Unveiling the Landscape of Inequality: A Comprehensive Guide to Disparity Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Landscape of Inequality: A Comprehensive Guide to Disparity Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Landscape of Inequality: A Comprehensive Guide to Disparity Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Landscape of Inequality: A Comprehensive Guide to Disparity Maps

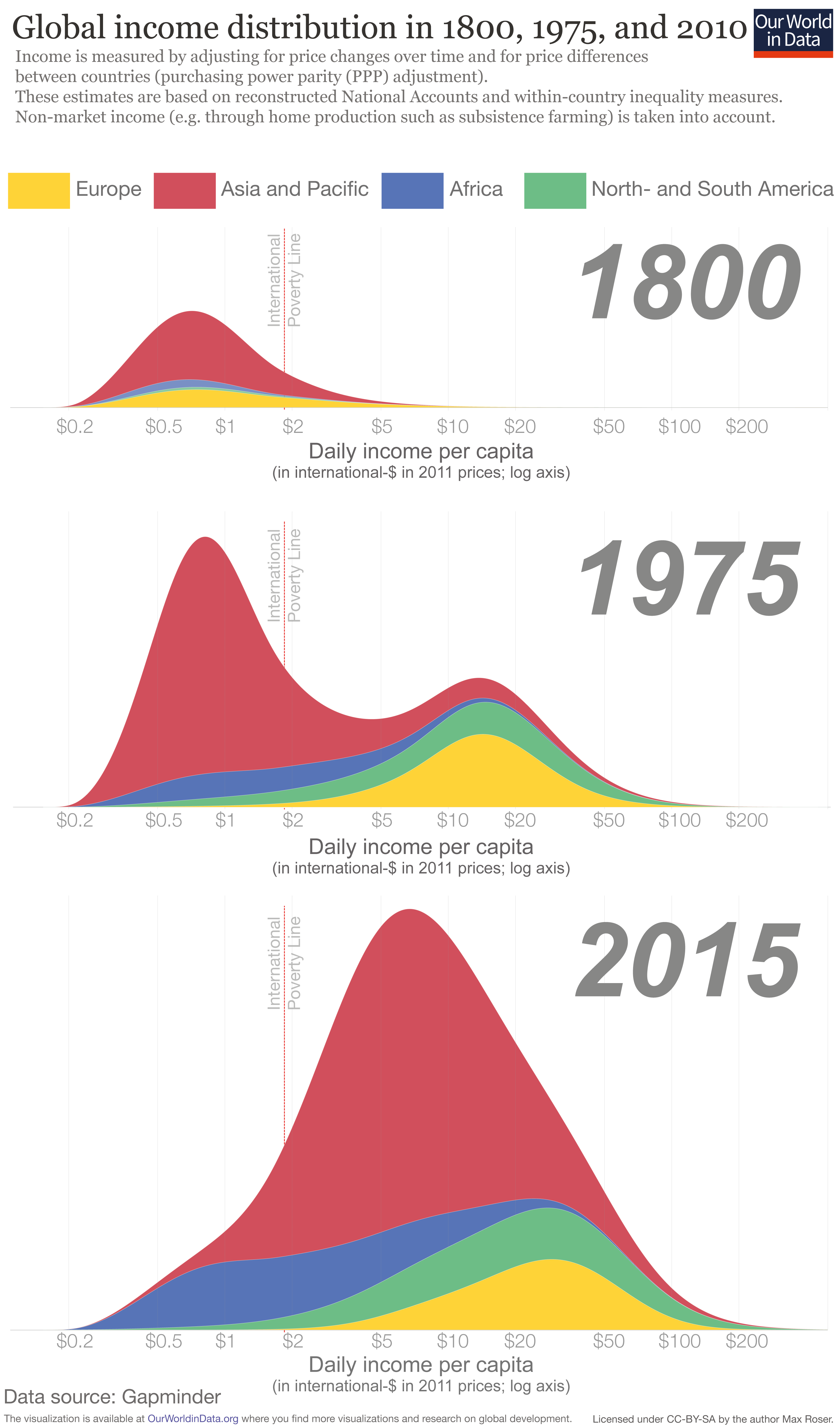
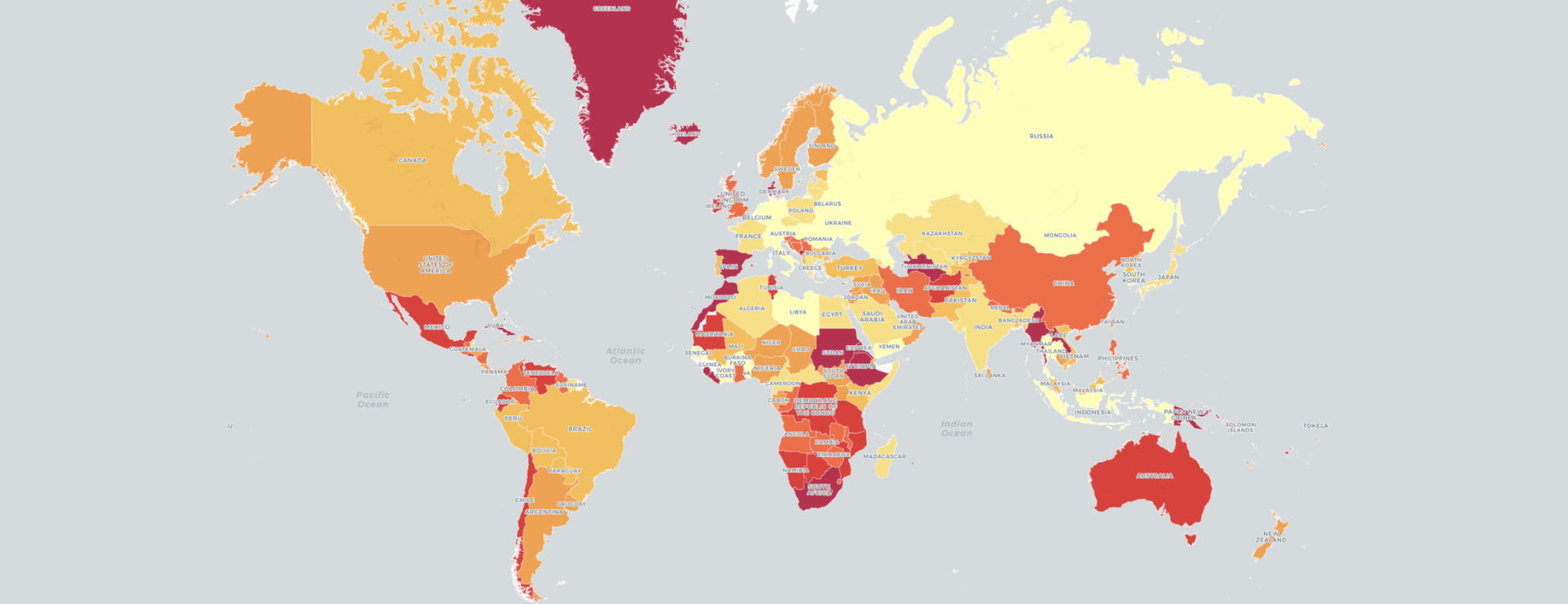
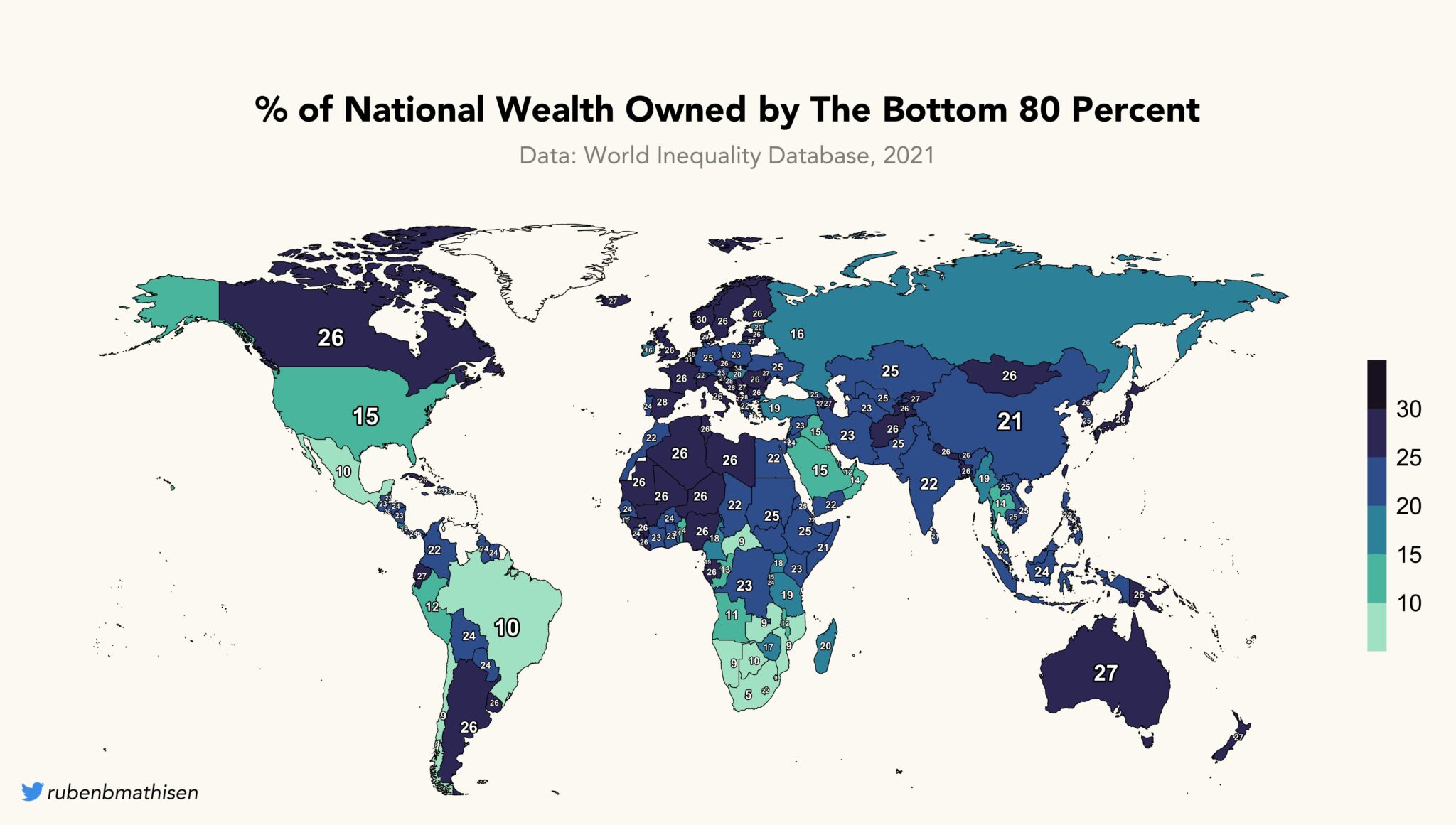
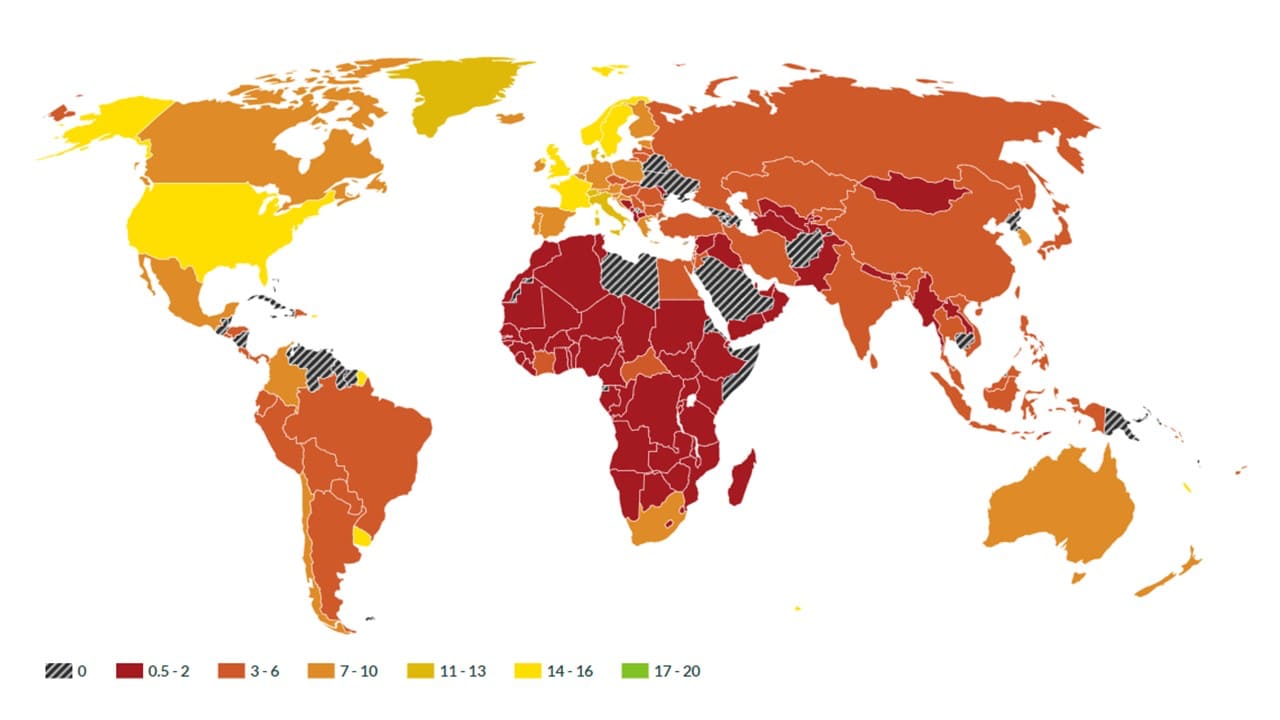
Disparity maps, visual representations of social and economic inequalities across geographic regions, are powerful tools for understanding and addressing societal challenges. They offer a unique perspective on the