Understanding the Essence of Heat Map Graphs
- 3.2 Construction and Interpretation of Heat Map Graphs
- 3.3 Applications of Heat Map Graphs
- 3.4 Advantages of Heat Map Graphs
- 3.5 Limitations of Heat Map Graphs
- 3.6 Frequently Asked Questions about Heat Map Graphs
- 3.7 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Unveiling Data Patterns: A Comprehensive Guide to Heat Map Graphs
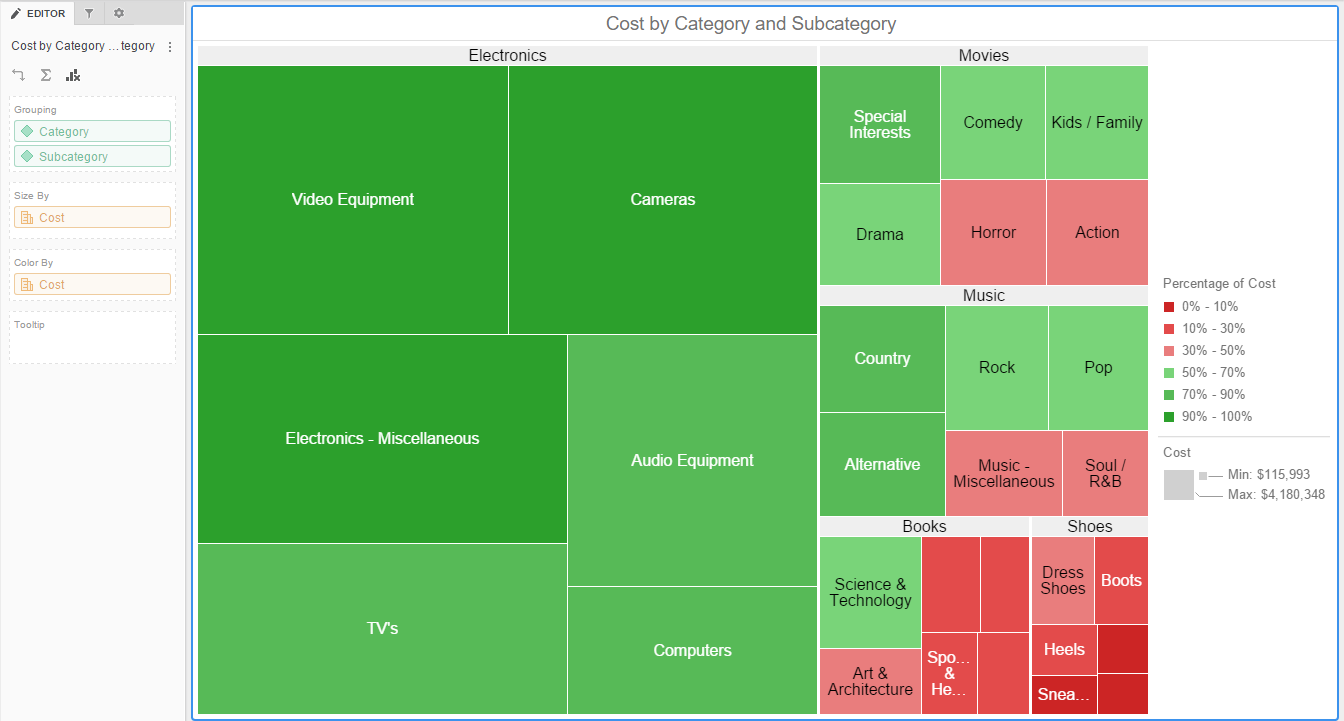
In the realm of data visualization, heat map graphs stand out as powerful tools for revealing hidden patterns and trends within complex datasets. These visually compelling representations utilize color gradients to depict the intensity or density of data points, enabling rapid identification of areas of interest and facilitating informed decision-making. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of heat map graphs, exploring their construction, applications, benefits, and limitations.
