Unveiling the Power of Perceptual Mapping: A Comprehensive Guide to Strategic Insights
Related Articles: Unveiling the Power of Perceptual Mapping: A Comprehensive Guide to Strategic Insights
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Power of Perceptual Mapping: A Comprehensive Guide to Strategic Insights. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling the Power of Perceptual Mapping: A Comprehensive Guide to Strategic Insights
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling the Power of Perceptual Mapping: A Comprehensive Guide to Strategic Insights
- 3.1 Defining Perceptual Mapping: A Visual Journey into Customer Perception
- 3.2 Understanding the Benefits of Perceptual Mapping: Navigating the Competitive Landscape
- 3.3 The Steps Involved in Creating a Perceptual Mapping: A Guided Journey
- 3.4 Types of Perceptual Mapping Techniques: Exploring the Spectrum of Visualizations
- 3.5 Perceptual Mapping Tools: Enhancing Efficiency and Accuracy
- 3.6 FAQs about Perceptual Mapping: Addressing Common Queries
- 3.7 Tips for Creating Effective Perceptual Maps: Maximizing Insights and Value
- 3.8 Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Perceptual Mapping for Strategic Success
- 4 Closure
Unveiling the Power of Perceptual Mapping: A Comprehensive Guide to Strategic Insights

In the competitive landscape of today’s business world, understanding customer perception is paramount. This is where perceptual mapping tools emerge as invaluable assets, providing a visual representation of how consumers perceive different brands or products within a specific market. By illuminating the intricate web of customer preferences and brand positioning, perceptual mapping empowers businesses to make informed decisions regarding product development, marketing strategies, and competitive advantage.
Defining Perceptual Mapping: A Visual Journey into Customer Perception
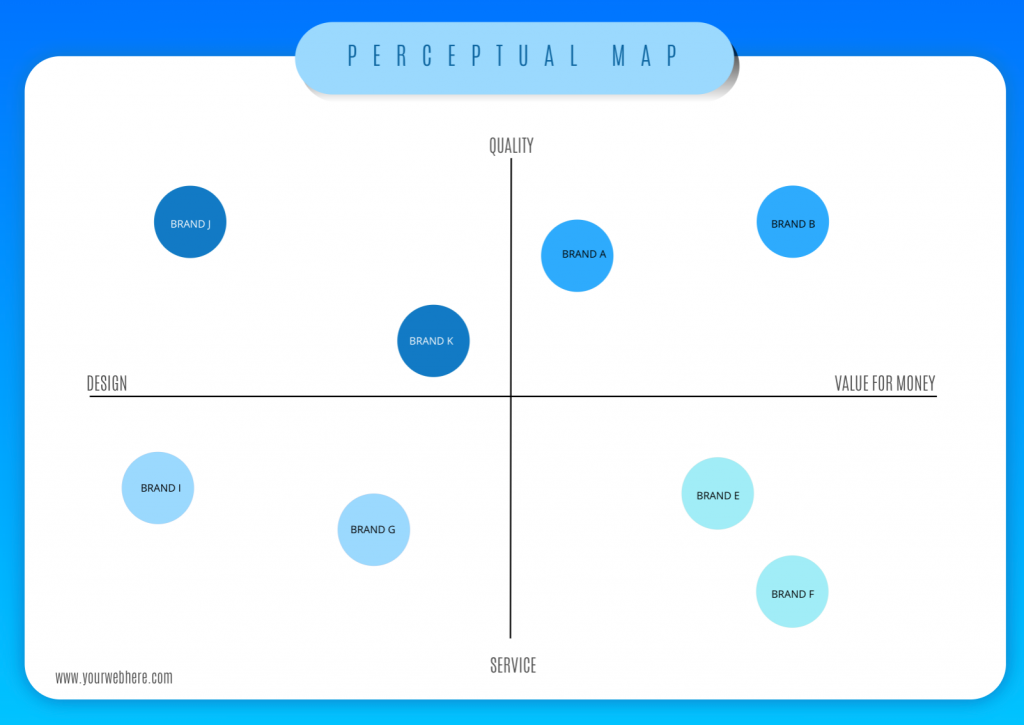
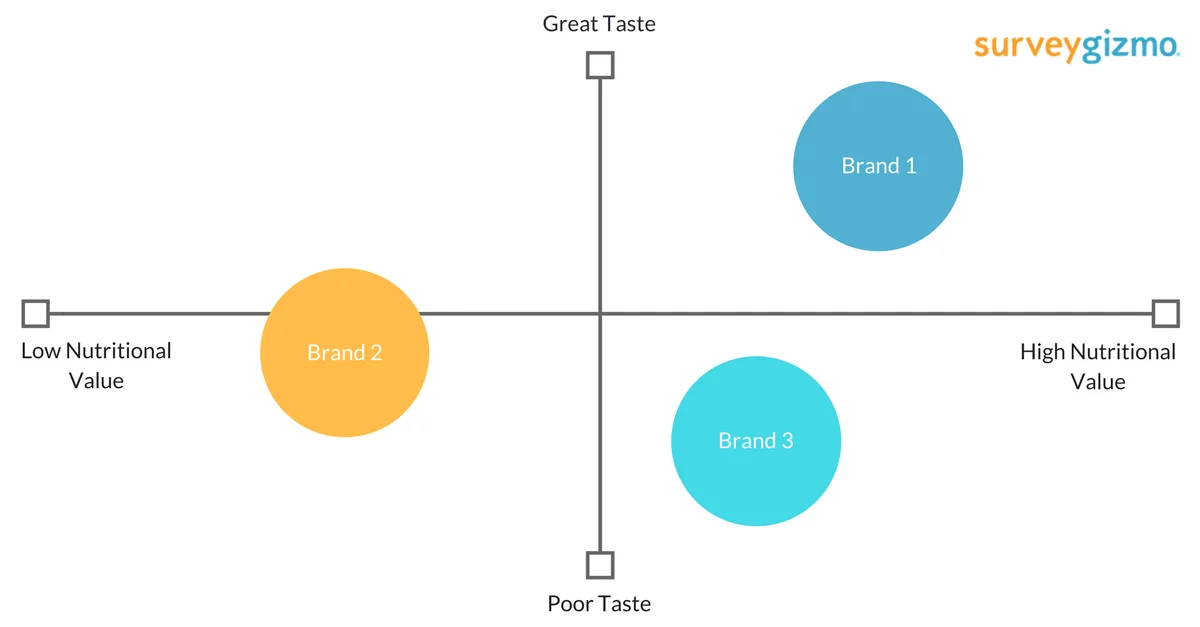
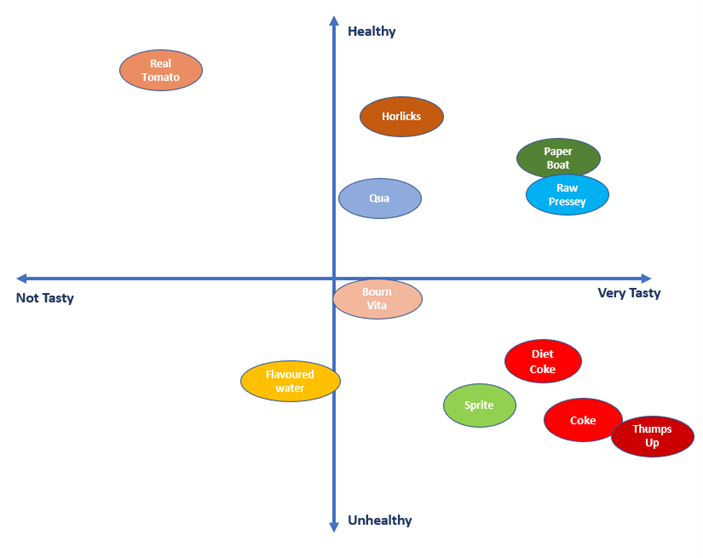
Perceptual mapping, often referred to as positioning maps or competitive mapping, is a powerful analytical tool that visually depicts the relative positions of competing products or brands in the minds of consumers. It leverages data gleaned from market research, surveys, and customer feedback to construct a two-dimensional (or sometimes multi-dimensional) map, where each axis represents a key attribute or characteristic relevant to the target audience.
These attributes can encompass factors like price, quality, features, benefits, brand image, or any other aspect that influences consumer decision-making. The resulting map then positions brands or products based on their perceived performance along these dimensions.