distribution of resources, opportunities, and outcomes, highlighting areas where disparities are most pronounced. By illuminating these differences, disparity maps empower policymakers, community leaders, and researchers to identify areas requiring attention and develop targeted interventions.
Understanding the Essence of Disparity Maps
Imagine a map where the color intensity reflects the level of poverty, access to healthcare, or educational attainment in different neighborhoods. This is the essence of a disparity map. By visually representing data on various social and economic indicators, these maps provide a clear and concise picture of the uneven distribution of resources and opportunities within a given area.
Types of Disparity Maps and Their Applications
Disparity maps can be tailored to encompass a wide range of social and economic indicators, offering insights into diverse aspects of inequality. Some common examples include:
- Income Disparity Maps: These maps depict the distribution of income levels across different geographic regions. Highlighted areas with low income levels can indicate potential pockets of poverty and socioeconomic vulnerability.
- Healthcare Disparity Maps: By visualizing access to healthcare services, these maps reveal disparities in health outcomes and highlight areas with limited access to quality healthcare.
- Education Disparity Maps: These maps showcase the distribution of educational attainment, identifying regions with lower literacy rates or limited access to quality education.
- Housing Disparity Maps: By visualizing the distribution of housing affordability and quality, these maps reveal areas with limited access to safe and affordable housing.
- Environmental Disparity Maps: These maps highlight the unequal distribution of environmental burdens and benefits, exposing areas disproportionately affected by pollution or lack of access to green spaces.
The Power of Visualization: How Disparity Maps Enhance Understanding
Disparity maps excel in conveying complex data in a readily understandable format. Compared to tables or reports, visual representations offer a compelling and intuitive way to grasp the extent of inequality. Key benefits include:
- Clear and Concise Communication: Disparity maps communicate complex data in a visually appealing and easily digestible manner, making it accessible to a wider audience.