Understanding the Essence of Heat Map Graphs
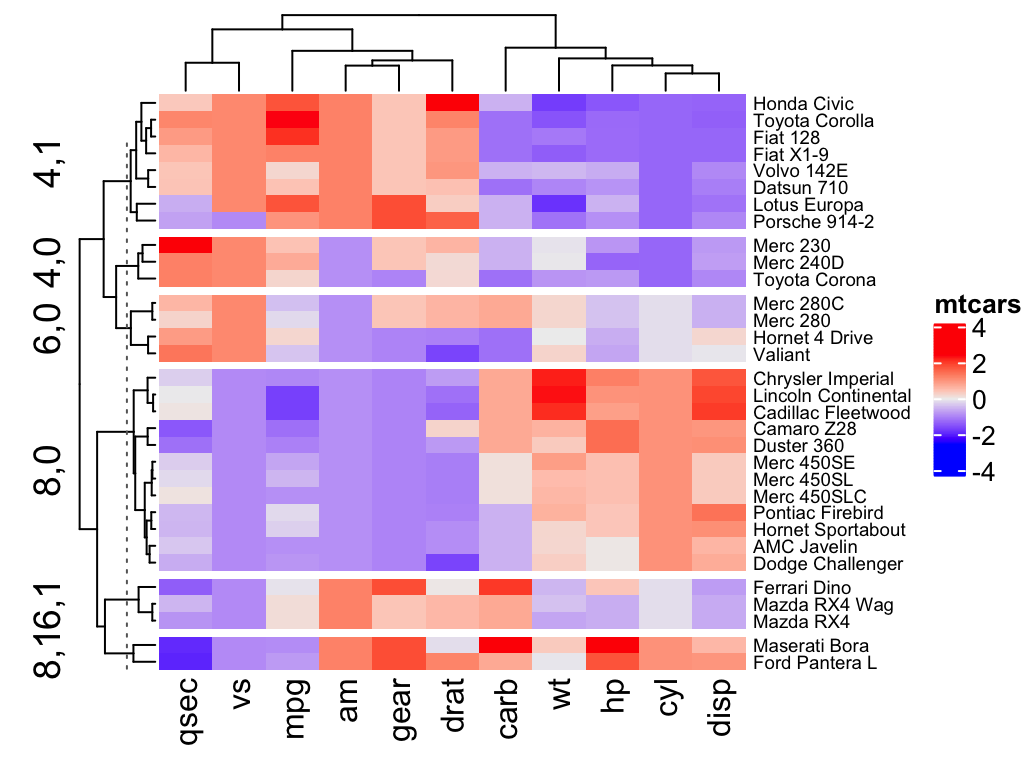
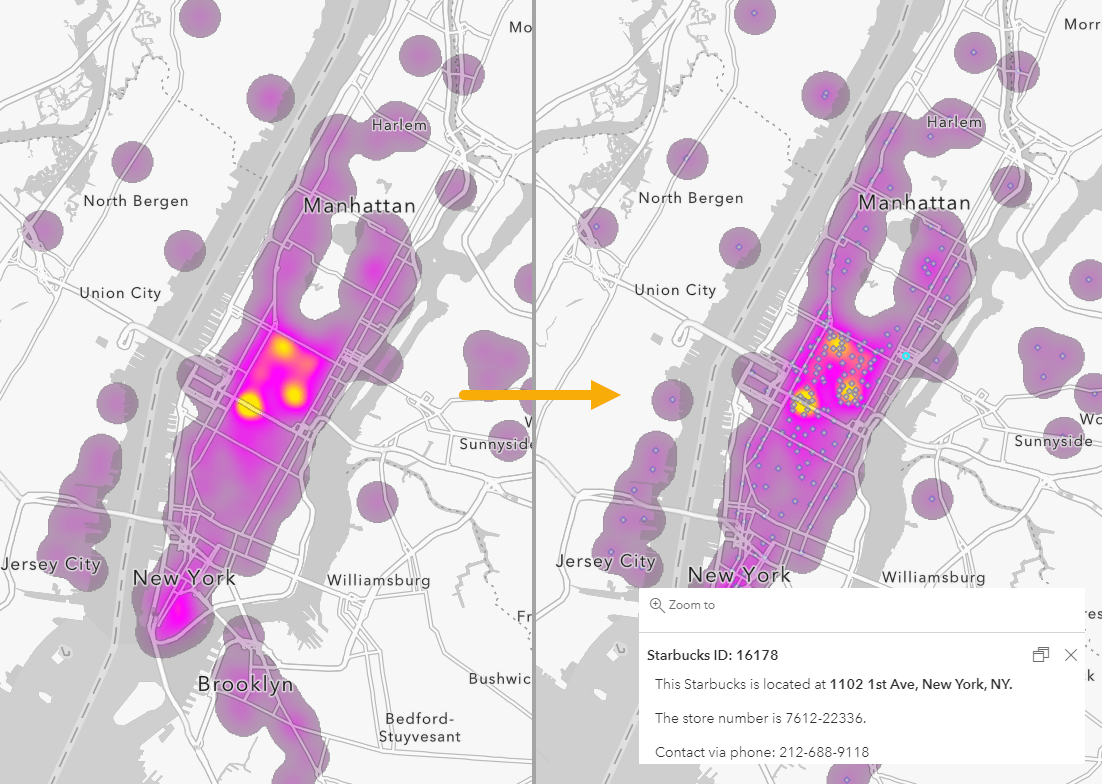
A heat map graph, also known as a heat map, is a graphical representation that uses color variations to depict the distribution of data values across a two-dimensional space. This space can be a physical map, a matrix, or even a representation of a website layout. The color intensity corresponds to the magnitude of the data value, with hotter colors indicating higher values and cooler colors representing lower values.
For instance, a heat map displaying website user activity might depict areas of high user engagement with brighter colors, highlighting popular sections, while areas of low interaction would be represented with cooler colors. Similarly, a heat map representing sales data could showcase regions with high sales volume in vibrant hues, while regions with lower sales would be represented with muted colors.
Construction and Interpretation of Heat Map Graphs
The construction of a heat map graph involves several key steps:
-
Data Preparation: The initial step involves gathering and preparing the data for visualization. This may include cleaning, filtering, and transforming the data into a suitable format for representation.
-
Grid Definition: The data is then mapped onto a grid, which can be a physical map, a matrix, or a representation of a website layout. Each cell within the grid corresponds to a specific data point.
-
Color Scheme Selection: A color scheme is chosen to represent the data values. The color palette should be visually appealing and intuitive, ensuring that higher values are represented with warmer colors and lower values with cooler colors.
-
Color Mapping: The data values are then mapped to the chosen color scheme. This involves assigning a specific color to each cell based on the data value it represents.
-