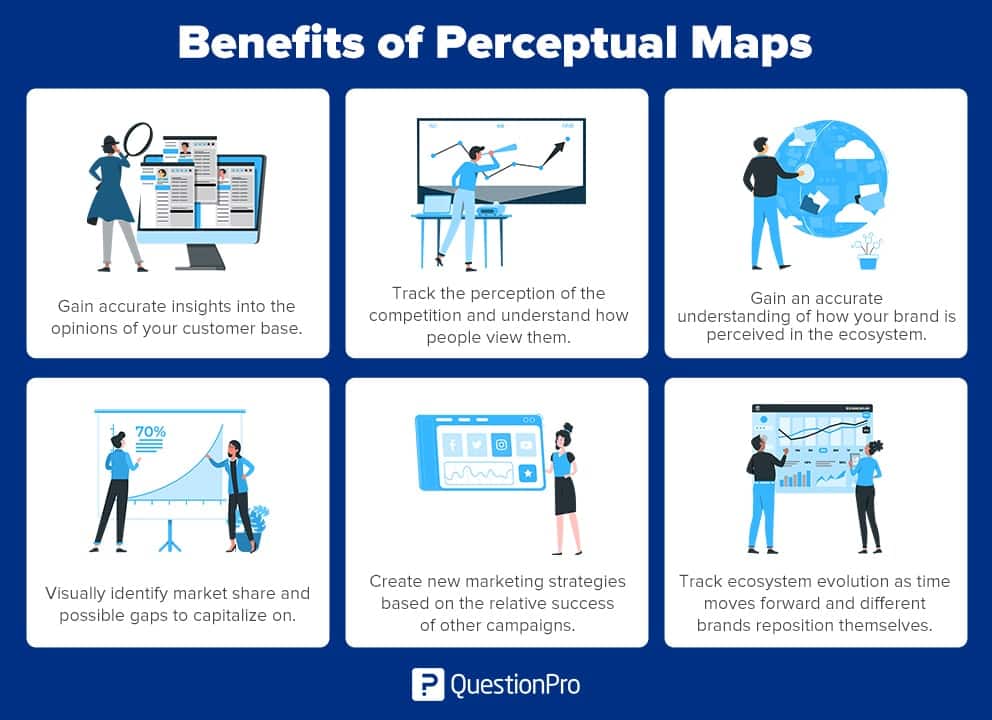
Understanding the Benefits of Perceptual Mapping: Navigating the Competitive Landscape
The application of perceptual mapping extends far beyond a mere visual representation. It serves as a strategic compass, guiding businesses towards informed decision-making by revealing critical insights into:
- Competitive Landscape Analysis: Perceptual mapping provides a clear visual representation of the competitive landscape, highlighting the strengths and weaknesses of competitors in relation to the target audience’s preferences. This enables businesses to identify potential market gaps, assess competitive threats, and devise strategies to differentiate themselves.
- Customer Segmentation and Targeting: By understanding how different customer segments perceive brands or products, businesses can effectively tailor their marketing efforts to specific groups. This allows for targeted messaging, optimized product features, and more effective communication strategies.
- Product Development and Positioning: Perceptual mapping helps businesses understand the existing market landscape and identify areas where new products or services can create value. This enables them to develop products that cater to unmet needs and position them strategically within the market.
- Brand Strategy and Positioning: Perceptual mapping provides valuable insights into how a brand is perceived by its target audience. It helps identify areas where the brand needs to strengthen its position, refine its messaging, and differentiate itself from competitors.
- Marketing Campaign Effectiveness: By tracking changes in brand perception over time, businesses can assess the effectiveness of their marketing campaigns. This allows for course correction and optimization of future marketing efforts.
The Steps Involved in Creating a Perceptual Mapping: A Guided Journey
Creating a robust and insightful perceptual mapping involves a structured process, encompassing the following key steps:
- Define the Market and Target Audience: Clearly define the specific market and target audience for the analysis. This includes identifying the relevant product or service category, defining the key customer segments, and understanding their needs and preferences.
- Identify Key Attributes: Determine the key attributes that influence consumer choices within the defined market. These attributes should be relevant to the target audience and should capture the essence of the product or service category.
- Data Collection and Analysis: Gather data from various sources, including market research reports, surveys, customer interviews, and competitor analysis. This data should be analyzed to understand how consumers perceive different brands or products based on the chosen attributes.
- Construct the Perceptual Map: Using the collected data, create a two-dimensional (or multi-dimensional) map, with each axis representing one of the key attributes. Plot the different brands or products on the map based on their perceived performance along these dimensions.