- Spatial Context: They provide a spatial context for understanding inequality, highlighting geographic patterns and trends. This allows for identifying specific areas requiring targeted interventions.
- Enhanced Awareness: By visually illustrating disparities, these maps raise awareness about social and economic inequalities, fostering public dialogue and action.
- Targeted Intervention: Disparity maps provide valuable data for policymakers and community leaders to develop and implement targeted interventions in areas with significant disparities.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: By offering a clear picture of the distribution of resources and outcomes, disparity maps support data-driven decision making, leading to more effective and equitable policies.
Beyond the Visual: Data Sources and Methodology
The construction of disparity maps relies on robust data sources and appropriate methodologies. Common data sources include:
- Census Data: Comprehensive demographic data collected by national statistical agencies provides a valuable foundation for creating disparity maps.
- Government Surveys: Data from surveys conducted by government agencies, such as health surveys or income surveys, offer insights into specific social and economic indicators.
- Community Data: Data collected by local organizations, community groups, or non-governmental organizations can provide valuable insights into specific local challenges.
The methodology employed for creating disparity maps varies depending on the data source and the indicator being visualized. Common methods include:
- Choropleth Mapping: This method uses color gradients to represent different levels of an indicator across geographic regions.
- Dot Density Mapping: This method uses dots to represent the frequency of an indicator within a geographic area, providing a visual representation of its density.
- Heat Mapping: This method uses color gradients to highlight areas with high concentrations of an indicator, allowing for the identification of hotspots.
Challenges and Considerations in Disparity Mapping
While powerful tools for understanding and addressing inequality, disparity maps face certain challenges and considerations:
- Data Availability and Quality: The accuracy and completeness of data are crucial for creating reliable disparity maps. Data limitations can lead to misleading conclusions and hinder the effectiveness of interventions.
- Data Aggregation and Generalization: Aggregating data at a regional level can obscure local variations and inequalities within communities. Careful consideration of data aggregation levels is essential.
- Misinterpretation and Bias: Disparity maps can be misinterpreted if not accompanied by contextual information and a clear understanding of the underlying data sources and methodologies.
- Ethical Considerations: It is crucial to ensure that disparity maps are used ethically and responsibly, avoiding the perpetuation of stereotypes or the stigmatization of specific communities.
FAQs about Disparity Maps
Q: What are some common examples of indicators used in disparity maps?
A: Common indicators include income, poverty rate, access to healthcare, educational attainment, housing affordability, crime rates, environmental pollution levels, and access to green spaces.
Q: How can disparity maps be used to inform policy decisions?
A: Disparity maps can help policymakers identify areas with significant disparities and allocate resources accordingly. They can also be used to evaluate the effectiveness of existing policies and inform the development of new interventions.
Q: What are some ethical considerations associated with disparity maps?
A: It is essential to avoid using disparity maps to stigmatize or perpetuate stereotypes about specific communities. Data should be presented in a responsible and sensitive manner, and efforts should be made to ensure that interventions are equitable and culturally appropriate.
Q: How can individuals contribute to the creation and use of disparity maps?
A: Individuals can contribute by supporting organizations that collect and analyze data on social and economic inequalities. They can also advocate for policies that promote data transparency and accessibility.
Tips for Utilizing Disparity Maps Effectively
- Consider the context: Always examine disparity maps in the context of the underlying data sources, methodologies, and potential biases.
- Focus on actionable insights: Utilize disparity maps to identify specific areas requiring attention and develop targeted interventions.
- Engage stakeholders: Collaborate with community members, local organizations, and policymakers to ensure that interventions are tailored to the needs of the community.
- Monitor progress and adapt interventions: Regularly evaluate the impact of interventions and make adjustments as needed to maximize their effectiveness.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Visualization for a More Equitable Future
Disparity maps are powerful tools for understanding and addressing social and economic inequalities. By visually representing data on various indicators, these maps provide a clear and concise picture of the uneven distribution of resources and opportunities. By embracing the power of visualization, we can foster public awareness, inform policy decisions, and work towards a more equitable future.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Landscape of Inequality: A Comprehensive Guide to Disparity Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
