Unveiling the Secrets of Map Measurement: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Unveiling the Secrets of Map Measurement: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Secrets of Map Measurement: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling the Secrets of Map Measurement: A Comprehensive Guide
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling the Secrets of Map Measurement: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3.1 The Foundation: Understanding Map Scales
- 3.2 Traditional Methods: Measuring with Rulers and Compasses
- 3.3 The Digital Era: Embracing Technology for Enhanced Measurement
- 3.4 Applications of Map Measurement: Unveiling the Power of Spatial Analysis
- 3.5 Tips for Accurate Map Measurement
- 3.6 Conclusion: Unlocking the Potential of Maps
- 4 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 5 Closure
Unveiling the Secrets of Map Measurement: A Comprehensive Guide

Maps, the visual representations of our world, hold a wealth of information beyond their surface appearance. The ability to measure distances, areas, and even volumes on a map unlocks a deeper understanding of geographical relationships, enabling informed decision-making in various fields. Whether you are an avid traveler planning your next adventure, a researcher analyzing spatial data, or a student studying geography, mastering the art of map measurement is a valuable skill.
This guide delves into the intricacies of map measurement, providing a comprehensive overview of methods, tools, and applications. We will explore both traditional and digital approaches, equipping you with the knowledge and skills to accurately measure distances, calculate areas, and interpret spatial relationships on maps.
The Foundation: Understanding Map Scales
The cornerstone of map measurement lies in understanding the map scale. The map scale represents the ratio between a distance on the map and the corresponding distance on the ground. It essentially tells you how much smaller the map is compared to the real world.
Types of Map Scales:
- Verbal Scale: A statement that describes the ratio directly, for example, "1 inch equals 10 miles."
- Representative Fraction (RF): A numerical ratio expressed as a fraction, for example, 1:100,000, indicating that one unit on the map represents 100,000 units on the ground.
- Graphic Scale: A visual representation of the scale using a bar with marked distances, allowing direct measurement using a ruler.
Determining the Map Scale:
- Look for the scale bar: Most maps include a graphic scale bar.
- Check for a scale statement: The verbal scale is often found in the map legend.
- Calculate the scale: If the scale is not explicitly provided, you can calculate it by measuring a known distance on the map and comparing it to the corresponding distance on the ground.
Traditional Methods: Measuring with Rulers and Compasses
For centuries, maps have been measured using basic tools like rulers and compasses. These methods, while simple, provide a foundation for understanding map measurement principles.
Measuring Distances:
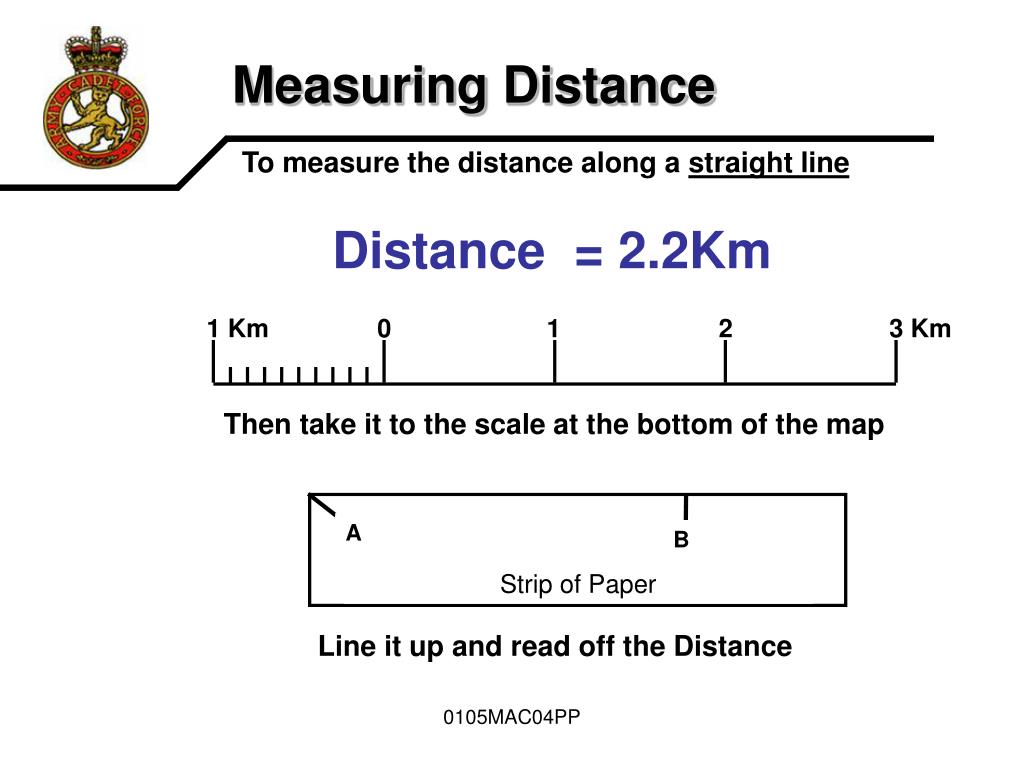
- Direct Measurement: Use a ruler to measure the distance between two points directly on the map. Convert the measurement using the map scale.
