Unveiling the Tapestry of Eurasia: A Comprehensive Guide to its Physical Geography
Related Articles: Unveiling the Tapestry of Eurasia: A Comprehensive Guide to its Physical Geography
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Tapestry of Eurasia: A Comprehensive Guide to its Physical Geography. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Tapestry of Eurasia: A Comprehensive Guide to its Physical Geography

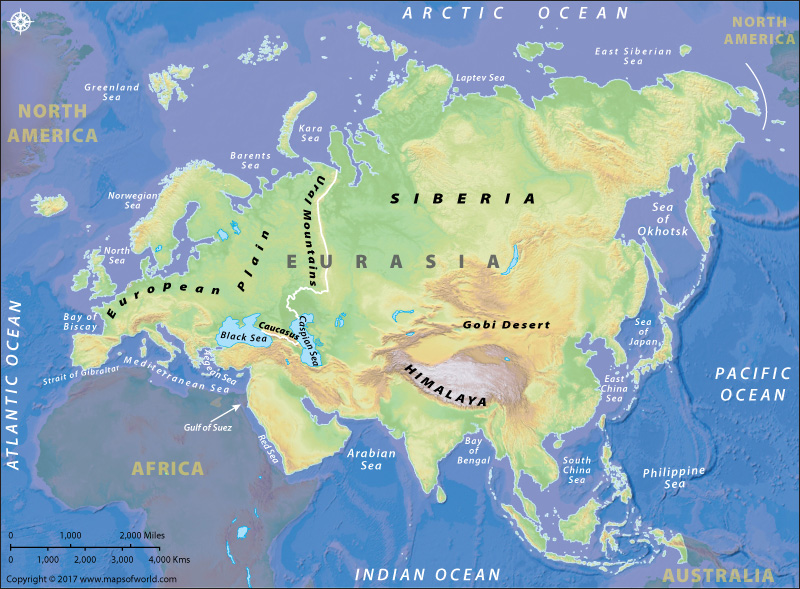
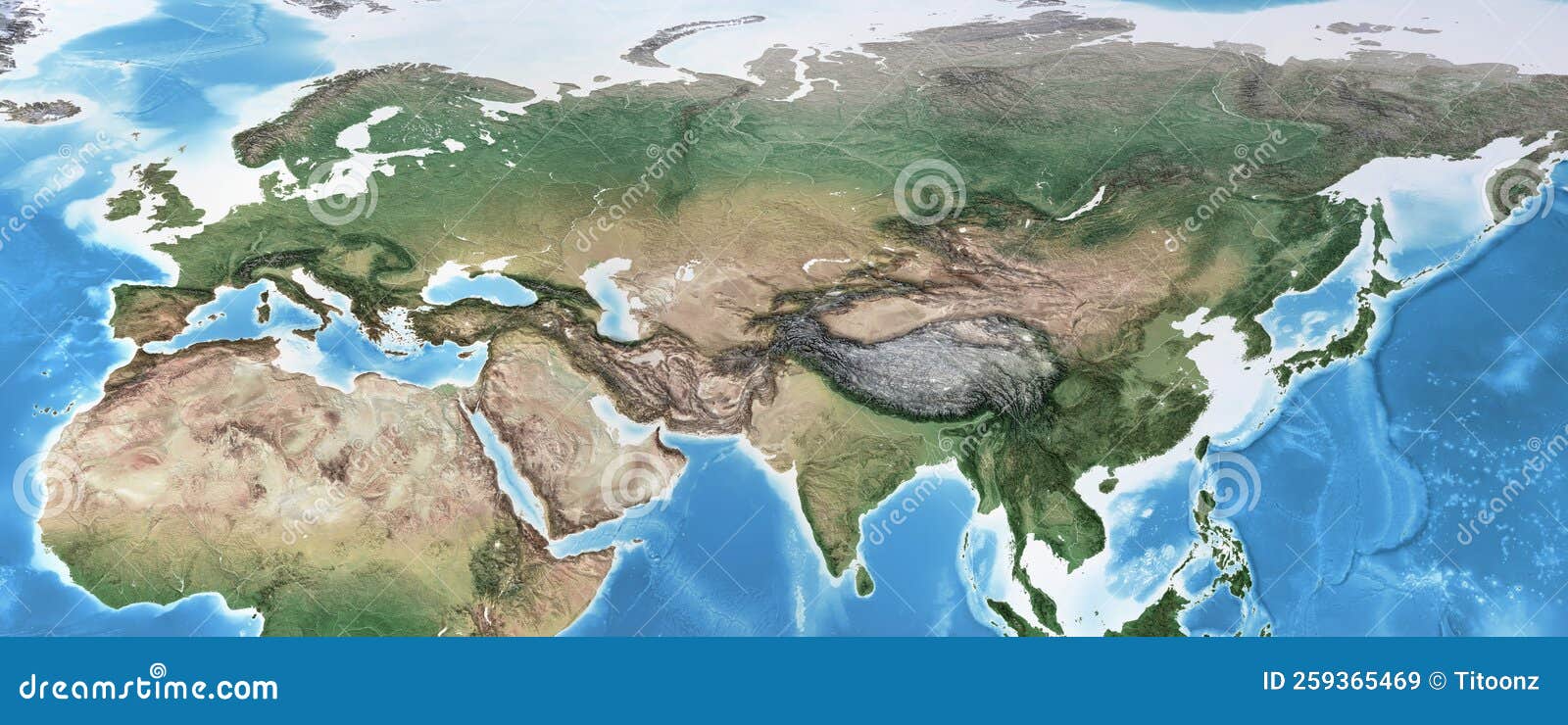
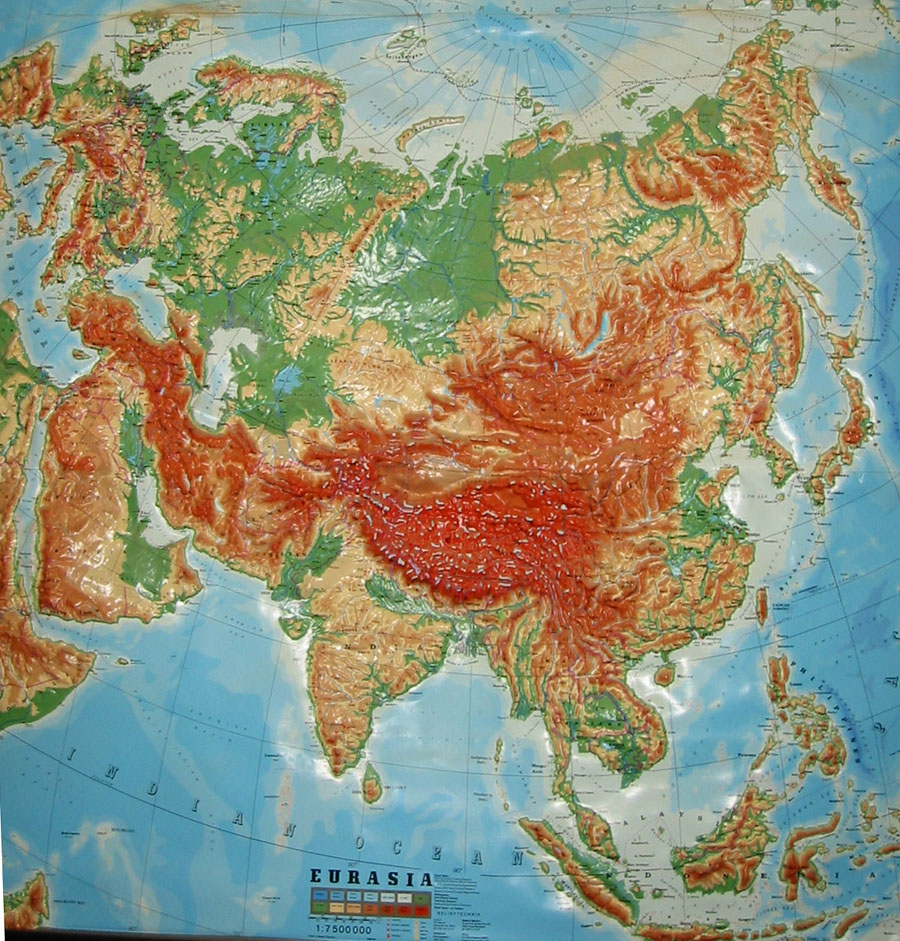
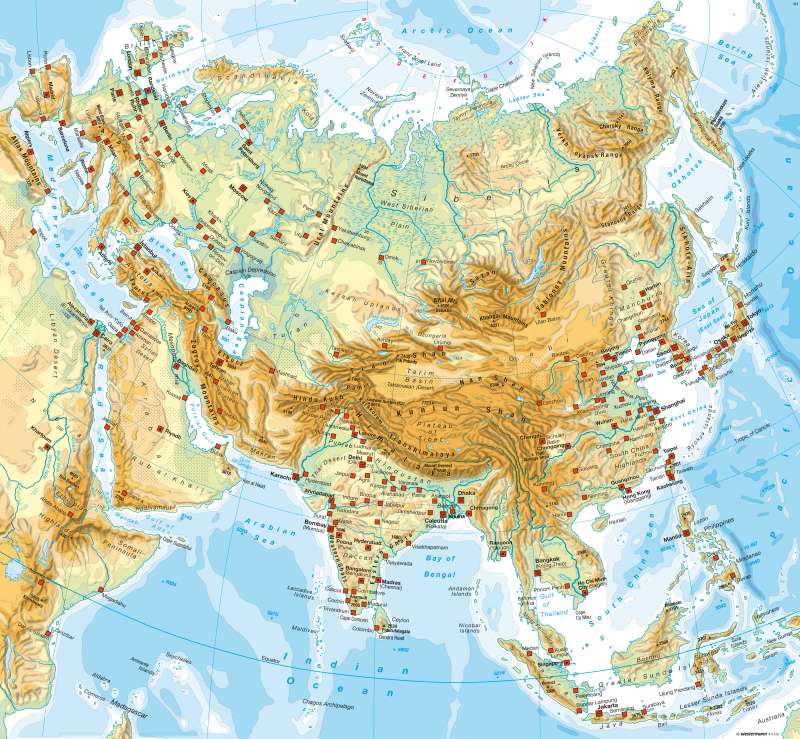
Eurasia, the world’s largest contiguous landmass, is a tapestry woven with diverse landscapes, a symphony of geographical features that have shaped its history, culture, and global significance. Understanding the physical map of Eurasia is akin to unlocking the secrets of this vast and intricate region, offering insights into its climate, resources, and the very fabric of human civilization.
