Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Contour Topographic Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Contour Topographic Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Contour Topographic Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Contour Topographic Maps
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Contour Topographic Maps
- 3.1 The Essence of Contour Lines: Tracing Elevation
- 3.2 Constructing a Contour Map: From Data to Visualization
- 3.3 Deciphering the Landscape: Interpreting Contour Maps
- 3.4 Applications of Contour Maps: A Diverse Range of Uses
- 3.5 FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about Contour Maps
- 3.6 Tips for Effective Contour Map Use
- 3.7 Conclusion: The Power of Visualizing Terrain
- 4 Closure
Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Contour Topographic Maps

Topographic maps, often referred to as contour maps, are essential tools for visualizing and understanding the three-dimensional terrain of the Earth’s surface. They provide a detailed representation of elevation changes, revealing the shape and form of landscapes, from gentle rolling hills to towering mountains. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of contour topographic maps, exploring their construction, interpretation, and diverse applications.
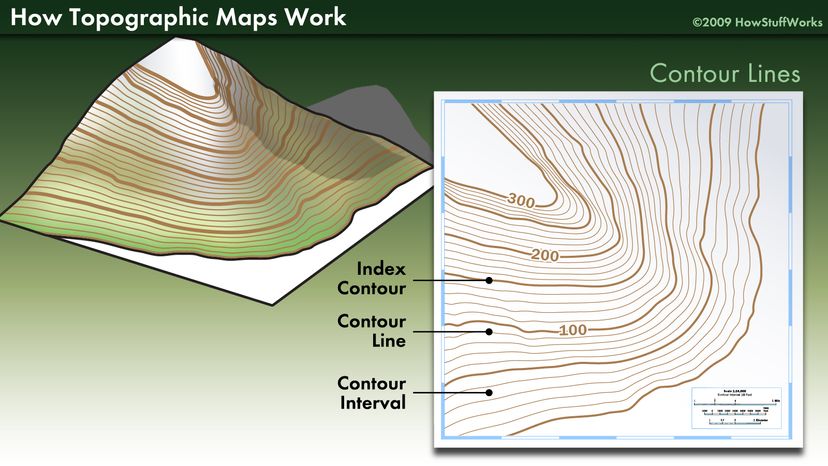
The Essence of Contour Lines: Tracing Elevation
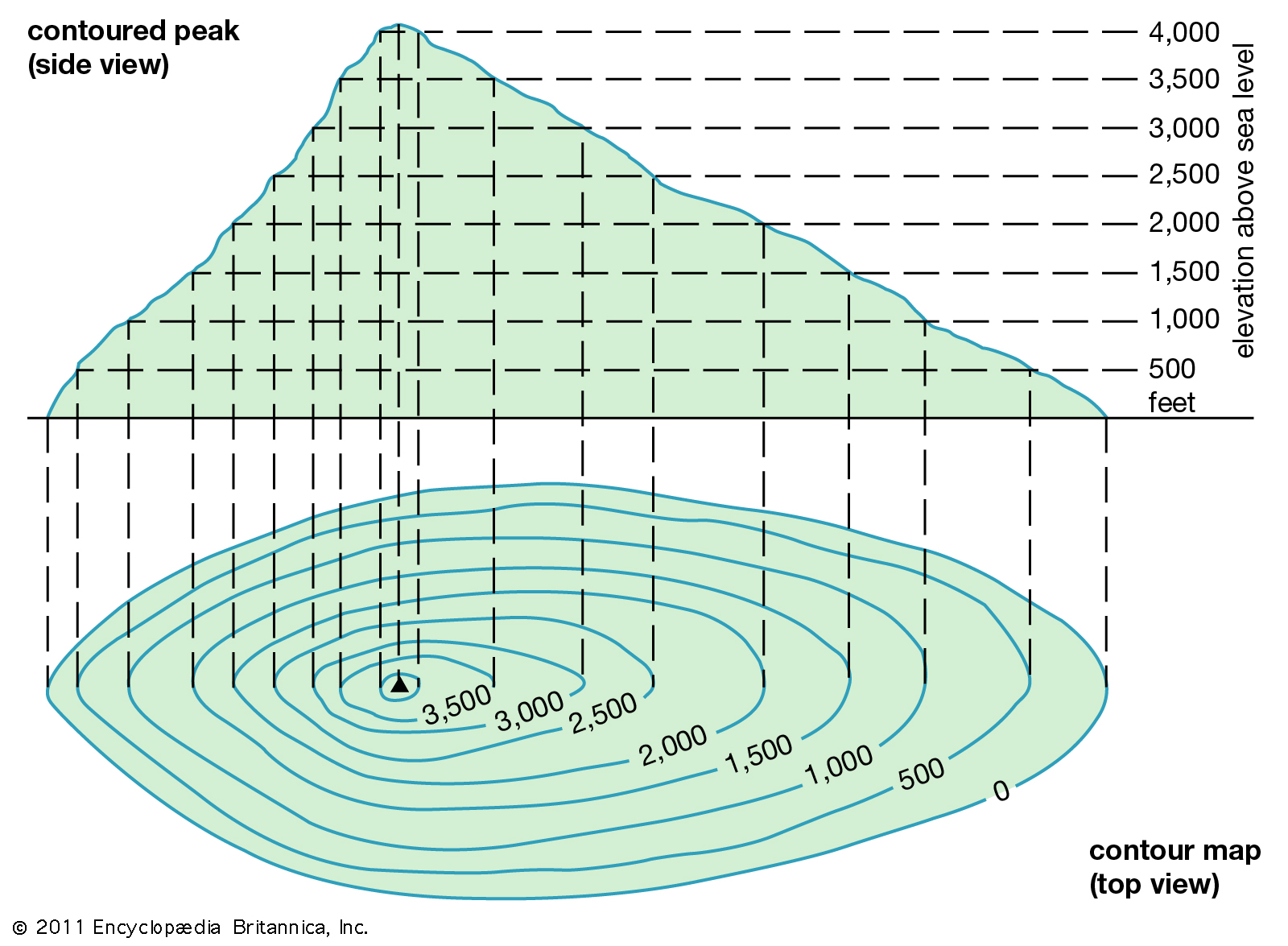
At the heart of a contour map lies the concept of contour lines. These lines connect points of equal elevation, effectively slicing through the landscape at specific heights. Imagine a series of horizontal planes cutting through a mountain. The intersection of each plane with the mountain’s surface would create a contour line. Each contour line represents a specific elevation, with the difference in elevation between adjacent lines being known as the contour interval.