- Compass and String Method: Use a compass to draw an arc between two points. Measure the length of the arc using a string and then convert the measurement using the map scale.
Calculating Areas:
- Grid Method: Divide the area on the map into smaller squares or rectangles. Calculate the area of each square or rectangle and sum them to obtain the total area.
- Planimeter Method: A planimeter is a mechanical device used to trace the perimeter of an area on the map. It provides a direct reading of the area.
The Digital Era: Embracing Technology for Enhanced Measurement
The advent of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and digital mapping tools has revolutionized map measurement. These technologies offer greater precision, efficiency, and versatility, allowing for complex analysis and visualization of spatial data.
GIS Software:
- ArcGIS: A powerful GIS software widely used in various fields for map analysis, data management, and visualization.
- QGIS: A free and open-source GIS software providing similar functionalities as ArcGIS, making it accessible to a broader audience.
Digital Mapping Tools:
- Google Earth: A popular online platform offering a virtual globe and interactive maps, allowing users to measure distances, areas, and volumes.
- Online Map Measurement Tools: Numerous online tools specifically designed for measuring distances, areas, and perimeters on maps.
Advantages of Digital Measurement:
- Precision: Digital tools offer higher accuracy and precision compared to traditional methods.
- Efficiency: Automate measurements and calculations, saving time and effort.
- Flexibility: Easily adjust map scales, layers, and projections for customized analysis.
- Visualization: Create interactive maps and visualizations for better understanding of spatial relationships.
Applications of Map Measurement: Unveiling the Power of Spatial Analysis
Map measurement finds practical applications in various fields, impacting decision-making and problem-solving across diverse domains.
Urban Planning:
- Land Use Analysis: Measure the area of different land use categories to assess urban sprawl, identify development opportunities, and plan for sustainable growth.
- Traffic Flow Optimization: Measure distances and travel times to optimize traffic flow patterns, improve public transportation, and reduce congestion.
Environmental Studies:
- Habitat Mapping: Measure the size and distribution of different habitats to understand biodiversity, monitor ecosystem health, and plan conservation efforts.
- Climate Change Analysis: Measure changes in land cover, ice caps, and sea levels to study the impact of climate change and inform mitigation strategies.
Business and Economics:
- Market Analysis: Measure distances and areas to identify target markets, assess market potential, and optimize logistics and distribution networks.
- Real Estate Valuation: Measure property boundaries and sizes to assess land value, analyze property investments, and facilitate real estate transactions.
Navigation and Travel:
- Route Planning: Measure distances and travel times to plan optimal routes for driving, cycling, or hiking.
- Exploration and Adventure: Measure distances and elevations to plan expeditions, navigate remote areas, and track progress.
Tips for Accurate Map Measurement
- Choose the appropriate map scale: Select a map with a scale that provides sufficient detail for the desired measurement.
- Use accurate tools: Ensure your ruler, compass, or digital tools are calibrated and in good working order.
- Consider map projections: Map projections distort shapes and distances. Be aware of the projection used and its potential impact on measurements.
- Account for terrain: Maps are two-dimensional representations of a three-dimensional world. Consider terrain features and their impact on distances and areas.
- Double-check your measurements: Always verify your measurements to minimize errors and ensure accuracy.
Conclusion: Unlocking the Potential of Maps
Map measurement is a fundamental skill with far-reaching applications. By understanding the principles of map scales, mastering traditional and digital measurement techniques, and recognizing the diverse applications across various fields, you can unlock the power of maps to gain insights, make informed decisions, and solve problems. Whether you are a seasoned professional or an enthusiastic learner, embracing map measurement empowers you to navigate the world with greater understanding and clarity.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What is the best way to measure a map?
A: The best method depends on the specific task and available resources. For basic distance and area measurements, traditional tools like rulers and compasses are sufficient. For more complex analyses and high-precision measurements, digital tools like GIS software and online map measurement tools are recommended.
Q: How do I measure distances on a map?
A: Use a ruler to measure the distance between two points directly on the map. Then, use the map scale to convert the measurement to real-world units. Alternatively, use a compass and string to measure the arc between two points and convert the measurement using the map scale.
Q: How do I calculate areas on a map?
A: For simple areas, use the grid method by dividing the area into squares or rectangles. Calculate the area of each square or rectangle and sum them to obtain the total area. For more complex shapes, use a planimeter or digital tools like GIS software or online map measurement tools.
Q: What is a map scale and why is it important?
A: The map scale represents the ratio between a distance on the map and the corresponding distance on the ground. It tells you how much smaller the map is compared to the real world. Understanding the map scale is crucial for accurate measurement and interpretation of map data.
Q: Can I measure distances on a map without knowing the scale?
A: It is impossible to measure distances accurately without knowing the map scale. The scale is the key to converting map measurements to real-world units.
Q: What are some common mistakes to avoid when measuring a map?
A: Common mistakes include using the wrong map scale, misinterpreting map projections, neglecting terrain features, and not double-checking measurements. Always be mindful of these factors to ensure accuracy.
Q: How can I learn more about map measurement?
A: Numerous online resources, books, and courses offer in-depth information about map measurement. Explore online tutorials, GIS software documentation, and geography textbooks to enhance your understanding and skills.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Secrets of Map Measurement: A Comprehensive Guide. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!