The Grand Canvas: Unveiling the Landscape
Eurasia’s physical geography is a testament to the immense forces that have sculpted the Earth’s surface over millennia. From towering mountain ranges to sprawling plains, from vast deserts to fertile river valleys, its landscape is a captivating blend of extremes.
Mountains that Define Horizons:
- The Himalayas: This majestic mountain range, home to the world’s highest peaks, including Mount Everest, forms a natural barrier between South Asia and the Tibetan Plateau. Its towering peaks influence weather patterns, creating distinct microclimates and supporting unique ecosystems.
- The Caucasus Mountains: Located between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, these mountains act as a geographical divide between Europe and Asia, harboring diverse ethnicities and cultures.
- The Ural Mountains: Stretching from north to south, these mountains mark a traditional boundary between Europe and Asia, influencing climate and providing a rich source of mineral resources.
- The Altai Mountains: Located in Central Asia, these mountains are a source of major rivers and are home to diverse wildlife, including snow leopards and argali sheep.
Plains that Stretch to the Horizon:
- The Great European Plain: Extending from the Atlantic coast to the Ural Mountains, this vast plain is a fertile agricultural region, supporting a dense population and a vibrant economy.
- The West Siberian Plain: Located in western Siberia, this plain is characterized by vast forests, wetlands, and permafrost, making it a critical habitat for a wide range of species.
- The Turan Plain: Situated in Central Asia, this plain is dominated by deserts and semi-deserts, with limited rainfall and extreme temperatures.
Deserts that Speak of Aridity:
- The Arabian Desert: The largest hot desert in the world, this vast expanse of sand dunes and rocky terrain covers much of the Arabian Peninsula, presenting unique challenges for human habitation.