Visualization: The final step involves displaying the color-coded grid, creating a visual representation of the data distribution.
Interpreting a heat map graph involves identifying areas of high and low data values based on the color intensity. Areas with warmer colors indicate higher values, while areas with cooler colors represent lower values. The visual patterns and trends revealed by the heat map can be further analyzed to gain insights into the data.
Applications of Heat Map Graphs
Heat map graphs find wide-ranging applications across various fields, including:
-
Business Analytics: Heat maps are valuable tools for analyzing customer behavior, website traffic, and sales data. They can help identify popular product categories, understand user navigation patterns, and optimize marketing campaigns.
-
Healthcare: Heat maps are used in healthcare to visualize patient data, such as hospital bed occupancy, disease prevalence, and medical imaging results. They can aid in resource allocation, disease surveillance, and treatment planning.
-
Finance: Heat maps are employed in finance to analyze market trends, identify investment opportunities, and manage risk. They can help visualize stock performance, market sentiment, and portfolio allocation.
-
Urban Planning: Heat maps are used in urban planning to analyze population density, traffic flow, and crime rates. They can aid in urban development, infrastructure planning, and public safety initiatives.
-
Environmental Science: Heat maps are used in environmental science to visualize climate data, air pollution levels, and wildlife distribution. They can help understand environmental trends, identify areas of concern, and inform conservation efforts.
Advantages of Heat Map Graphs
Heat map graphs offer several advantages over other data visualization methods:
-
Visual Clarity: Heat maps provide a clear and concise visual representation of data distribution, making it easy to identify patterns and trends.