Understanding Contour Line Characteristics:
- Spacing: The spacing between contour lines reveals the steepness of the terrain. Closely spaced lines indicate a steep slope, while widely spaced lines suggest a gentle incline.
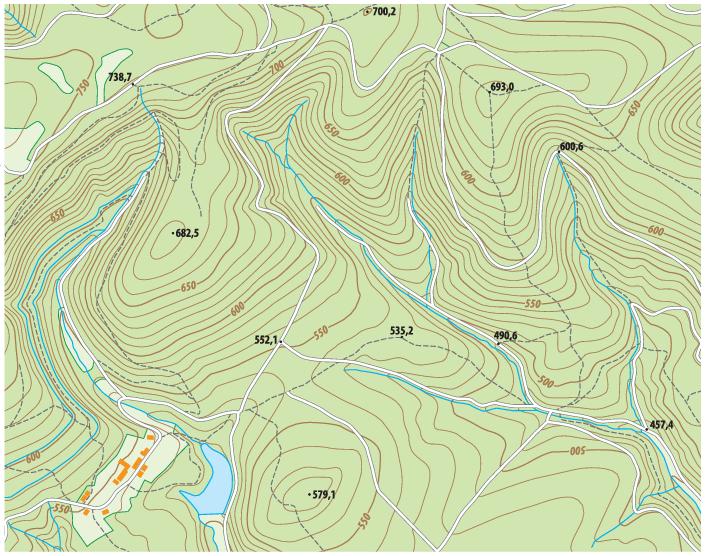
- Shape: The shape of contour lines reflects the form of the terrain. Circular or oval contours indicate hills or depressions, while jagged or irregular lines denote rugged or mountainous areas.
- Direction: Contour lines never cross each other, as they represent points of equal elevation. They may converge at a point, indicating a peak or a pit.
Constructing a Contour Map: From Data to Visualization
The creation of a contour topographic map involves several key steps:
- Data Collection: Elevation data is gathered using various methods, including aerial photography, satellite imagery, ground surveys, and GPS readings.
- Data Processing: The collected elevation data is then processed and organized into a digital elevation model (DEM). This model represents the terrain in a grid format, with each grid cell containing an elevation value.
- Contour Generation: Specialized software algorithms are employed to generate contour lines from the DEM. These algorithms connect points of equal elevation, creating a continuous representation of the terrain.
- Map Production: The generated contour lines are then overlaid on a base map, which typically includes geographical features like roads, rivers, and settlements. The resulting map provides a comprehensive visualization of the landscape.
Deciphering the Landscape: Interpreting Contour Maps
Once a contour map is created, it can be used to extract valuable information about the terrain. Here are some key elements to consider when interpreting a contour map:
1. Elevation: The elevation of any point on the map can be determined by identifying the contour line passing through that point. The elevation of the line itself represents the elevation of the point.
2. Slope: The steepness of the terrain can be assessed by examining the spacing of contour lines. Closely spaced lines indicate a steep slope, while widely spaced lines suggest a gentle incline.
3. Terrain Features: Contour lines reveal the shape and form of the terrain. Circular or oval contours indicate hills or depressions, while jagged or irregular lines denote rugged or mountainous areas.
4. Drainage Patterns: Contour lines can help identify drainage patterns. Water flows perpendicular to contour lines, descending from higher to lower elevations. This is evident in the presence of V-shaped patterns, where the apex points uphill.
5. Landform Identification: By analyzing the shape, spacing, and direction of contour lines, it is possible to identify various landforms, such as hills, valleys, ridges, saddles, and cliffs.