- Interpretation and Insights: Analyze the resulting perceptual map to identify key insights, such as brand positioning, competitive advantages, market gaps, and customer preferences. This analysis should be used to inform strategic decisions regarding product development, marketing, and competitive strategy.
Types of Perceptual Mapping Techniques: Exploring the Spectrum of Visualizations
Different techniques exist for creating perceptual mapping, each offering unique advantages and suitability for specific applications:
- Multidimensional Scaling (MDS): MDS is a statistical technique used to represent complex data in a lower-dimensional space, often visually. This method uses a distance-based approach to map brands or products based on their perceived similarities or differences.
- Perceptual Positioning Maps: These maps are created based on direct consumer ratings or rankings of brands or products on a set of attributes. This approach offers a straightforward visualization of consumer perceptions and is widely used in market research.
- Preference Maps: Preference maps capture consumer preferences for different product features or attributes. These maps can be used to identify areas where consumers have strong preferences or where there is potential for new product development.
- Cluster Analysis: This technique groups brands or products based on their similarities in terms of consumer perceptions. Cluster analysis helps identify distinct market segments and understand the competitive dynamics within each segment.
Perceptual Mapping Tools: Enhancing Efficiency and Accuracy
Several software tools and platforms are available to simplify the process of creating perceptual maps and extract valuable insights from data. These tools often incorporate advanced statistical techniques, intuitive interfaces, and data visualization capabilities, empowering businesses to create accurate and insightful maps:
- SPSS: A comprehensive statistical software package that offers powerful features for data analysis, including multidimensional scaling and cluster analysis.
- JMP: A statistical discovery software platform that provides a user-friendly interface for creating perceptual maps and exploring data relationships.
- R: An open-source statistical programming language that offers a wide range of packages for data visualization and analysis, including techniques for perceptual mapping.
- Google Sheets: A versatile spreadsheet application that can be used to create simple perceptual maps and analyze data.
FAQs about Perceptual Mapping: Addressing Common Queries
1. What are the limitations of perceptual mapping?
While perceptual mapping is a powerful tool, it does have limitations. The accuracy of the map depends on the quality and representativeness of the data collected. Moreover, perceptual mapping can be influenced by biases in consumer perception and the specific attributes chosen for analysis.
2. How often should perceptual mapping be conducted?
The frequency of perceptual mapping should be determined based on the dynamism of the market and the need for updated insights. In rapidly evolving industries, regular mapping (e.g., annually or semi-annually) may be necessary, while more stable industries might require mapping less frequently.
3. Can perceptual mapping be used for internal analysis?
Yes, perceptual mapping can be used for internal analysis to understand how different departments or teams perceive the company’s products, services, or brand. This can help improve internal alignment and communication.
4. What are some examples of successful perceptual mapping applications?
Perceptual mapping has been successfully applied by various companies across different industries. Examples include:
- Apple: Used perceptual mapping to reposition its products from "computers for the masses" to "stylish and user-friendly devices."
- Coca-Cola: Utilized perceptual mapping to understand consumer perceptions of its various beverage brands and develop targeted marketing campaigns.
- Toyota: Employed perceptual mapping to identify opportunities for new product development and position its vehicles in the competitive automotive market.
Tips for Creating Effective Perceptual Maps: Maximizing Insights and Value
- Focus on Relevant Attributes: Choose attributes that are truly important to the target audience and accurately reflect the product or service category.
- Use Clear and Concise Language: Ensure that the attributes and labels used on the map are easily understood and interpreted by the target audience.
- Consider the Number of Attributes: Too many attributes can create a cluttered and confusing map. Aim for a manageable number of attributes that capture the most important dimensions of the market.
- Use Visual Aids: Incorporate visual aids such as different colors, shapes, or symbols to enhance the clarity and impact of the map.
- Test and Validate: Before finalizing the map, test it with a representative sample of the target audience to ensure that it accurately reflects their perceptions.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Perceptual Mapping for Strategic Success
Perceptual mapping is a powerful tool that enables businesses to gain a deeper understanding of consumer perception, competitive dynamics, and market opportunities. By leveraging this visual representation of customer preferences and brand positioning, businesses can make informed decisions regarding product development, marketing strategies, and competitive advantage, ultimately driving strategic success in today’s dynamic market landscape. Embracing the power of perceptual mapping empowers businesses to navigate the competitive landscape with clarity, precision, and a strategic edge.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Power of Perceptual Mapping: A Comprehensive Guide to Strategic Insights. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