-
Data Density: They can effectively represent large datasets, enabling the visualization of complex relationships and interactions.
-
Intuitive Interpretation: The use of color gradients makes the interpretation of heat maps intuitive, allowing for quick and easy understanding of data trends.
-
Interactive Exploration: Heat maps can be interactive, allowing users to zoom in on specific areas of interest and explore data in more detail.
-
Comparative Analysis: Heat maps can be used to compare different datasets, highlighting differences and similarities in data distributions.
Limitations of Heat Map Graphs
While heat map graphs offer numerous advantages, they also have some limitations:
-
Data Overlap: Heat maps can be difficult to interpret when data points overlap, making it challenging to discern individual values.
-
Color Sensitivity: The interpretation of heat maps can be influenced by individual color perception, which can lead to subjective interpretations.
-
Limited Data Dimensions: Heat maps are typically limited to visualizing two-dimensional data, making it difficult to represent data with higher dimensions.
-
Data Distortion: Heat maps can distort data relationships, particularly when dealing with non-linear data distributions.
Frequently Asked Questions about Heat Map Graphs
1. What types of data are suitable for heat map representation?
Heat maps are best suited for representing data that can be categorized into two dimensions, such as geographical location, time periods, or website elements. Data that can be represented as numerical values or frequencies is also suitable for heat map visualization.
2. What are some popular software tools for creating heat map graphs?
Several software tools are available for creating heat maps, including:
-
Microsoft Excel: Excel offers built-in heat map functionality, allowing users to create basic heat maps with ease.
-
Google Sheets: Google Sheets also provides heat map functionality, enabling users to create and share heat maps online.
-
Tableau: Tableau is a powerful data visualization tool that offers advanced heat map capabilities, including interactive features and customization options.
-
Power BI: Power BI is another powerful data visualization tool that provides comprehensive heat map functionality, including data filtering, drill-down capabilities, and integration with other data sources.
-
R: R is a statistical programming language that provides a wide range of packages for creating heat maps, offering flexibility and customization options.
3. How can I enhance the readability and clarity of my heat map graphs?
To enhance the readability and clarity of heat map graphs, consider these tips:
-
Use a clear and intuitive color scheme: Choose a color palette that is visually appealing and easily interpretable, ensuring that higher values are represented with warmer colors and lower values with cooler colors.
-
Avoid overusing color gradients: Too many color gradients can make the heat map difficult to interpret. Use a limited number of color gradients to represent the data effectively.
-
Include a legend: A legend should be included to clearly explain the color mapping and data values represented by the heat map.
-
Label axes and data points: Label axes and data points appropriately to provide context and enhance clarity.
-
Use appropriate grid size: The grid size should be chosen based on the data distribution and the desired level of detail.
4. How can I use heat maps to gain actionable insights from my data?
Heat maps can be used to gain actionable insights from data by:
-
Identifying areas of high and low activity: Analyze the color intensity to identify areas with high and low data values, revealing patterns and trends.
-
Comparing different datasets: Compare heat maps representing different datasets to identify similarities and differences in data distributions.
-
Identifying outliers and anomalies: Heat maps can highlight unusual data points that deviate from the overall trend, enabling further investigation.
-
Testing hypotheses and assumptions: Use heat maps to visualize data and test hypotheses about relationships and trends.
-
Communicating insights to stakeholders: Use heat maps to effectively communicate data insights to stakeholders, facilitating informed decision-making.
Conclusion
Heat map graphs are powerful tools for visualizing data distribution and revealing hidden patterns and trends. By effectively representing data with color gradients, heat maps provide a clear and concise visual representation that facilitates intuitive interpretation and informed decision-making. Their applications extend across diverse fields, making them invaluable tools for analyzing data, identifying areas of interest, and gaining insights into complex relationships. By understanding the principles of heat map construction, interpretation, and application, individuals and organizations can leverage this powerful visualization technique to unlock the potential of their data and drive informed decision-making.

![]()




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling Data Patterns: A Comprehensive Guide to Heat Map Graphs. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