Applications of Contour Maps: A Diverse Range of Uses
Contour topographic maps are indispensable tools in a wide range of fields, including:
1. Civil Engineering: Contour maps are crucial for planning and designing infrastructure projects, such as roads, bridges, and dams. They provide essential information about the terrain, allowing engineers to optimize design choices, minimize environmental impact, and ensure structural stability.
2. Urban Planning: Contour maps aid in urban planning by providing insights into the topography of a site, influencing the layout of buildings, streets, and public spaces. They help identify suitable locations for development, minimize environmental damage, and optimize resource utilization.
3. Environmental Studies: Contour maps are essential for understanding and managing environmental issues. They can be used to assess the impact of development on the environment, identify areas prone to erosion or flooding, and map out areas suitable for conservation or restoration.
4. Geology and Hydrology: Contour maps assist in understanding geological formations and hydrological processes. They can be used to identify geological features, analyze groundwater flow, and map out areas prone to landslides or erosion.
5. Military Operations: Contour maps are vital for military planning and execution. They provide detailed information about the terrain, enabling strategic deployment, route planning, and target identification.
6. Recreation and Outdoor Activities: Contour maps are essential for hikers, climbers, and outdoor enthusiasts. They provide a clear representation of the terrain, helping individuals plan routes, identify points of interest, and assess the difficulty of trails.
7. Aviation: Contour maps are used in aviation to understand the topography of flight paths and identify potential hazards, such as mountains or steep terrain. They help pilots navigate safely and efficiently.
8. Agriculture: Contour maps are helpful in agricultural planning, enabling farmers to optimize land use, manage irrigation, and minimize erosion. They provide insights into the slope of fields, helping farmers create contour farming systems to conserve soil and water.
9. Archaeology: Contour maps assist archaeologists in understanding the topography of archaeological sites, identifying potential areas for excavation, and analyzing the relationship between human settlements and the landscape.
10. Disaster Management: Contour maps are essential for disaster preparedness and response. They help identify areas at risk of flooding, landslides, or earthquakes, enabling authorities to plan evacuation routes, deploy resources effectively, and mitigate potential damage.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about Contour Maps
1. What is the difference between a topographic map and a contour map?
While often used interchangeably, there is a subtle distinction. A topographic map is a general term for a map that depicts the surface features of the Earth, including elevation, while a contour map specifically utilizes contour lines to represent elevation.
2. How do I read a contour map?
The key to reading a contour map lies in understanding the contour lines. Remember that each line represents a specific elevation, and the spacing between lines indicates the steepness of the terrain.
3. What is the contour interval?
The contour interval is the difference in elevation between adjacent contour lines. It is typically indicated on the map legend.
4. What are index contours?
Index contours are thicker contour lines that are labeled with their elevation. They help in quickly identifying the elevation of specific areas on the map.
5. What are hachures?
Hachures are short, parallel lines that are used to indicate the direction of slope on a contour map. They are typically drawn perpendicular to the contour lines.
6. How can I create a contour map?
Contour maps can be created using specialized software that processes elevation data from various sources, such as aerial photography, satellite imagery, or ground surveys.
7. Are contour maps accurate?
The accuracy of a contour map depends on the quality of the elevation data used to create it. Modern maps created using high-resolution data are generally very accurate.
8. What are the limitations of contour maps?
Contour maps are static representations of the terrain and do not account for changes in elevation over time due to factors like erosion, landslides, or human activities.
9. How do I use a contour map for hiking?
Contour maps can be invaluable for hikers, providing information about the elevation changes along trails, identifying points of interest, and assessing the difficulty of the route.
10. Where can I find contour maps?
Contour maps are available from various sources, including government agencies, mapping companies, and online repositories.
Tips for Effective Contour Map Use
1. Familiarize Yourself with the Legend: The map legend provides essential information, including the contour interval, scale, and symbols used to represent different features.
2. Identify Key Features: Pay attention to prominent features on the map, such as peaks, valleys, ridges, and saddles.
3. Understand the Terrain: Analyze the spacing and shape of contour lines to understand the steepness and form of the terrain.
4. Use a Pencil: Use a pencil to trace routes, mark points of interest, and make notes on the map.
5. Practice: The best way to improve your contour map reading skills is to practice. Start with simple maps and gradually work your way up to more complex ones.
6. Combine with Other Data: Contour maps can be combined with other data sources, such as satellite imagery or aerial photography, to gain a more comprehensive understanding of the landscape.
7. Consider the Context: Always consider the context of the map, including its scale, date of creation, and intended purpose.
8. Stay Informed: New technologies and techniques are constantly emerging in the field of topographic mapping. Stay informed about the latest developments and advancements.
Conclusion: The Power of Visualizing Terrain
Contour topographic maps offer a powerful and versatile tool for visualizing and understanding the Earth’s surface. They provide a detailed representation of elevation changes, revealing the shape and form of landscapes and enabling informed decision-making in various fields. From civil engineering and urban planning to environmental studies and recreational activities, contour maps play a crucial role in our understanding and interaction with the natural world. By mastering the art of interpreting contour maps, we unlock a deeper appreciation for the intricacies of terrain and gain valuable insights into the complexities of our planet.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Contour Topographic Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!