- The Karakum Desert: Located in Turkmenistan, this desert is known for its shifting sand dunes and ancient ruins, offering a glimpse into the region’s rich history.
- The Gobi Desert: Situated in Mongolia and northern China, this desert is characterized by its cold, arid climate and vast expanses of sand and gravel.
Rivers that Carve Paths Through Time:
- The Volga River: The longest river in Europe, the Volga flows through Russia, providing vital transportation routes and supporting a rich ecosystem.
- The Danube River: This international river flows through ten countries in Central and Eastern Europe, serving as a crucial waterway for trade and transportation.
- The Yangtze River: The third longest river in the world, the Yangtze flows through China, playing a vital role in agriculture, transportation, and hydropower generation.
Seas and Oceans that Shape Coastlines:
- The Mediterranean Sea: A historic crossroads of civilizations, this sea connects Europe, Africa, and Asia, influencing trade, culture, and climate.
- The Black Sea: A large inland sea bordered by Russia, Ukraine, Turkey, and others, the Black Sea is a vital waterway for shipping and fishing.
- The Caspian Sea: The largest enclosed body of water in the world, the Caspian Sea is a critical source of oil and gas resources, and its shores are home to diverse cultures and ecosystems.
The Significance of Eurasia’s Physical Geography
Understanding the physical geography of Eurasia is crucial for comprehending its role in global affairs, its economic potential, and its environmental challenges.
- Strategic Location: Eurasia’s strategic location between Europe and Asia has made it a crossroads of trade, migration, and cultural exchange for centuries. Its diverse landscapes and resources have attracted empires and civilizations throughout history, shaping the geopolitical landscape of the world.
- Economic Potential: Eurasia is rich in natural resources, including oil, gas, minerals, and fertile land. Its vast plains and river valleys support agriculture, while its mountains contain valuable mineral deposits. Harnessing these resources effectively is key to regional economic growth and development.
- Environmental Challenges: Eurasia faces significant environmental challenges, including climate change, deforestation, pollution, and water scarcity. Understanding the physical geography of the region is essential for developing sustainable solutions to these challenges.
FAQs about the Physical Map of Eurasia
Q: What are the main physical features of Eurasia?
A: Eurasia is characterized by a diverse range of physical features, including towering mountain ranges, sprawling plains, vast deserts, and fertile river valleys.
Q: How does the physical geography of Eurasia influence its climate?
A: The physical geography of Eurasia plays a significant role in shaping its climate. Mountain ranges act as barriers to moisture, creating distinct microclimates. Plains are often subject to extreme temperatures, while deserts are characterized by aridity.
Q: What are some of the environmental challenges facing Eurasia?
A: Eurasia faces significant environmental challenges, including climate change, deforestation, pollution, and water scarcity. These challenges are exacerbated by the region’s vast size, diverse ecosystems, and rapid economic growth.
Q: How does the physical geography of Eurasia affect its cultural diversity?
A: The diverse landscapes of Eurasia have shaped its cultural diversity. Mountain ranges and deserts have often acted as barriers to communication, leading to the development of distinct cultures and languages.
Tips for Studying the Physical Map of Eurasia
- Use a variety of resources: Explore maps, atlases, documentaries, and online resources to gain a comprehensive understanding of Eurasia’s physical geography.
- Focus on key features: Identify the major mountain ranges, plains, deserts, and rivers, and understand their significance in shaping the region’s landscape.
- Consider the impact of physical geography on human activity: Explore how the physical features of Eurasia have influenced settlement patterns, economic development, and cultural traditions.
- Engage in critical thinking: Analyze the relationships between different physical features and their impact on the environment, society, and economy.
Conclusion
The physical map of Eurasia is a window into the region’s complex and fascinating history, its diverse cultures, and its global significance. Understanding its diverse landscapes, its strategic location, and its environmental challenges is crucial for appreciating the intricate tapestry of this vast and dynamic region. As we continue to explore the physical geography of Eurasia, we gain a deeper understanding of its role in the world and the challenges and opportunities it presents for the future.
-map-of-eurasia-small.jpg)
/Eurasia_location_map_-_Physical-5c21c2ba46e0fb0001c9c702.jpg)


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Tapestry of Eurasia: A Comprehensive Guide to its Physical Geography. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
